Disclaimer: Early unlock articles don’t seem to be regarded as as ultimate variations. Any adjustments might be mirrored within the on-line model within the month the object is formally launched.
Creator affiliations: Iowa State College School of Veterinary Drugs, Ames, Iowa, USA (E.R. Burrough, D.R. Magstadt, P.C. Gauger, J. Zhang, C. Siepker, M. Mainenti, G. Li, P.J. Gorden, P.J. Plummer, R. Major); Daybreak Veterinary Provider PLLC, Amarillo, Texas, USA (B. Petersen); Veterinary Analysis & Consulting Products and services LLC, Hays, Kansas, USA (S.J. Timmermans); Texas A&M Veterinary Clinical Diagnostic Laboratory, School Station, Texas, USA (A.C. Thompson)
Extremely pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) viruses pose a danger to wild birds and poultry globally, and HPAI H5N1 viruses are of even higher fear as a result of their widespread spillover into mammals. In past due 2021, the Eurasian pressure of H5N1 (clade 2.3.4.4b) used to be detected in North The united states (1,2) and initiated an endemic that persisted into 2024. Spillover detections and deaths from this clade had been reported in each terrestrial and marine mammals in the US (3,4). The detection of HPAI H5N1 clade 2.3.4.4b virus in critical circumstances of human illness in Ecuador (5) and Chile (6) raises additional considerations in regards to the pandemic doable of particular HPAI viruses.
In February 2024, veterinarians had been alerted to a syndrome happening in lactating dairy livestock within the panhandle area of northern Texas. Nonspecific sickness accompanied by means of lowered feed consumption and rumination and an abrupt drop in milk manufacturing advanced in affected animals. The milk from most influenced cows had a thickened, creamy yellow look very similar to colostrum. On affected farms, prevalence seemed to top 4–6 days after the primary animals had been affected after which tapered off inside of 10–14 days; in a while, maximum animals had been slowly returned to common milking. Medical indicators had been regularly reported in multiparous cows all over center to past due lactation; ≈10%–15% sickness and minimum dying of livestock had been seen on affected farms. Preliminary submissions of blood, urine, feces, milk, and nasal swab samples and postmortem tissues to regional diagnostic laboratories didn’t divulge a constant, particular reason for lowered milk manufacturing. Milk cultures had been ceaselessly detrimental, and serum chemistry checking out confirmed mildly larger aspartate aminotransferase, gamma-glutamyl transferase, creatinine kinase, and bilirubin values, while whole blood counts confirmed variable anemia and leukocytopenia.
In early March 2024, an identical scientific circumstances had been reported in dairy livestock in southwestern Kansas and northeastern New Mexico; deaths of untamed birds and home cats had been additionally seen inside of affected websites within the Texas panhandle. In >1 dairy farms in Texas, deaths happened in home cats fed uncooked colostrum and milk from ill cows that had been within the sanatorium parlor. Antemortem scientific indicators in affected cats had been depressed psychological state, stiff frame actions, ataxia, blindness, circling, and copious oculonasal discharge. Neurologic tests of affected cats published the absence of threat reflexes and pupillary gentle responses with a vulnerable blink reaction.
On March 21, 2024, milk, serum, and contemporary and glued tissue samples from livestock situated in affected dairies in Texas and a couple of deceased cats from an affected Texas dairy farm had been gained on the Iowa State College Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory (ISUVDL; Ames, IA, USA). Tomorrow, an identical units of samples had been gained from livestock situated in affected dairies in Kansas. Milk and tissue samples from livestock and tissue samples from the cats examined nice for influenza A virulent disease (IAV) by means of screening PCR, which used to be showed and characterised as HPAI H5N1 virus by means of the United States Division of Agriculture Nationwide Veterinary Products and services Laboratory. Detection ended in an preliminary press unlock by means of the United States Division of Agriculture Animal and Plant Well being Inspection Provider on March 25, 2024, confirming HPAI virus in dairy livestock (7). We file the characterizations carried out on the ISUVDL for HPAI H5N1 viruses infecting livestock and cats in Kansas and Texas.
