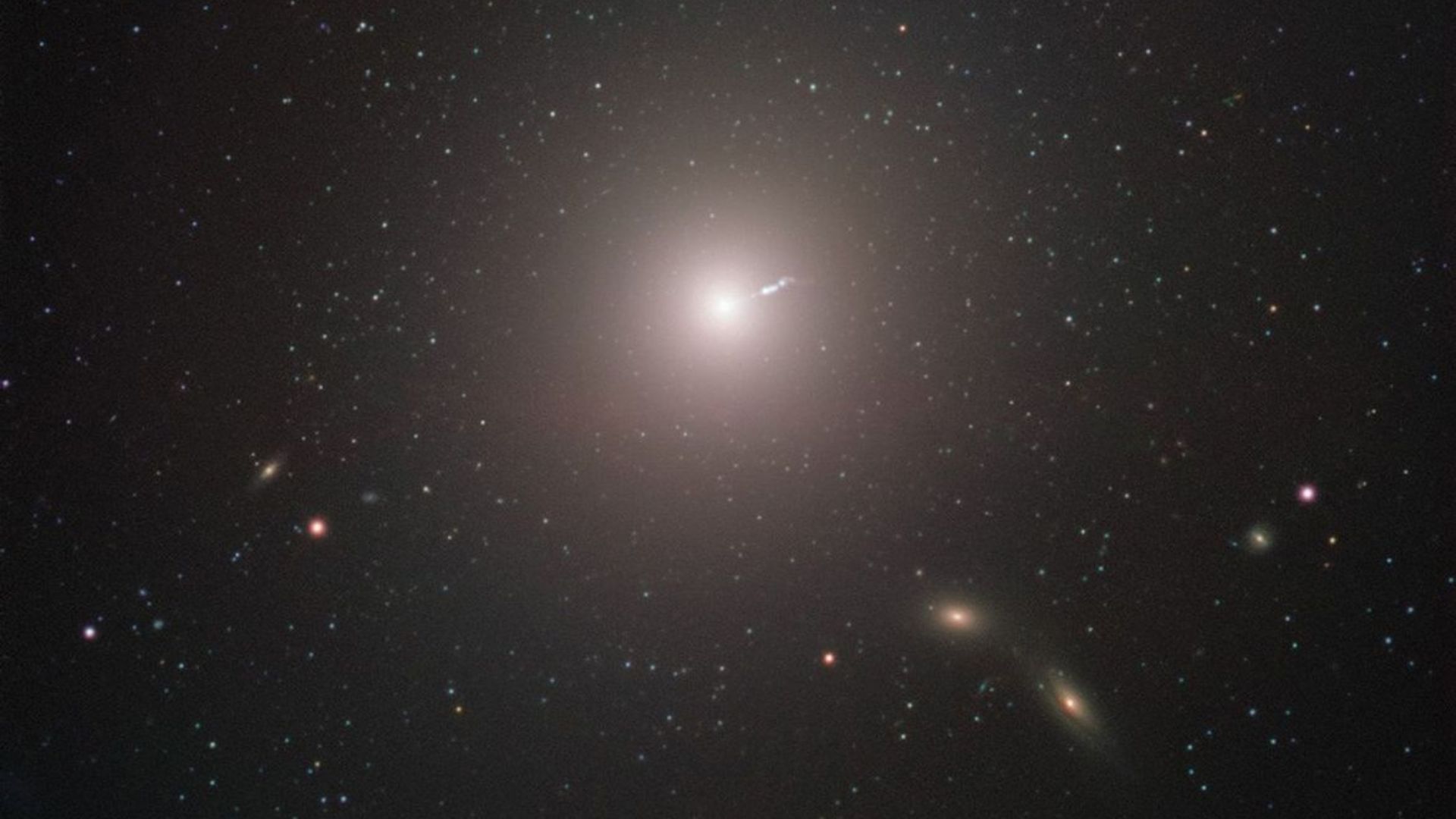
In 2019, the arena was once mesmerized by means of the first-ever symbol of a black hollow, courtesy of the Match Horizon Telescope (EHT).
