Teleoperated rovers may quickly be running at the moon, with human controllers on Earth manipulating the rovers’ equipment just about, making an allowance for higher dexterity when taking samples, digging or assembling.Researchers from the robotics laboratory on the College of Bristol in England have examined their new teleoperations machine on the Eu Area Company’s (ESA) Eu Centre for Area Programs and Telecommunications at Harwell in Oxfordshire. By way of controlling a digital simulation of a rover, they have been ready to control a robot arm to dig a pattern of faux lunar regolith (known as simulant). The method negates the will for digicam feeds, which is able to lag as a result of the 1.3-second time prolong between Earth and the moon. The alerts between the teleoperators and robot missions at the moon may in long term be relayed by way of satellites belonging to ESA’s deliberate Moonlight venture.”This simulation may … assist us perform lunar robots remotely from Earth, keeping off the issue of sign delays,” mentioned Bristol’s Joe Louca in a commentary.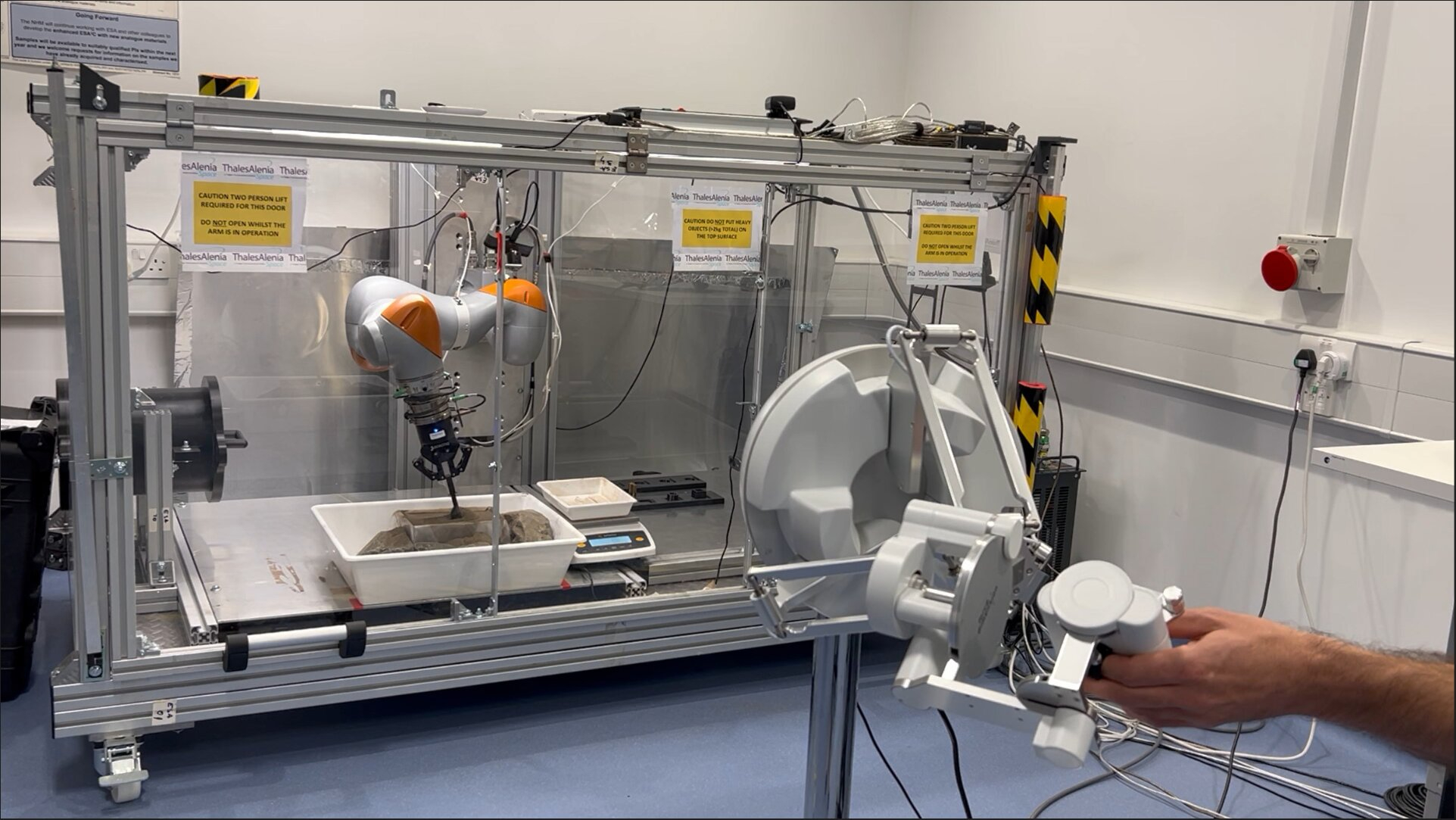  A teleoperated machine scooping up simulant, which is a correct copy of lunar regolith. (Symbol credit score: Joe Louca)The digital simulation additionally accommodates “haptic” interactions. In different phrases, it provides the person a way of contact, mimicking the tactile homes of lunar regolith within the moon’s low gravity. This provides teleoperators a better sense of ways a lot power they’ve to make use of to dig into regolith, or to raise up a pattern in a scoop. Thus far, the haptic interactions have handiest been incorporated within the digital variations of elementary duties, comparable to urgent regolith into the bottom or dragging a scoop via it, however now not but for extra advanced duties.Similar: Moon robots may construct stone partitions to give protection to lunar bases from rocket exhaust”We will be able to alter how robust gravity is on this style, and supply haptic comments, so lets give astronauts a way of ways moon mud would really feel and behave in lunar prerequisites — which has a 6th of the gravitational pull of the Earth,” mentioned Louca. The machine is also used to coach astronauts who would possibly someday move to the moon by way of giving them a practical simulation of what to anticipate.Breaking house information, the newest updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!”One possibility may well be to have astronauts use this simulation to organize for upcoming lunar exploration missions,” mentioned Louca.Alternatively, earlier than that may occur, Louca says there are consider problems to conquer. Earlier research have proven that there’s a mental barrier to trusting whether or not the digital machine {that a} person is working is appearing because it