Milk samples (circumstances 2–5) and contemporary and formalin-fixed tissues (circumstances 1, 3–5) from dairy livestock had been gained on the ISUVDL from Texas on March 21 and from Kansas on March 22, 2024. The livestock exhibited nonspecific sickness and lowered lactation, as described in the past. The tissue samples for diagnostic checking out got here from 3 cows that had been euthanized and three that died naturally; all postmortem examinations had been carried out at the premises of affected farms.
The our bodies of two grownup home shorthaired cats from a north Texas dairy farm had been gained on the ISUVDL for an entire postmortem exam on March 21, 2024. The cats had been discovered useless and not using a obvious indicators of damage and had been from a resident inhabitants of ≈24 home cats that have been fed milk from ill cows. Medical illness in cows on that farm used to be first famous on March 16; the cats turned into ill on March 17, and a number of other cats died in a cluster all over March 19–20. In overall, >50% of the cats at that dairy turned into sick and died. We accrued cerebrum, cerebellum, eye, lung, middle, spleen, liver, lymph node, and kidney tissue samples from the cats and positioned them in 10% neutral-buffered formalin for histopathology.
At ISUVDL, we trimmed, embedded in paraffin, and processed formalin-fixed tissues from affected livestock and cats for hematoxylin/eosin staining and histologic analysis. For immunohistochemistry (IHC), we ready 4-µm–thick sections from paraffin-embedded tissues, positioned them on Superfrost Plus slides (VWR, and dried them for 20 mins at 60°C. We used a Ventana Discovery Extremely IHC/ISH analysis platform (Roche, for deparaffinization till and together with counterstaining. We bought all merchandise except for the principle antibody from Roche. Computerized deparaffination used to be adopted by means of enzymatic digestion with protease 1 for 8 mins at 37°C and endogenous peroxidase blockading. We bought the principle influenza A virulent disease antibody from the hybridoma cellular line H16-L10–4R5 (ATCC, and diluted at 1:100 in Discovery PSS diluent; we incubated sections with antibody for 32 mins at room temperature. Subsequent, we incubated the sections with a hapten-labeled conjugate, Discovery anti-mouse HQ, for 16 mins at 37°C adopted by means of a 16-minute incubation with the pony radish peroxidase conjugate, Discovery anti-HQ HRP. We used a ChromoMap DAB package for antigen visualization, adopted by means of counterstaining with hematoxylin after which bluing. Sure controls had been sections of IAV-positive swine lung. Unfavorable controls had been sections of mind, lung, and eyes from cats no longer inflamed with IAV.
We diluted milk samples 1:3 vol/vol in phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4 (Gibco/Thermo Fisher Medical, by means of blending 1 unit quantity of milk and three unit volumes of phosphate buffered saline. We ready 10% homogenates of mammary glands, brains, lungs, spleens, and lymph nodes in Earle’s balanced salt resolution (Sigma-Aldrich, Processing used to be no longer vital for ocular fluid, rumen content material, or serum samples. After processing, we extracted samples in keeping with a Nationwide Animal Well being Laboratory Community (NAHLN) protocol that had 2 NAHLN-approved deviations for ISUVDL consisting of the MagMax Viral RNA Isolation Equipment for 100 µL pattern volumes and a Kingfisher Flex software (each Thermo Fisher Medical).
We carried out real-time opposite transcription PCR (rRT-PCR) by means of the use of an NAHLN-approved assay with 1 deviation, which used to be the VetMAX-Gold SIV Detection package (Thermo Fisher Medical), to display screen for the presence of IAV RNA. We examined samples in conjunction with the VetMAX XENO Interior Sure Regulate to watch the conceivable presence of PCR inhibitors. Every rRT-PCR 96-well plate had 2 nice amplification controls, 2 detrimental amplification controls, 1 nice extraction keep watch over, and 1 detrimental extraction keep watch over. We ran the rRT-PCR on an ABI 7500 Rapid thermocycler and analyzed information with Design and Research Device 2.7.0 (each Thermo Fisher Medical). We regarded as samples with cycle threshold (Ct) values <40.0 to be nice for virus.
After the screening rRT-PCR, we analyzed IAV RNA–nice samples for the H5 subtype and H5 clade 2.3.4.4b by means of the use of the similar RNA extraction and NAHLN-approved rRT-PCR protocols as described in the past, in keeping with usual working procedures. We carried out PCR at the ABI 7500 Rapid thermocycler by means of the use of suitable controls to locate H5-specific IAV. We regarded as samples with Ct values <40.0 to be nice for the IAV H5 subtype.
