Planets round different stars want to be ready for excessive climate prerequisites, consistent with a brand new find out about from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and ESA’s (Eu House Company’s) XMM-Newton that tested the results of X-rays on possible planets round the commonest form of stars.
Astronomers discovered that just a planet with greenhouse gases in its setting like Earth and at a reasonably massive distance clear of the megastar they studied would have a possibility to toughen lifestyles as we understand it round a close-by megastar.
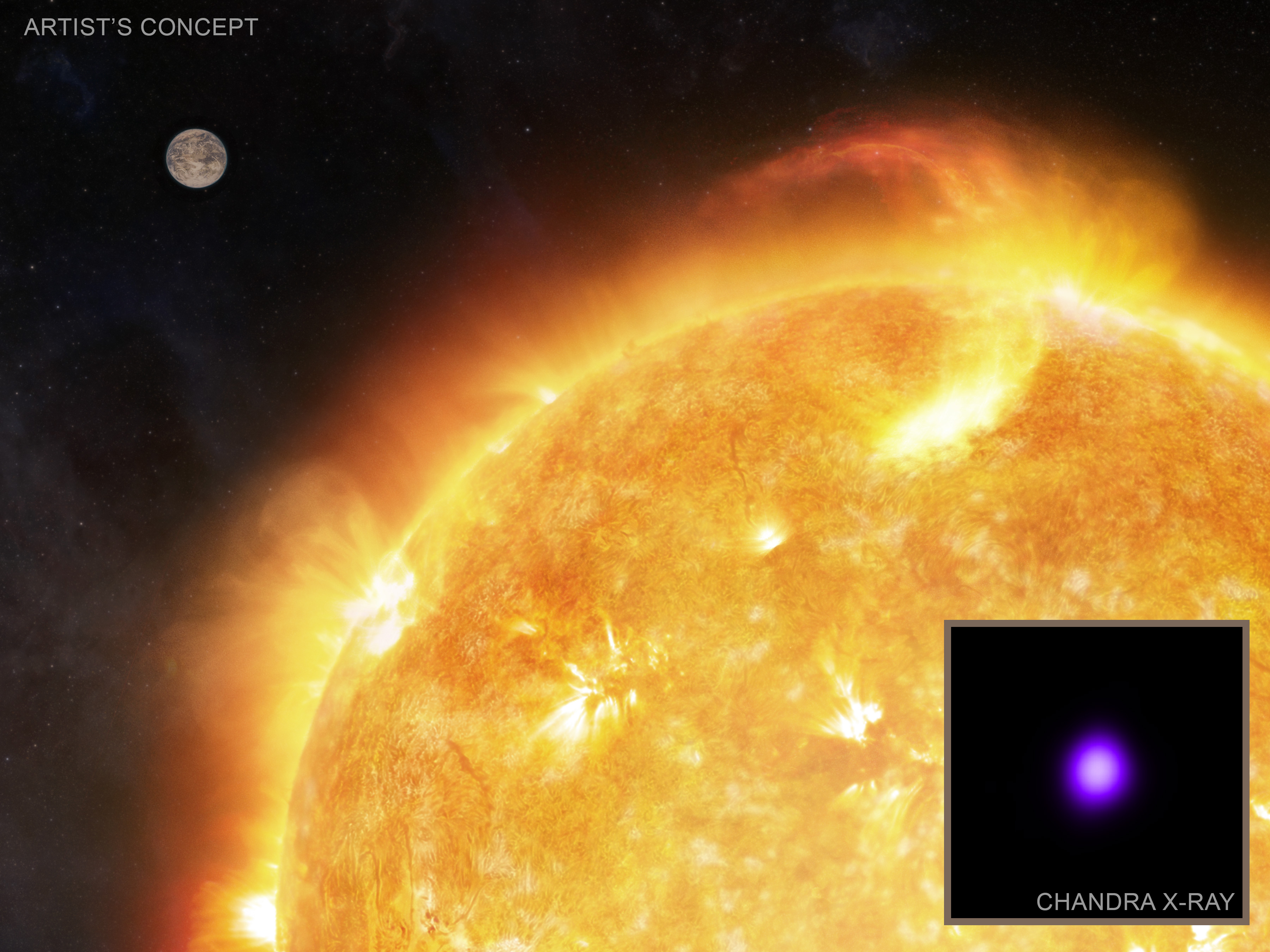
Wolf 359 is a pink dwarf with a mass a few 10th that of the Solar. Purple dwarf stars are the commonest stars within the universe and are living for billions of years, offering considerable time for lifestyles to broaden. At a distance of simplest 7.8 light-years away, Wolf 359 could also be probably the most closest stars to the sun machine.