must in truth. Louca’s group has quantified the potency and trustworthiness in their digital machine, discovering that, when scooping up regolith simulant, the machine was once environment friendly 100% of the time and faithful 92.5% of the time. Pouring simulant out of the inside track was once rather less dependable, however they discovered that by way of limiting the orientation of the inside track whilst sporting the simulant, it may well be carried out extra exactly.
A teleoperated machine scooping up simulant, which is a correct copy of lunar regolith. (Symbol credit score: Joe Louca)The digital simulation additionally accommodates “haptic” interactions. In different phrases, it provides the person a way of contact, mimicking the tactile homes of lunar regolith within the moon’s low gravity. This provides teleoperators a better sense of ways a lot power they’ve to make use of to dig into regolith, or to raise up a pattern in a scoop. Thus far, the haptic interactions have handiest been incorporated within the digital variations of elementary duties, comparable to urgent regolith into the bottom or dragging a scoop via it, however now not but for extra advanced duties.Similar: Moon robots may construct stone partitions to give protection to lunar bases from rocket exhaust”We will be able to alter how robust gravity is on this style, and supply haptic comments, so lets give astronauts a way of ways moon mud would really feel and behave in lunar prerequisites — which has a 6th of the gravitational pull of the Earth,” mentioned Louca. The machine is also used to coach astronauts who would possibly someday move to the moon by way of giving them a practical simulation of what to anticipate.Breaking house information, the newest updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!”One possibility may well be to have astronauts use this simulation to organize for upcoming lunar exploration missions,” mentioned Louca.Alternatively, earlier than that may occur, Louca says there are consider problems to conquer. Earlier research have proven that there’s a mental barrier to trusting whether or not the digital machine {that a} person is working is appearing because it must in truth. Louca’s group has quantified the potency and trustworthiness in their digital machine, discovering that, when scooping up regolith simulant, the machine was once environment friendly 100% of the time and faithful 92.5% of the time. Pouring simulant out of the inside track was once rather less dependable, however they discovered that by way of limiting the orientation of the inside track whilst sporting the simulant, it may well be carried out extra exactly.