We performed genomic sequencing of two milk samples from inflamed dairy livestock from Texas and a couple of tissue samples (lung and mind) from cats that died at a special Texas dairy. We subjected the whole-genome sequencing information to bioinformatics research to collect the 8 other IAV section sequences in keeping with in the past described strategies (8). We used the hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA) sequences for phylogenetic research. We bought reference sequences for the HA and NA segments of IAV H5 clade 2.3.4.4 from publicly to be had databases, together with GISAID ( and GenBank. We aligned the sequences by means of the use of MAFFT model 7.520 device ( to create a couple of collection alignments for next phylogenetic research. We used IQTree2 ( to build the phylogenetic tree from the aligned sequences. The device used to be configured to robotically determine the optimum substitution type by means of the use of the ModelFinder Plus possibility, making sure the choice of probably the most appropriate type for the dataset and, thereby, bettering the accuracy of the reconstructed tree. We visualized the ensuing phylogenetic tree by means of the use of iTOL ( a web based platform for interactive tree exploration and annotation.
Gross Lesions in Cows and Cats
All cows had been in excellent frame situation with good enough rumen fill and no exterior indications of illness. Postmortem examinations of the affected dairy cows published company mammary glands standard of mastitis; alternatively, mammary gland lesions weren’t constant. Two cows that had been acutely sick earlier than postmortem exam had grossly commonplace milk and no odd mammary gland lesions. The gastrointestinal tract of a few cows had small abomasal ulcers and shallow linear erosions of the intestines, however the ones observations had been additionally no longer constant in all animals. The colon contents had been brown and sticky, suggesting reasonable dehydration. The feces contained feed debris that seemed to have gone through minimum ruminal fermentation. The rumen contents had commonplace colour and look however seemed to have gone through minimum fermentation.
The two grownup cats (1 intact male, 1 intact feminine) gained on the ISUVDL had been in good enough frame and postmortem situation. Exterior exam used to be unremarkable. Delicate hemorrhages had been seen within the subcutaneous tissues over the dorsal cranium, and multifocal meningeal hemorrhages had been seen within the cerebrums of each cats. The gastrointestinal tracts had been empty, and no different gross lesions had been seen.
Microscopic Lesions in Cows and Cats
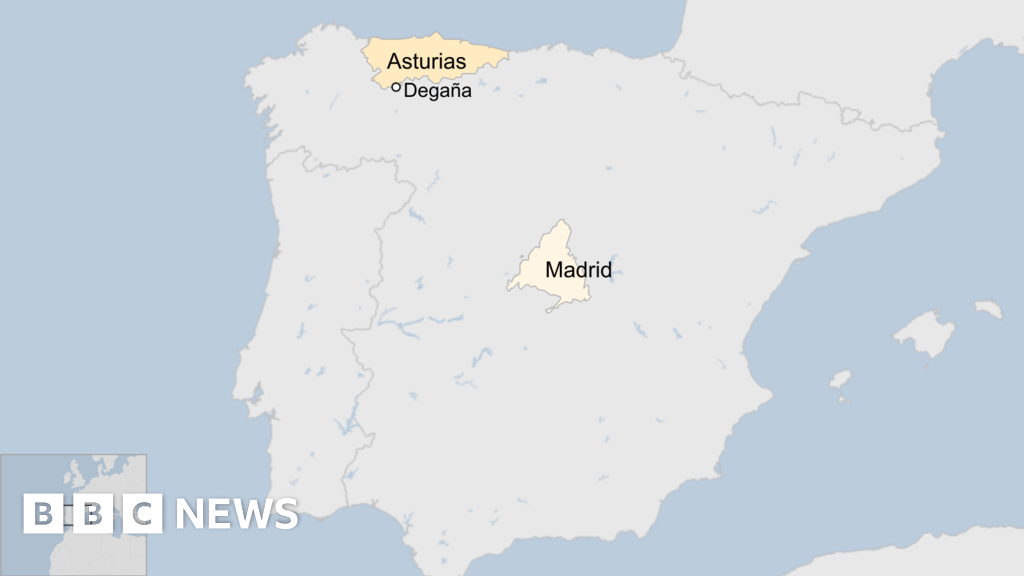
Determine 1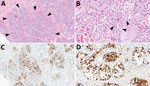 Determine 1. Mammary gland lesions in livestock in learn about of extremely pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b virus an infection in home dairy livestock and cats, United States, 2024. A, B) Mammary gland…The manager microscopic lesion seen in affected cows used to be reasonable acute multifocal neutrophilic mastitis (Determine 1); alternatively, mammary glands weren’t gained from each and every cow. 3 cows had delicate neutrophilic or lymphocytic hepatitis. As a result of they had been grownup livestock, different seen microscopic lesions (e.g., delicate lymphoplasmacytic interstitial nephritis and gentle to reasonable lymphocytic abomasitis) had been presumed to be nonspecific, age-related adjustments. We didn’t practice main lesions within the different evaluated tissues. We carried out IHC for IAV antigen on all evaluated tissues; the one tissues with nice immunoreactivity had been mastitic mammary glands from 2 cows that confirmed nuclear and cytoplasmic labeling of alveolar epithelial cells and cells inside of lumina (Determine 1) and multifocal germinal facilities inside of a lymph node from 1 cow (Desk 1).
