A hidden threat would possibly exist underneath Antarctica that might boost up ice soften, a brand new find out about says.
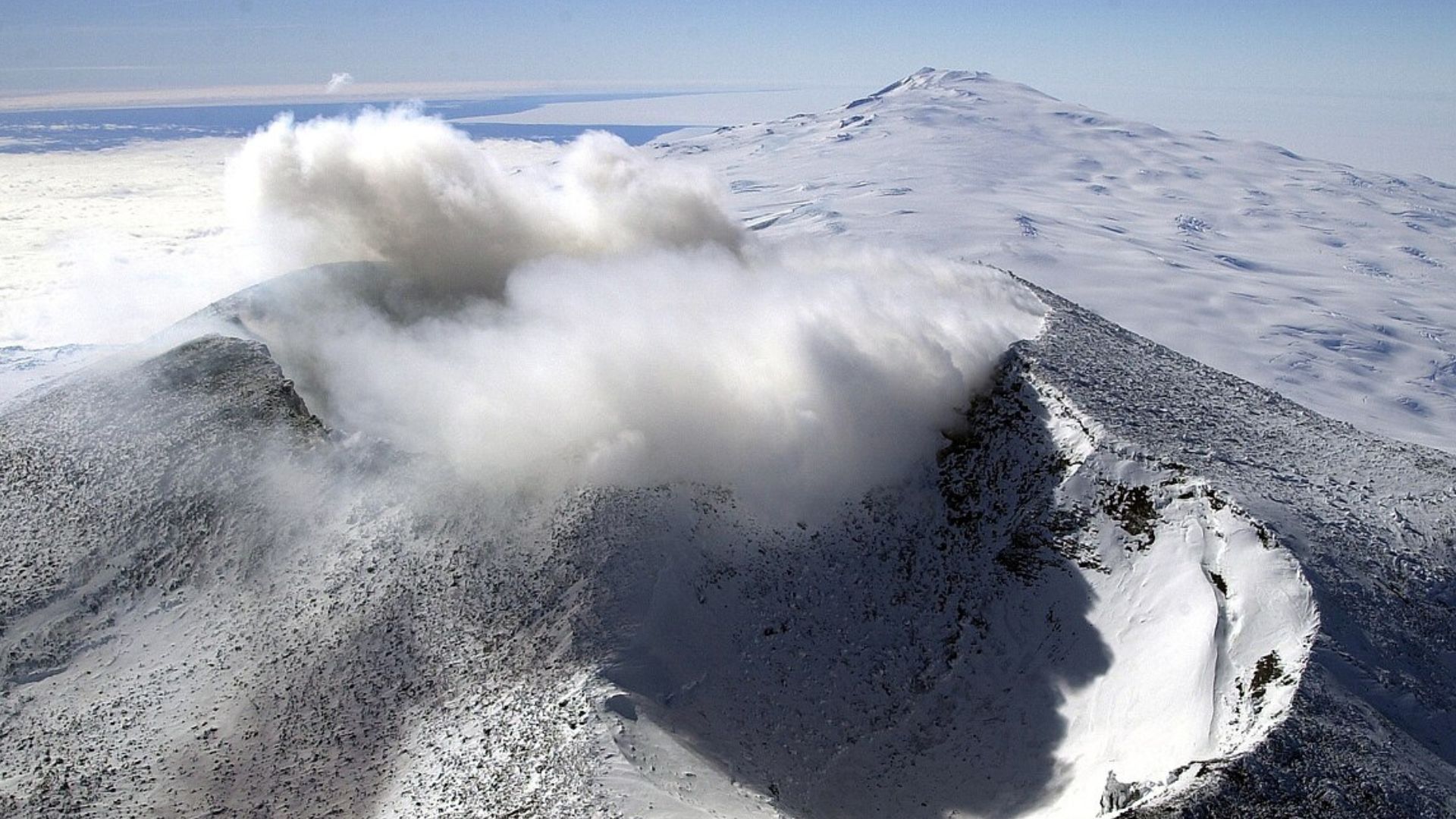
Antarctica isn’t just a passive, icy panorama, however a geologically energetic area with a fancy community of volcanoes — lots of which stay hidden underneath the ice.
This risk exists a number of kilometers underneath the West Antarctic Ice Sheet, which is extremely at risk of the affects of local weather trade.
Researchers from Brown College performed 4,000 laptop simulations to inspect how ice sheet loss influences Antarctica’s buried volcanoes.
“The West Antarctic Ice Sheet is especially at risk of cave in, but its place atop an energetic volcanic rift is seldom regarded as,” the find out about famous.
Ice soften may just affect underlying volcanoes
Mount Erebus is among the recognized energetic volcanoes in Antarctica with a power lava lake. But even so the extra visual ones, Antarctica hosts no less than 100 different volcanoes, reported EOS.org.
A few of these volcanoes are buried deep underneath the thick ice sheet, making them tricky to look at immediately.
Proof means that the Antarctic ice sheet is melting at an alarming charge because of carbon emissions. This melting has vital penalties, now not only for international sea ranges, but in addition for the snoozing volcanoes underneath.
The find out about displays that the elimination of the heavy ice sheet can majorly affect the conduct of underlying volcanoes. Additionally, the sluggish ice soften could have the possible to extend each the frequency and the depth of subglacial eruptions.
The melting of ice sheets reduces the immense drive exerted at the underlying rock and the magma chambers inside. This drive relief permits the magma to extend. This results in larger drive at the partitions of its containing chamber. This larger interior drive can destabilize the device, doubtlessly resulting in volcanic eruptions.
That is very similar to a soda bottle. The drive within helps to keep the carbonation dissolved. Whilst you open the bottle, the drive drops, and the carbonation fizzes out.
In a similar fashion, the relief in drive from ice sheet melting permits the gases dissolved throughout the magma to extend, expanding the total drive throughout the chamber and doubtlessly triggering an eruption.
Correct prediction of sea-level upward push
Correct predictions of long run sea-level upward push rely in large part at the working out of the steadiness of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet.
For this, the fashions wish to imagine the advanced two-way courting between subglacial volcanoes and ice sheet melting.
The staff states that the eruptions of subglacial volcanoes will not be immediately observable at the floor of the ice sheet, however its penalties could be obvious.
The warmth launched via those eruptions can soften ice from underneath, which might weaken the ice sheet from inside. This interior melting additional reduces the drive at the underlying volcanoes.
This might create a self-perpetuating cycle the place ice soften results in extra volcanic eruptions, which in flip results in additional ice soften.
“Taking into account the elimination of km-thick ice sheets, we display that the speed of unloading influences the cumulative mass erupted and because of this the warmth launched into the ice,” the researchers wrote within the find out about paper.
“Those findings supply basic insights into the advanced volcano-ice interactions in West Antarctica and different subglacial volcanic settings,” it added.