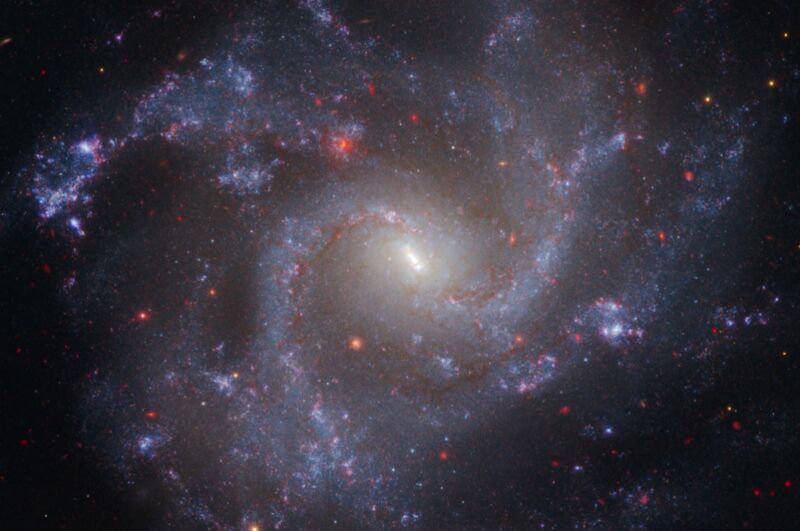
Magnify / This symbol of NGC 5468, about 130 million light-years from Earth, combines information from the Hubble and Webb area telescopes. NASA/ESA/CSA/STScI/A. Riess (JHU)
Astronomers have made new measurements of the Hubble Consistent, a measure of ways temporarily the Universe is increasing, via combining information from the Hubble House Telescope and the James Webb House Telescope. Their effects showed the accuracy of Hubble’s previous size of the consistent’s price, in keeping with their contemporary paper revealed in The Astrophysical Magazine Letters, with implications for a long-standing discrepancy in values acquired via other observational strategies referred to as the “Hubble pressure.”
There was once a time when scientists believed the Universe was once static, however that modified with Albert Einstein’s basic idea of relativity. Alexander Friedmann revealed a collection of equations appearing that the Universe would possibly if truth be told be increasing in 1922, with Georges Lemaitre later making an unbiased derivation to reach at that very same conclusion. Edwin Hubble showed this growth with observational information in 1929. Previous to this, Einstein have been looking to alter basic relativity via including a cosmological consistent so as to get a static universe from his idea; after Hubble’s discovery, legend has it, he referred to that effort as his largest blunder.
As in the past reported, the Hubble consistent is a measure of the universe’s growth expressed in gadgets of kilometers consistent with 2d consistent with megaparsec. So, each and every 2d, each and every megaparsec of the Universe expands via a undeniable selection of kilometers. Differently to think about that is on the subject of a somewhat desk bound object a megaparsec away: Every 2d, it will get quite a few kilometers extra far away.
What number of kilometers? That is the drawback right here. There are principally 3 strategies scientists use to measure the Hubble consistent: taking a look at close by items to peer how briskly they’re transferring, gravitational waves produced via colliding black holes or neutron stars, and measuring tiny deviations within the afterglow of the Large Bang referred to as the Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB). Then again, the more than a few strategies have get a hold of other values. For example, monitoring far away supernovae produced a worth of 73 km/s Mpc, whilst measurements of the CMB the usage of the Planck satellite tv for pc produced a worth of 67 km/s Mpc.
Simply ultimate 12 months, researchers made a 3rd, unbiased measure of the Universe’s growth via monitoring the habits of a gravitationally lensed supernova, the place the distortion in space-time led to via an enormous object acts as a lens to enlarge an object within the background. The most efficient suits of the ones fashions all ended up fairly beneath the price of the Hubble consistent derived from the CMB, with the variation being inside the statistical error. Values nearer to these derived from measurements of alternative supernovae had been a significantly worse have compatibility for the knowledge. The process is new, with really extensive uncertainties, but it surely did supply an unbiased approach of having on the Hubble Consistent.
Commercial
 Magnify / Comparability of Hubble and Webb perspectives of a Cepheid variable famous person.NASA/ESA/CSA/STScI/A. Riess (JHU)
Magnify / Comparability of Hubble and Webb perspectives of a Cepheid variable famous person.NASA/ESA/CSA/STScI/A. Riess (JHU)
“We have now measured it the usage of knowledge within the cosmic microwave background and gotten one price,” Ars Science Editor John Timmer wrote. “And now we have measured it the usage of the plain distance to things within the present-day Universe and gotten a worth that differs via about 10 %. So far as somebody can inform, there is not anything incorrect with both size, and there is not any obtrusive strategy to get them to agree.” One speculation is that the early universe in short skilled some roughly “kick” from repulsive gravity (comparable to the perception of darkish power) that then mysteriously grew to become off and vanished. Nevertheless it stays a speculative thought, albeit a doubtlessly thrilling one for physicists.
This newest size builds on ultimate 12 months’s affirmation according to Webb information that Hubble’s measurements of the growth fee had been correct, a minimum of for the primary few “rungs” of the “cosmic distance ladder.” However there was once nonetheless the potential for as-yet-undetected mistakes that would possibly building up the deeper (and therefore additional again in time) one seemed into the universe, in particular for brightness measurements of extra far away stars.
So a brand new staff made further observations of Cepheid variable stars—a complete of one,000 in 5 host galaxies as some distance out as 130 million light-years—and correlated them with the Hubble information. The Webb telescope is in a position to see previous the interstellar mud that has made Hubble’s personal photographs of the ones stars extra blurry and overlapping, so astronomers may extra simply distinguish between particular person stars.
The consequences additional showed the accuracy of the Hubble information. “We’ve now spanned the entire vary of what Hubble noticed, and we will be able to rule out a size error as the reason for the Hubble Rigidity with very top self belief,” stated co-author and staff chief Adam Riess, a physicist at Johns Hopkins College. “Combining Webb and Hubble offers us the most productive of each worlds. We discover that the Hubble measurements stay dependable as we climb farther alongside the cosmic distance ladder. With size mistakes negated, what stays is the true and thrilling chance that we’ve got misunderstood the Universe.”
The Astrophysical Magazine Letters, 2024. DOI: 10.3847/2041-8213/ad1ddd (About DOIs).





:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25799626/247465_Barbie_Phone_AJohnson_0002.jpg)




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-2190687584-73d2fde2b83c4d429c888c0bf249a930.jpg)