Determine 1. Mammary gland lesions in livestock in learn about of extremely pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b virus an infection in home dairy livestock and cats, United States, 2024. A, B) Mammary gland…The manager microscopic lesion seen in affected cows used to be reasonable acute multifocal neutrophilic mastitis (Determine 1); alternatively, mammary glands weren’t gained from each and every cow. 3 cows had delicate neutrophilic or lymphocytic hepatitis. As a result of they had been grownup livestock, different seen microscopic lesions (e.g., delicate lymphoplasmacytic interstitial nephritis and gentle to reasonable lymphocytic abomasitis) had been presumed to be nonspecific, age-related adjustments. We didn’t practice main lesions within the different evaluated tissues. We carried out IHC for IAV antigen on all evaluated tissues; the one tissues with nice immunoreactivity had been mastitic mammary glands from 2 cows that confirmed nuclear and cytoplasmic labeling of alveolar epithelial cells and cells inside of lumina (Determine 1) and multifocal germinal facilities inside of a lymph node from 1 cow (Desk 1).
Determine 2 Determine 2. Lesions in cat tissues in learn about of extremely pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b virus an infection in home dairy livestock and cats, United States, 2024. Tissue sections had been stained with…Each cats had microscopic lesions in line with critical systemic virus an infection, together with critical subacute multifocal necrotizing and lymphocytic meningoencephalitis with vasculitis and neuronal necrosis, reasonable subacute multifocal necrotizing and lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia, reasonable to critical subacute multifocal necrotizing and lymphohistiocytic myocarditis, and reasonable subacute multifocal lymphoplasmacytic chorioretinitis with ganglion cellular necrosis and attenuation of the inner plexiform and nuclear layers (Desk 2; Determine 2). We carried out IHC for IAV antigen on a couple of tissues (mind, eye, lung, middle, spleen, liver, and kidney). We detected nice IAV immunoreactivity in mind (intracytoplasmic, intranuclear, and axonal immunolabeling of neurons), lung, and middle, and multifocal and segmental immunoreactivity inside of all layers of the retina (Determine 2).
Determine 2. Lesions in cat tissues in learn about of extremely pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b virus an infection in home dairy livestock and cats, United States, 2024. Tissue sections had been stained with…Each cats had microscopic lesions in line with critical systemic virus an infection, together with critical subacute multifocal necrotizing and lymphocytic meningoencephalitis with vasculitis and neuronal necrosis, reasonable subacute multifocal necrotizing and lymphocytic interstitial pneumonia, reasonable to critical subacute multifocal necrotizing and lymphohistiocytic myocarditis, and reasonable subacute multifocal lymphoplasmacytic chorioretinitis with ganglion cellular necrosis and attenuation of the inner plexiform and nuclear layers (Desk 2; Determine 2). We carried out IHC for IAV antigen on a couple of tissues (mind, eye, lung, middle, spleen, liver, and kidney). We detected nice IAV immunoreactivity in mind (intracytoplasmic, intranuclear, and axonal immunolabeling of neurons), lung, and middle, and multifocal and segmental immunoreactivity inside of all layers of the retina (Determine 2).