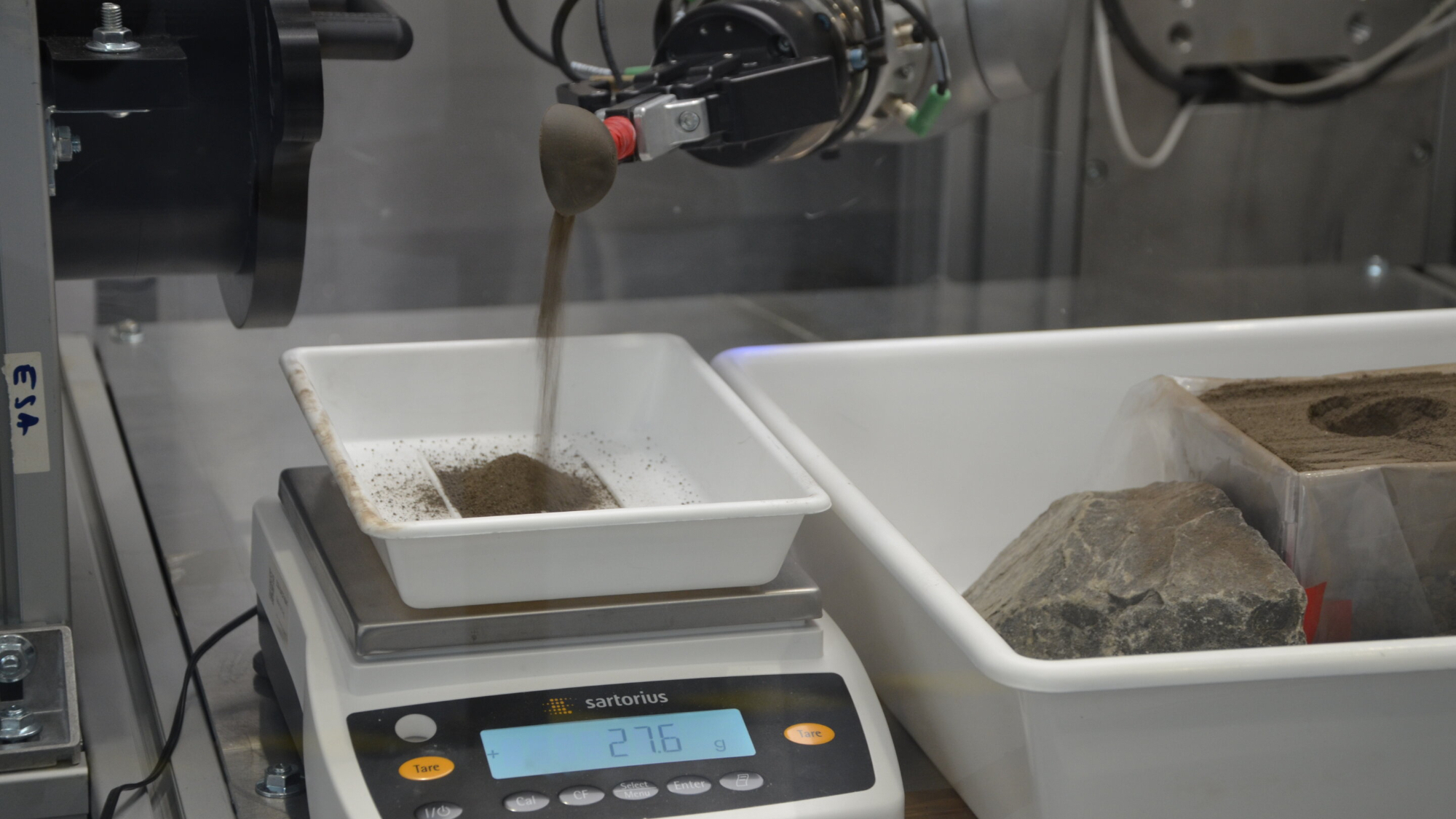 Pouring subject material from a scoop the use of the digital teleoperation was once discovered to be quite much less correct than scooping it up within the first position. (Symbol credit score: Joe Louca)Even if designed with the moon in thoughts, in concept the similar teleoperation tactics is also used for missions to Mars. This may well be specifically useful for the difficult job of retrieving pattern tubes from a rover and loading them onto some other automobile that might blast off from Mars and convey the samples again to Earth. Because the finances and timeline on NASA’s Mars present sample-return venture have spiraled out of management, the gap company has solicited trade to assist increase an answer. Rocket Lab gained a freelance just lately to behavior an in depth learn about right into a imaginable answer for retrieving the Perseverance rover’s samples, despite the fact that it can be too quickly for teleoperation to play a job. Alternatively, different sample-return and exploration missions to the moon, Mars and different rocky our bodies comparable to asteroids would possibly all take pleasure in teleoperation at some point.”Within the subsequent decade we are going to see a number of crewed and uncrewed missions to the moon, comparable to NASA’s Artemis program and China’s Chang’e program,” mentioned Louca. “This simulation is usually a precious instrument to strengthen preparation or operation for those missions.”
Pouring subject material from a scoop the use of the digital teleoperation was once discovered to be quite much less correct than scooping it up within the first position. (Symbol credit score: Joe Louca)Even if designed with the moon in thoughts, in concept the similar teleoperation tactics is also used for missions to Mars. This may well be specifically useful for the difficult job of retrieving pattern tubes from a rover and loading them onto some other automobile that might blast off from Mars and convey the samples again to Earth. Because the finances and timeline on NASA’s Mars present sample-return venture have spiraled out of management, the gap company has solicited trade to assist increase an answer. Rocket Lab gained a freelance just lately to behavior an in depth learn about right into a imaginable answer for retrieving the Perseverance rover’s samples, despite the fact that it can be too quickly for teleoperation to play a job. Alternatively, different sample-return and exploration missions to the moon, Mars and different rocky our bodies comparable to asteroids would possibly all take pleasure in teleoperation at some point.”Within the subsequent decade we are going to see a number of crewed and uncrewed missions to the moon, comparable to NASA’s Artemis program and China’s Chang’e program,” mentioned Louca. “This simulation is usually a precious instrument to strengthen preparation or operation for those missions.”
Faraway-control robots may assist humanity discover the moon and Mars