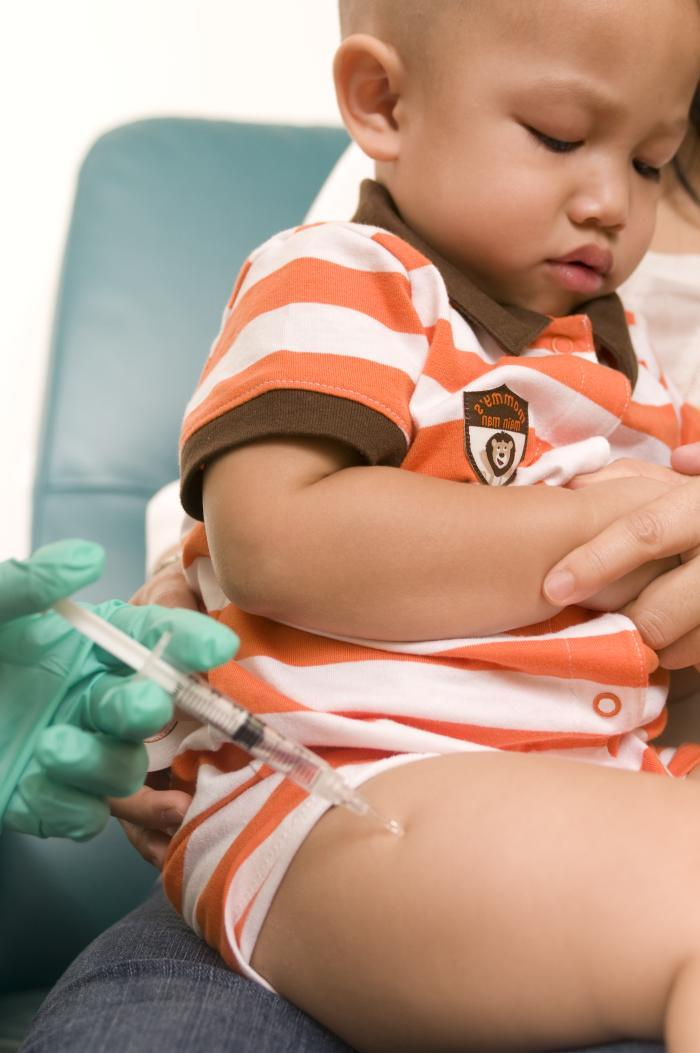
Define of the learn about for the detection of SARS-CoV-2-reactive CD4+ T cells in numerous teams of sufferers. Credit score: Science Translational Drugs (2024). DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adl1997
5 years in the past, on the outset of the coronavirus pandemic, a phenomenon become abundantly transparent: Preschool-age youngsters hardly evolved serious circumstances of COVID-19.
It wasn’t that youngsters below the age of five had been warding off an infection. On the contrary, they had been coming down with COVID like everybody else. In america, the Facilities for Illness Keep an eye on and Prevention estimates that greater than 90% of kids from infancy via age 17 had been uncovered to SARS-CoV-2, the virus that reasons COVID.
What made the youngest inhabitants of kids other is their normally hanging avoidance of serious coronavirus an infection. That reality has led scientists international to hunt a solution to a deceptively easy query: How does the youngest inhabitants of kids, regardless of the place they’re on this planet, frequently elude serious COVID?
Now, a big staff of immunologists and doctor–scientists from a couple of establishments in France has performed an in-depth learn about that compares the immune reaction of preschoolers to older youngsters and adults. The staff targeted at the adaptive immune reaction—the actions of T cells and B cells—to know the way the youngest amongst us are normally spared from serious, even deadly infections.
“The principle possibility issue for serious [coronavirus] illness is age,” writes Dr. Benoît Manfroi, lead writer of the analysis, revealed in Science Translational Drugs. “Kids display the bottom possibility, and older adults are probably the most inclined,” Manfroi added.
With different viral infections, probably the most inclined populations are normally at two extremes in age: the very younger and the very previous. The analysis staff pointed to influenza and respiration syncytial virus—RSV—as simply two of a couple of viruses that reason vital morbidity and mortality within the two inclined age teams.
That rule of thumb fails to use, then again, when the an infection is led to through SARS-CoV-2, or every other coronavirus in a position to inflicting serious infections. In america, the CDC characterizes preschoolers’ courting with SARS-CoV-2 in in a different way—with statistics. Children below age 5 constitute 6% of the entire U.S. inhabitants, but most effective 0.1% of COVID-19 deaths have came about on this age staff. Preschool-age youngsters who’ve evolved serious COVID generally tend to have comorbidities, research have proven.