PCR Knowledge from Cows and Cats
We examined quite a lot of samples from 8 clinically affected mature dairy cows by means of IAV screening and H5 subtype-specific PCR (Desk 3). Milk and mammary gland homogenates constantly confirmed low Ct values: 12.3–16.9 by means of IAV screening PCR, 17.6–23.1 by means of H5 subtype PCR, and 14.7–20.0 by means of H5 2.3.4.4 clade PCR (case 1, cow 1; case 2, cows 1 and a couple of; case 3, cow 1; and case 4, cow 1). We forwarded the samples to the Nationwide Veterinary Products and services Laboratory, which showed the virus used to be an HPAI H5N1 virus pressure.
When to be had, we additionally examined tissue homogenates (e.g., lung, spleen, and lymph nodes), ocular fluid, and rumen contents from 6 cows by means of IAV and H5 subtype-specific PCR (Desk 3). On the other hand, the PCR findings weren’t constant. As an example, the tissue homogenates and ocular fluid examined nice in some however no longer all cows. In case 5, cow 1, the milk pattern examined detrimental by means of IAV screening PCR, however the spleen homogenate examined nice by means of IAV screening, H5 subtype, and H5 2.3.4.4 PCR. For two cows (case 3, cow 1; and case 4, cow 1) that had each milk and rumen contents to be had, each samples examined nice for IAV. Nonetheless, all IAV-positive nonmammary gland tissue homogenates, ocular fluid, and rumen contents had markedly increased Ct values against this to the low Ct values for milk and mammary gland homogenate samples.
We examined mind and lung samples from the two cats (case 6, cats 1 and a couple of) by means of IAV screening and H5 subtype-specific PCR (Desk 3). Each pattern varieties had been nice by means of IAV screening PCR; Ct values had been 9.9–13.5 for mind and 17.4–24.4 for lung samples, indicating prime quantities of virus nucleic acid in the ones samples. The H5 subtype and H5 2.3.4.4 PCR effects had been additionally nice for the mind and lung samples; Ct values had been in line with the IAV screening PCR (Desk 3).
Phylogenetic Analyses
We assembled the sequences of all 8 segments of the HPAI viruses from each cow milk and cat tissue samples. We used the hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA) sequences particularly for phylogenetic research to delineate the clade of the HA gene and subtype of the NA gene.
Determine 3 Determine 3. Phylogenetic research of hemagglutinin gene sequences in learn about of extremely pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b virus an infection in home dairy livestock and cats, United States, 2024. Colours point out other…For HA gene research, each HA sequences derived from cow milk samples exhibited a prime level of similarity, sharing 99.88% nucleotide id, while the two HA sequences from cat tissue samples confirmed whole id at 100%. The HA sequences from the milk samples had 99.94% nucleotide identities with HA sequences from the cat tissues, leading to a definite subcluster comprising all 4 HA sequences, which clustered at the side of different H5N1 viruses belonging to clade 2.3.4.4b (Determine 3). The HA sequences had been deposited in GenBank (accession nos. PP599465 [case 2, cow 1], PP599473 [case 2, cow 2], PP692142 [case 6, cat 1], and PP692195 [case 6, cat 2]).
Determine 3. Phylogenetic research of hemagglutinin gene sequences in learn about of extremely pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b virus an infection in home dairy livestock and cats, United States, 2024. Colours point out other…For HA gene research, each HA sequences derived from cow milk samples exhibited a prime level of similarity, sharing 99.88% nucleotide id, while the two HA sequences from cat tissue samples confirmed whole id at 100%. The HA sequences from the milk samples had 99.94% nucleotide identities with HA sequences from the cat tissues, leading to a definite subcluster comprising all 4 HA sequences, which clustered at the side of different H5N1 viruses belonging to clade 2.3.4.4b (Determine 3). The HA sequences had been deposited in GenBank (accession nos. PP599465 [case 2, cow 1], PP599473 [case 2, cow 2], PP692142 [case 6, cat 1], and PP692195 [case 6, cat 2]).
