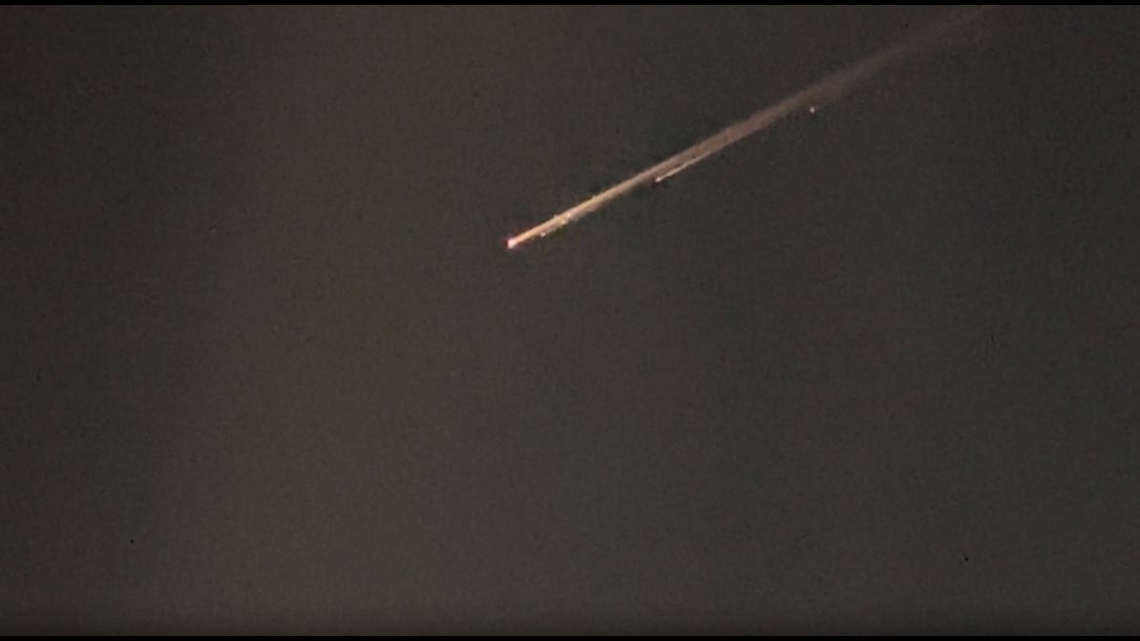
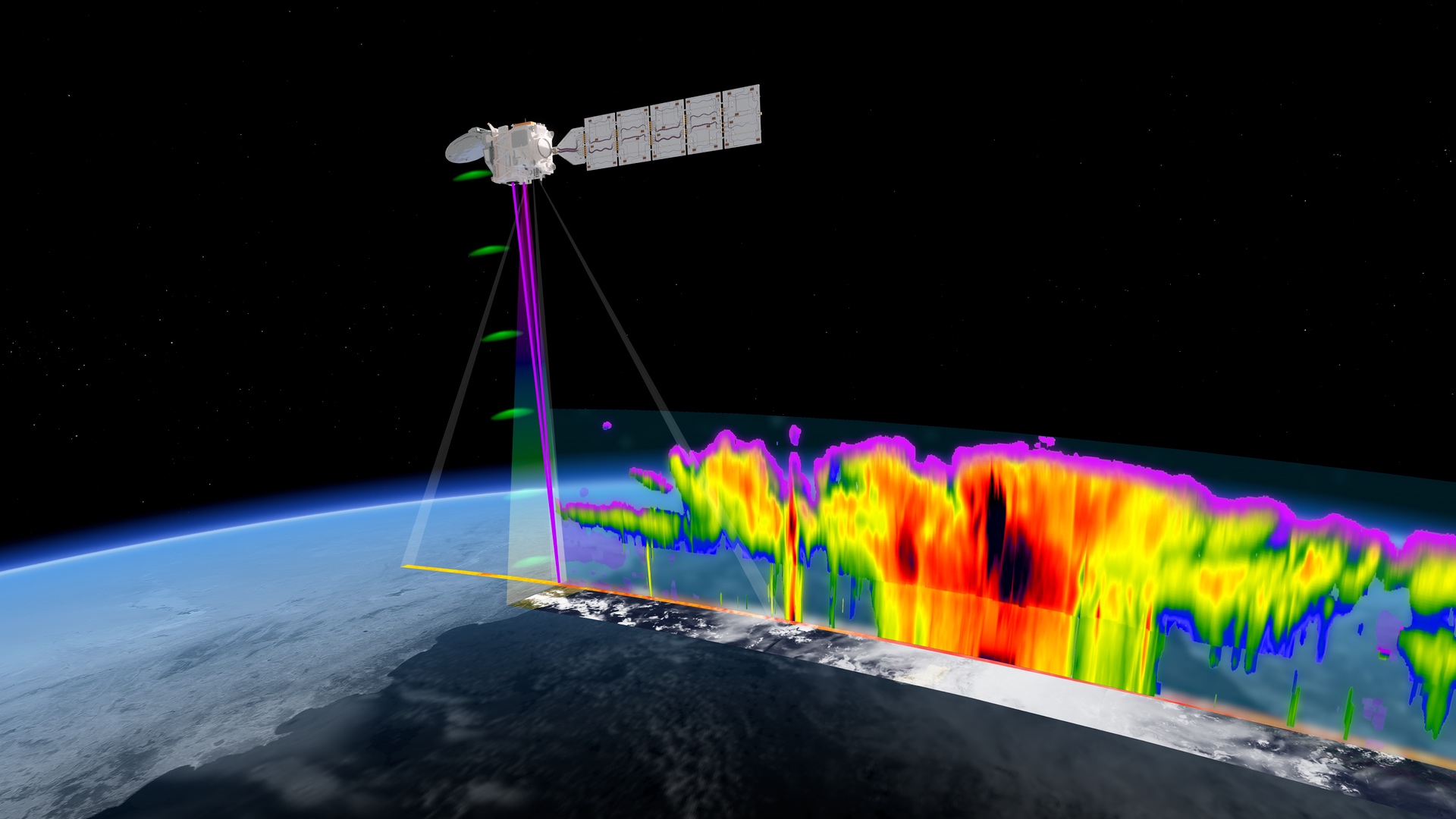
WASHINGTON — A Falcon 9 effectively introduced an Earth science project for Europe and Japan Would possibly 28 as a part of the Eu House Company’s ongoing, if brief, reliance on SpaceX for area get admission to.