To higher perceive the immune reaction to SARS-CoV-2 in preschool-age youngsters, the French staff performed a wide-ranging learn about that integrated other people of every age, 89 individuals altogether. Incorporated had been preschoolers, older youngsters, and adults with gentle or serious COVID prior to, all over, and 11 months after an infection. Scientists accrued information on adaptive immune responses, sometimes called received immunity, or pathogen-specific immune responses.
All the way through SARS-CoV-2 an infection, youngsters below age 5 had a decrease and phenotypically distinct antiviral CD4+ T cellular reaction when put next with older youngsters and adults with gentle illness. This more youthful cohort additionally evolved phenotypically distinct reminiscence T and B cellular responses after restoration when put next with individuals from different age teams.
For instance, preschoolers’ distinctive reminiscence T cells had marked inflammatory options when put next with different cohorts. And their virus-reactive reminiscence B cells had been fewer in quantity than the ones of older youngsters and adults.
Variations within the immune responses of older youngsters and adults, the French research discovered, replicate the maturation of the immune gadget. Manfroi and co-workers recommend the advisable immune reaction distinctive to preschoolers permits them to persistently keep away from serious an infection.
“The immune programs of preschoolers are subjected to distinctive exterior influences, being extra often uncovered to microbes when put next with the ones of adults, particularly to respiration viruses, together with endemic human coronaviruses,” added Manfroi, relating to the 4 recognized coronaviruses that reason the typical chilly.
The emergence of SARS-CoV-2 wasn’t the primary time that clinical scientists seen extraordinarily younger sufferers warding off serious illness led to through a coronavirus. Kids below age 5 had been normally spared serious an infection when uncovered to SARS-CoV-1, the coronavirus that induced a 2002–2003 outbreak. Infections started in China prior to spreading in different places in Asia. SARS-CoV-1 additionally unfold to North The usa and South Africa.
The International Well being Group estimated the mortality price for more youthful adults used to be between 10% and 15%, however amongst other people 65 and older, mortality exceeded 50%. The normally gentle illness in youngsters below the age of five took clinical scientists through wonder.
“Host resistance to infectious sicknesses is in large part made up our minds through the immune gadget, which takes a number of years to mature after delivery. Babies to begin with depend on maternal antibodies and innate immunity for the reason that innate immune gadget matures sooner than its adaptive counterpart,” asserted Manfroi, who used to be amongst dozens of scientists engaging in an arm of the analysis at INSERM, or Insitut nationwide de los angeles santé et de los angeles recherche médicale in Paris.
Different collaborators had been from Institut Necker Enfants Malades; Institut Pasteur; Hôpitaux Universitaires Paris; Sorbonne Université, and Université Paris Cité, amongst different analysis facilities. Outdoor of France, staff individuals hailed from Germany and Guyana.
The French effects arrive at the heels of an American-led learn about revealed within the magazine Cellular in 2023. Scientists at Stanford College in California led a world staff that still concluded preschool-age youngsters have milder circumstances of COVID-19.
The Stanford analysis discovered that amongst adults inflamed with SARS-CoV-2, antibodies particular to the virus rose briefly, then dropped off dramatically, declining 10-fold in six months.
Babies’ antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 rose slower and not dropped. Antibodies both stayed on the similar stage or endured to upward push right through a 300-day commentary duration.
Dr. Bali Pulendran, lead investigator, attributed preschoolers’ gentle bouts with COVID to an abundance of inflammation-promoting proteins—cytokines—within the nasal hollow space. Key amongst the ones proteins used to be alpha-interferon, which is noteworthy for shutting down viral replication in inflamed cells, Pulendran mentioned in a remark.
Manfroi and co-workers, in the meantime, recognize that their learn about had a number of obstacles. “A primary main limitation lies within the loss of evaluation of tissues rather than blood, in particular of mucosal websites the use of both nasal swabs or biopsies from adenoids or tonsils,” the staff concluded, noting it “has been reported the use of swab samples that babies and small children have robustly up-regulated expression of inflammatory cytokines at mucosal websites all over the extreme section of an infection when put next with adults.”
Additional information:
Benoît Manfroi et al, Preschool-age youngsters deal with a definite reminiscence CD4 + T cellular and reminiscence B cellular reaction after SARS-CoV-2 an infection, Science Translational Drugs (2024). DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adl1997
© 2024 Science X Community
Quotation:
Extensive research explains why preschoolers are much less more likely to expand serious COVID-19 (2024, October 15)
retrieved 17 October 2024
from
This report is matter to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal learn about or analysis, no
phase is also reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions most effective.