Determine 4 Determine 4. Phylogenetic research of neuraminidase gene sequences in learn about of extremely pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b virus an infection in home dairy livestock and cats, United States, 2024. Colours point out other…For NA gene research, the two NA sequences bought from cow milk samples confirmed 99.93% nucleotide id. Additionally, the NA sequences derived from the milk samples exhibited whole nucleotide identities (100%) with the ones from the cat tissues. The 4 NA sequences had been grouped inside the N1 subtype of HPAI viruses (Determine 4). The NA sequences had been deposited in GenBank (accession nos. PP599467 [case 2, cow 1], PP599475 [case 2, cow 2], PP692144 [case 6, cat 1], and PP692197 [case 6, cat 2]).
Determine 4. Phylogenetic research of neuraminidase gene sequences in learn about of extremely pathogenic avian influenza A(H5N1) clade 2.3.4.4b virus an infection in home dairy livestock and cats, United States, 2024. Colours point out other…For NA gene research, the two NA sequences bought from cow milk samples confirmed 99.93% nucleotide id. Additionally, the NA sequences derived from the milk samples exhibited whole nucleotide identities (100%) with the ones from the cat tissues. The 4 NA sequences had been grouped inside the N1 subtype of HPAI viruses (Determine 4). The NA sequences had been deposited in GenBank (accession nos. PP599467 [case 2, cow 1], PP599475 [case 2, cow 2], PP692144 [case 6, cat 1], and PP692197 [case 6, cat 2]).
This situation collection differs from maximum earlier stories of IAV an infection in bovids, which indicated livestock had been inapparently inflamed or proof against an infection (9). We describe an H5N1 pressure of IAV in dairy livestock that led to obvious systemic sickness, lowered milk manufacturing, and considerable virus losing in milk. The magnitude of this discovering is additional emphasised by means of the prime dying fee (≈50%) of cats on farm premises that had been fed uncooked colostrum and milk from affected cows; scientific illness and lesions advanced that had been in line with earlier stories of H5N1 an infection in cats possibly derived from eating inflamed wild birds (10–12). Even supposing publicity to and intake of useless wild birds can’t be utterly dominated out for the cats described on this file, the identified intake of unpasteurized milk and colostrum from inflamed cows and the prime quantity of virus nucleic acid inside the milk make milk and colostrum intake a most probably course of publicity. Due to this fact, our findings counsel cross-species mammal-to-mammal transmission of HPAI H5N1 virus and lift new considerations referring to the potential of virus unfold inside of mammal populations. Horizontal transmission of HPAI H5N1 virus has been in the past demonstrated in experimentally inflamed cats (13) and ferrets (14) and is suspected to account for enormous dieoffs seen all over herbal outbreaks in mink (15) and sea lions (16). Long run experimental research of HPAI H5N1 virus in dairy livestock will have to search to verify cross-species transmission to cats and probably different mammals.
Medical IAV an infection in livestock has been every now and then reported within the revealed literature. The primary file happened in Japan in 1949, the place a brief process illness with pyrexia, anorexia, nasal discharge, pneumonia, and reduced lactation advanced in livestock (17). In 1997, a an identical situation happened in dairy cows in southwest England resulting in a sporadic drop in milk manufacturing (18), and IAV seroconversion used to be later related to lowered milk yield and breathing illness (19–21). Emerging antibody titers towards human-origin influenza A viruses (H1N1 and H3N2) had been later once more reported in dairy livestock in England, which ended in an acute fall in milk manufacturing all over October 2005–March 2006 (22). Restricted stories of IAV isolation from livestock exist; maximum stories happened all over the Sixties and Seventies in Hungary and within the former Soviet Union, the place H3N2 used to be recovered from livestock experiencing breathing illness (9,23). Direct detection of IAV in milk and the prospective transmission from livestock to cats thru feeding of unpasteurized milk has no longer been in the past reported.