“Wolf 359 can assist us unencumber the secrets and techniques round stars and habitability,” stated Scott Wolk of the Middle for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian (CfA), who led the find out about. “It’s so shut and it belongs to such the most important elegance of stars – it’s a really perfect aggregate.”
As a result of pink dwarfs are essentially the most prevalent kinds of stars, astronomers have seemed laborious to search out exoplanets round them. Astronomers have discovered some proof for 2 planets in orbit round Wolf 359 the usage of optical telescopes, however the ones conclusions had been challenged by means of different scientists.
“Whilst we don’t have evidence of planets round Wolf 359 but, it sort of feels very imaginable that it hosts more than one planets,” Wolk added. “This makes it a very good check mattress to have a look at what planets would revel in round this sort of megastar.”
Wolk and his colleagues used Chandra and XMM to review the quantities of secure X-rays and excessive ultraviolet (UV) radiation – essentially the most full of life form of UV radiation – that Wolf 359 would unharness at the imaginable planets round it.
They discovered that Wolf 359 is generating sufficient harmful radiation that just a planet with greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide in its setting – and situated at a reasonably massive distance from the megastar – would most probably have the ability to maintain lifestyles.
“Simply being a ways sufficient clear of the megastar’s damaging radiation wouldn’t be sufficient to make it liveable,” stated co-author Vinay Kashyap, additionally of CfA. “A planet round Wolf 359 would additionally want to be blanketed in greenhouse gases like Earth is.”
To review the results of full of life radiation at the habitability of the planet applicants, the staff regarded as the megastar’s liveable zone – the area round a celeb the place liquid water may just exist on a planet’s floor.
The outer prohibit of the liveable zone for Wolf 359 is ready 15% of the gap between Earth and the Solar, since the pink dwarf is far much less vivid than the Solar. Neither of the planet applicants for the program is situated in Wolf 359’s liveable zone, with one too with regards to the megastar and the opposite too a ways out.
“If the interior planet is there, the X-ray and excessive UV radiation it’s subjected to would smash the ambience of this planet in simplest about 1,000,000 years,” stated co-author Ignazio Pillitteri of CfA and the Nationwide Institute for Astrophysics in Palermo, Italy.
The staff additionally regarded as the results of radiation on as-yet undetected planets inside the liveable zone. They concluded {that a} planet just like the Earth in the course of the liveable zone must have the ability to maintain an environment for nearly two billion years, whilst one close to the periphery may just closing indefinitely, helped by means of the warming results of greenhouse gases.
Every other large threat for planets orbiting stars like Wolf 359 is from X-ray flares, or occasional vivid bursts of X-rays, on best of the secure, on a regular basis output from the megastar. Combining observations made with Chandra and XMM-Newton resulted within the discovery of 18 X-ray flares from Wolf 359 over 3.5 days.
Extrapolating from those noticed flares, the staff expects that a lot more tough and harmful flares would happen over longer classes of time. The blended results of the secure X-ray and UV radiation and the flares imply that any planet situated within the liveable zone is not going to have an important setting lengthy sufficient for multicellular lifestyles, as we understand it on Earth, to shape and live to tell the tale. The exception is the liveable zone’s periphery if the planet has an important greenhouse impact.
Those effects had been offered on the 245th assembly of the American Astronomical Society in Nationwide Harbor, Maryland, and are being ready for newsletter in a magazine. NASA’s Marshall House Flight Middle in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the Chandra program. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory’s Chandra X-ray Middle controls science operations from Cambridge, Massachusetts, and flight operations from Burlington, Massachusetts.
Learn extra from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory.
Be informed extra in regards to the Chandra X-ray Observatory and its venture right here:
Megan Watzke
Chandra X-ray Middle
Cambridge, Mass.
617-496-7998
mwatzke@cfa.harvard.edu
Lane Figueroa
Marshall House Flight Middle, Huntsville, Alabama
256-544-0034
lane.e.figueroa@nasa.gov














:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-2226490793-c5e9f8c574474ef69232a57d4031cedf.jpg)