The deeper we glance into area, the additional again in time we see. Mild emanating from one of the vital more youthful galaxies in our universe has to commute for billions of years to achieve us, getting picked up through our tools, wealthy with knowledge from the cosmic morning time. And now not most effective can this gentle let us know the place now we have come from, however the place we may well be headed. To know the evolution of a number of of those early universe, “teenage” galaxies, a Northwestern College-led staff of astrophysicists have inspected information from the James Webb Area Telescope (JWST), which gazed again to geographical regions that shaped simply two-to-three billions years after the Giant Bang. The observations have thrown up some intriguing surprises. In particular, the staff analyzed effects from the Chemical Evolution Constrained the usage of Ionized Traces in Interstellar Aurorae (CECILIA) Survey to seek out that, now not most effective do those galaxies seem warmer than anticipated, however in addition they appear to host heavy parts, like nickel. Comparable: The James Webb Area Telescope catches far away younger galaxy devouring its neighbors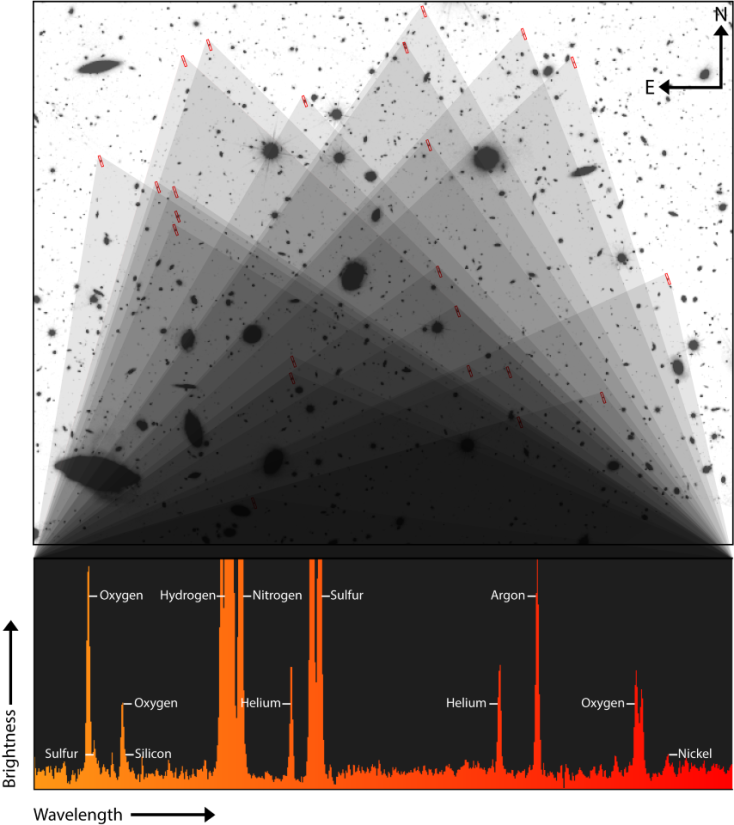 Mild from 23 far away galaxies, recognized with pink rectangles within the Hubble Area Telescope symbol on the best, had been mixed to seize extremely faint emission from 8 other parts, which can be labelled within the JWST spectrum on the backside. Even supposing scientists continuously in finding those parts on Earth, astronomers hardly, if ever, follow a lot of them in far away galaxies. (Symbol credit score: Aaron M. Geller, Northwestern, CIERA + IT-RCDS )The researchers concerned about 33 far away galaxies for a continuing 30 hour length. They then mixed wavelengths of sunshine gathered from 23 of the ones galaxies to create a composite image of what is going down in those buildings — those spectra include clues relating to such things as their reasonable temperatures and what parts may well be lurking inside of. “This washes out the main points of person galaxies however provides us a greater sense of a mean galaxy. It additionally lets in us to look fainter options,” Allison Strom, lead writer of the find out about and assistant professor of physics and astronomy at Northwestern College, stated in a remark. The composite image of the galaxies contained 8 identifiable parts: Hydrogen, helium, nitrogen, oxygen, silicon, sulfur, argon and nickel. Whilst the lighter parts had been anticipated, the presence of nickel, which is heavier than iron within the periodic desk, got here as quite of a marvel. “By no means in my wildest goals did I consider we might see nickel,” Strom stated.Even in older, within sight galaxies, nickel hardly is noticed — and that’s the reason after more than one lifestyles cycles of stars, that means more than one rounds of supernovas, and the chance for heavier parts to synthesize and unfold right through the galaxy. “Nobody ever talks about gazing nickel. Components need to be sparkling in fuel to ensure that us to look them. So, to ensure that us to look nickel, there could also be one thing distinctive concerning the stars throughout the galaxies,” Strom stated. Strom believes the upper noticed temperatures in those early galaxies may well be hooked up to their curious chemical composition in some way: “In the long run, the truth that we see the next function temperature is simply every other manifestation in their other chemical DNA for the reason that temperature and chemistry of fuel in galaxies are intrinsically related.”The find out about was once revealed Nov. 20 within the magazine The Astrophysical Magazine Letters.
Mild from 23 far away galaxies, recognized with pink rectangles within the Hubble Area Telescope symbol on the best, had been mixed to seize extremely faint emission from 8 other parts, which can be labelled within the JWST spectrum on the backside. Even supposing scientists continuously in finding those parts on Earth, astronomers hardly, if ever, follow a lot of them in far away galaxies. (Symbol credit score: Aaron M. Geller, Northwestern, CIERA + IT-RCDS )The researchers concerned about 33 far away galaxies for a continuing 30 hour length. They then mixed wavelengths of sunshine gathered from 23 of the ones galaxies to create a composite image of what is going down in those buildings — those spectra include clues relating to such things as their reasonable temperatures and what parts may well be lurking inside of. “This washes out the main points of person galaxies however provides us a greater sense of a mean galaxy. It additionally lets in us to look fainter options,” Allison Strom, lead writer of the find out about and assistant professor of physics and astronomy at Northwestern College, stated in a remark. The composite image of the galaxies contained 8 identifiable parts: Hydrogen, helium, nitrogen, oxygen, silicon, sulfur, argon and nickel. Whilst the lighter parts had been anticipated, the presence of nickel, which is heavier than iron within the periodic desk, got here as quite of a marvel. “By no means in my wildest goals did I consider we might see nickel,” Strom stated.Even in older, within sight galaxies, nickel hardly is noticed — and that’s the reason after more than one lifestyles cycles of stars, that means more than one rounds of supernovas, and the chance for heavier parts to synthesize and unfold right through the galaxy. “Nobody ever talks about gazing nickel. Components need to be sparkling in fuel to ensure that us to look them. So, to ensure that us to look nickel, there could also be one thing distinctive concerning the stars throughout the galaxies,” Strom stated. Strom believes the upper noticed temperatures in those early galaxies may well be hooked up to their curious chemical composition in some way: “In the long run, the truth that we see the next function temperature is simply every other manifestation in their other chemical DNA for the reason that temperature and chemistry of fuel in galaxies are intrinsically related.”The find out about was once revealed Nov. 20 within the magazine The Astrophysical Magazine Letters.
Far-off ‘teenage galaxies’ marvel astronomers with surprising heavy parts