An IAV-associated drop in milk manufacturing in dairy livestock seems to have happened all over >4 distinct classes and inside of 3 broadly separated geographic spaces: 1949 in Japan (17), 1997–1998 and 2005–2006 in Europe (19,21), and 2024 in the US (this file). The sporadic incidence of scientific illness in dairy livestock international may well be the results of adjustments in subclinical an infection charges and the presence or absence of enough baseline IAV antibodies in livestock to forestall an infection. Milk IgG, lactoferrin, and conglutinin have additionally been advised as host components that may cut back susceptibility of bovids to IAV an infection (9). Recent estimates of the seroprevalence of IAV antibodies in US livestock don’t seem to be effectively described within the revealed literature. One retrospective serologic survey in the US within the past due Nineties confirmed 27% of serum samples had nice antibody titers and 31% had low-positive titers for IAV H1 subtype-specific antigen in livestock and not using a proof of scientific infections (24). Antibody titers for H5 subtype-specific antigen have no longer been reported in US livestock.
The susceptibility of home cats to HPAI H5N1 is well-documented globally (10–12,25–28), and an infection ceaselessly leads to neurologic indicators in affected felids and different terrestrial mammals (4). Maximum circumstances in cats outcome from eating inflamed wild birds or infected poultry merchandise (12,27). The incubation length in cats is brief; scientific illness is ceaselessly seen 2–3 days after an infection (28). Mind tissue has been advised as the most productive diagnostic pattern to verify HPAI virus an infection in cats (10), and our effects give a boost to that discovering. One distinctive discovering within the cats from this file is the presence of blindness and microscopic lesions of chorioretinitis. The ones effects counsel that additional investigation into doable ocular manifestations of HPAI H5N1 virus an infection in cats may well be warranted.
The genomic sequencing and next research of scientific samples from each bovine and pussycat resources supplied substantial insights. The HA and NA sequences derived from each bovine milk and cat tissue samples from other Texas farms had a notable level of similarity. The ones findings strongly counsel a shared starting place for the viruses detected within the dairy livestock and cat tissues. Additional analysis, case collection investigations, and surveillance information are had to higher perceive and tell measures to curtail the scientific results, losing, and unfold of HPAI viruses amongst mammals. Even supposing pasteurization of business milk mitigates dangers for transmission to people, a 2019 US client learn about confirmed that 4.4% of adults ate up uncooked milk >1 time all over the former yr (29), indicating a necessity for public consciousness of the prospective presence of HPAI H5N1 viruses in uncooked milk.
Ingestion of feed infected with feces from wild birds inflamed with HPAI virus is presumed to be the perhaps preliminary supply of an infection within the dairy farms. Even supposing the precise supply of the virus is unknown, migratory birds (Anseriformes and Charadriiformes) are most probably resources since the Texas panhandle area lies within the Central Flyway, and the ones birds are the primary herbal reservoir for avian influenza viruses (30). HPAI H5N1 viruses are effectively tailored to home geese and ducks, and geese seem to be a big reservoir (31); alternatively, terns have additionally emerged as a very powerful supply of virus unfold (32). The mode of transmission amongst inflamed livestock could also be unknown; alternatively, horizontal transmission has been advised as a result of illness advanced in resident livestock herds in Michigan, Idaho, and Ohio farms that gained inflamed livestock from the affected areas, and the ones livestock examined nice for HPAI H5N1 (33). Experimental research are had to decipher the transmission routes and pathogenesis (e.g., replication websites and motion) of the virus inside of inflamed livestock.
In conclusion, we confirmed that dairy livestock are at risk of an infection with HPAI H5N1 virus and will shed virus in milk and, subsequently, may probably transmit an infection to different mammals by the use of unpasteurized milk. A discount in milk manufacturing and imprecise systemic sickness had been probably the most regularly reported scientific indicators in affected cows, however neurologic indicators and dying all of a sudden advanced in affected home cats. HPAI virus an infection will have to be regarded as in dairy livestock when an surprising and unexplained abrupt drop in feed consumption and milk manufacturing happens and for cats when fast onset of neurologic indicators and blindness broaden. The habitual nature of worldwide HPAI H5N1 virus outbreaks and detection of spillover occasions in a large host vary is relating to and suggests expanding virus adaptation in mammals. Surveillance of HPAI viruses in home manufacturing animals, together with livestock, is had to elucidate influenza virus evolution and ecology and save you cross-species transmission.
Dr. Burrough is a professor and diagnostic pathologist on the Iowa State College School of Veterinary Drugs and Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory. His analysis specializes in infectious sicknesses of cattle with an emphasis on swine.
Best