The Falcon 9 lifted off from Vandenberg House Pressure Base in California at 6:20 p.m. Japanese. The payload, the Earth Cloud Aerosol and Radiation Explorer (EarthCARE) spacecraft, separated from the higher degree about 10 mins after liftoff.
Simonetta Cheli, director of Earth statement systems at ESA, mentioned in a post-launch interview that controllers had been in touch with the spacecraft. “It’s all nominal and heading in the right direction.”
Spacecraft controllers will spend the weeks and months forward trying out the spacecraft’s tools and calibrating them, she mentioned. That may permit the primary unencumber of science knowledge from EarthCARE across the finish of this 12 months or early subsequent 12 months.
EarthCARE is an 800-million-euro ($870 million) ESA-led project to check clouds and aerosols within the environment. The spacecraft carries 4 tools, together with a cloud profiling radar supplied through the Jap area company JAXA at a price of 8.3 billion yen ($53 million). JAXA dubbed the spacecraft Hakuryu or “White Dragon” on account of the spacecraft’s look.
The two,200-kilogram spacecraft, flying in a sun-synchronous orbit at an altitude of 393 kilometers, will gather knowledge on clouds and aerosols within the environment, along side imagery and measurements of mirrored daylight and radiated warmth. That data will likely be used for atmospheric science, together with local weather and climate fashions.
“EarthCARE is there to check the impact of clouds and aerosols at the thermal stability of the Earth,” mentioned Dirk Bernaerts, ESA’s EarthCARE challenge supervisor, at a pre-launch briefing Would possibly 21. “It’s essential to watch all of them in combination on the identical location on the identical time. That’s what is exclusive about this spacecraft.”
Different spacecraft make an identical measurements, together with NASA’s Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, ocean Ecosystem (PACE) spacecraft introduced in February. “The statement ways are other,” he mentioned. “We follow the similar factor however follow rather other facets of the clouds and aerosols.” He added that EarthCARE would use PACE knowledge to lend a hand with calibration and validation of its observations.
Building of EarthCARE took about twenty years and ended in price expansion that Cheli estimated on the pre-launch briefing to be 30%. Maximilian Sauer, EarthCARE challenge supervisor at top contractor Airbus, mentioned a number of components contributed to the delays and overruns, together with technical problems with the tools in addition to results of the pandemic.
One lesson realized from EarthCARE, Cheli mentioned within the post-launch interview, used to be the desire for “strict control” of the challenge, which she mentioned suffered from demanding situations of coordinating paintings between companies and corporations. The project additionally underscored the significance of sturdy toughen from member states because it labored to conquer issues, she added.
Some other think about EarthCARE’s lengthen used to be a metamorphosis in release automobiles. EarthCARE used to be in the beginning slated to move on a Soyuz rocket however ESA misplaced get admission to to the automobile after Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. The project used to be first moved to Europe’s Vega C, however ESA determined closing June to release it as an alternative on a Falcon 9, mentioning delaying in returning that rocket to flight in addition to adjustments to the rocket’s payload fairing that may had been had to accommodate EarthCARE.
Technically, the shift in release automobiles used to be no longer a significant issue for the project. “All the way through the adjustments within the launchers we didn’t have to modify the design of the spacecraft,” mentioned Bernaerts.
He mentioned that, all the way through environmental assessments, engineers put the spacecraft via prerequisites simulating other release automobiles to organize for the possibility of converting automobiles. “From the instant we knew that Soyuz used to be no longer to be had, we now have been having a look at how stringently shall we check the spacecraft to envelope different candidate launchers. That’s what we did and that labored out in spite of everything.”
EarthCARE is the second one ESA-led project to release on a Falcon 9, after the Euclid area telescope closing July. Some other Falcon 9 will release ESA’s Hera asteroid project q4.
“We had a excellent enjoy with Euclid closing 12 months,” mentioned Josef Aschbacher, ESA director basic, in a post-launch interview. “Our groups and the SpaceX groups are operating in combination really well.”
The usage of the Falcon 9 is a stopgap till Ariane 6 enters products and services, with a primary release now scheduled for the primary part of July, and Vega C returns to flight on the finish of the 12 months. “I listen a number of questions on why we’re launching with Falcon and no longer with Ariane, and it’s actually excellent to peer the Ariane 6 inaugural flight coming nearer,” he mentioned.
The ones concerned with the project had been merely satisfied to after all get the spacecraft into orbit. “There’s a feeling of aid and happiness,” Cheli mentioned after the release.
“That is an emotional curler coaster,” mentioned Thorsten Fehr, EarthCARE project scientist at ESA, at the company webcast of the release in a while after payload separation. “This is without doubt one of the largest moments in my skilled existence ever.”
Similar