The hanging symbol depicted the supermassive black hollow on the middle of the galaxy M87, positioned in Virgo’s constellation.
Now, this similar black hollow is as soon as once more fascinating scientists with an abnormal gamma-ray flare that’s emitted photons loads of billions of occasions extra tough than visual gentle.
This intense flare, which has now not been seen in over a decade, helps researchers know the way debris, like electrons and positrons, reach such excessive energies within the excessive stipulations surrounding black holes.
First photographed black hollow
The black hollow in M87 is anything else however small; it produces a jet this is seven orders of magnitude—thousands and thousands of occasions—greater than the true tournament horizon or the skin boundary of the black hollow.
This fresh burst of high-energy radiation surpassed standard ranges detected by means of radio telescopes within the area surrounding the black hollow and lasted round 3 days.
Remarkably, this flare emerged from an area lower than 3 light-days broad—equating to simply below 15 billion miles.
Gamma rays, that are packets of electromagnetic calories referred to as photons, constitute the best calories wavelength within the galaxy’s electromagnetic spectrum.
They’re generally produced within the universe’s most up to date and maximum lively locales, equivalent to the place black holes live.
When it comes to M87’s flare, the gamma rays reached calories ranges of a number of teraelectronvolts, an immense measure of calories typically reserved for subatomic debris.
For comparability, this calories degree is comparable to the calories generated by means of a mosquito in flight, but it’s directed at trillions of occasions smaller debris.
As topic spirals right into a black hollow, it creates an accretion disk, a swirling mass of debris that boost up because of the gravitational calories loss.
Some debris are expelled from the black hollow’s poles as tough jets because of intense magnetic fields.
This chaotic procedure may end up in unexpected calories bursts, referred to as flares, however the problem stays that gamma rays can not achieve Earth’s floor.
Alternatively, about seventy years in the past, physicists came upon they might locate gamma rays not directly by means of watching the secondary radiation produced when those rays engage with the ambience.
Gamma rays
Weidong Jin, a postdoctoral researcher at UCLA and a lead creator of a vital find out about printed in Astronomy & Astrophysics, expressed ongoing interest in regards to the acceleration of debris close to black holes.
“The debris are extremely lively, touring at speeds with regards to that of sunshine, and we purpose to discover how and the place they gain this calories,” he stated.
The analysis gives probably the most detailed spectral information accumulated from M87 and modeling that complements our figuring out of those processes.
Jin was once instrumental in examining probably the most lively phase of the dataset, in particular very-high-energy gamma rays accrued by means of VERITAS, a ground-based gamma-ray observatory positioned on the Fred Lawrence Whipple Observatory in southern Arizona.
UCLA performed a pivotal position in creating VERITAS, from the electronics that learn the telescope’s observations to device for information research and function simulation.
This meticulous paintings enabled the flare detection by means of notable luminosity adjustments, indicating a vital deviation from earlier observations.
Along with VERITAS, greater than two dozen main ground- and space-based observatories participated in a multi-wavelength marketing campaign with the EHT in 2018.
This incorporated NASA’s Fermi-LAT, Hubble Area Telescope, NuSTAR, and the Chandra and Swift telescopes, together with 3 of the arena’s biggest imaging atmospheric Cherenkov telescope arrays: VERITAS, H.E.S.S., and MAGIC.
Those amenities can locate X-ray photons in addition to high-energy gamma rays.
Some of the essential datasets analyzed within the find out about is the spectral calories distribution.
“This spectrum unearths how calories from astronomical entities like M87 distributes throughout other gentle wavelengths,” Jin defined.
“It’s very similar to making a rainbow and measuring the calories in each and every colour.”
This research performs a essential position in revealing the mechanisms using the acceleration of high-energy debris throughout the supermassive black hollow’s jet.
The authors additionally famous an intriguing fluctuation within the place and attitude of the black hollow’s tournament horizon and its jet, suggesting a dating between the debris and the development horizon throughout other scales.
Jin concluded, “M87’s black hollow includes a bipolar jet stretching hundreds of light-years from its core. This find out about gives an extraordinary likelihood to additional examine the origins of those phenomena.”