The primary ice-free day within the Arctic Ocean may arrive once this decade, warns a brand new find out about.Climatologists from Colorado College (CU) Boulder and the College of Gothenburg have used pc fashions to research when the Arctic would possibly revel in its first ice-free day. On this context, ‘ice-free’ manner a sea ice space of one million sq. kilometers (386,000 sq. miles) or much less.
The crew used 11 other local weather fashions to run 366 simulations of local weather alternate from 2023 to 2100. They discovered that the primary ice-free day within the Arctic seemed throughout somewhat quite a lot of probabilities: it would happen in as low as 3 years, or it will now not occur through the top of the century.
Then again, nearly all of simulations predicted that this fateful day would arrive inside 7 to two decades. That was once the case even though people decreased their greenhouse gasoline emissions – which we are doing a horrible activity of to this point.
9 of the simulations reached an ice-free day inside 3 to 6 years. This situation is not going however poses a prime possibility, so the researchers investigated the stipulations that resulted in one of these fast transition.
All it could take is an strangely heat fall, wintry weather, and spring, which primes the next summer time to soften extra sea ice. If this trend holds for 3 consecutive years, the primary ice-free day would happen through September of a given 12 months. The quantity of sea ice within the Arctic area is declining at exceptional charges. (Céline Heuzé/College of Gothenburg)An ice-free day would not be a one-off match both. Extra would in fact apply, sooner or later culminating in complete months under the ice-free threshold.
The quantity of sea ice within the Arctic area is declining at exceptional charges. (Céline Heuzé/College of Gothenburg)An ice-free day would not be a one-off match both. Extra would in fact apply, sooner or later culminating in complete months under the ice-free threshold.
“The primary ice-free day within the Arctic may not alternate issues dramatically,” says Alexandra Jahn, CU Boulder climatologist.
“However it’ll display that now we have basically altered some of the defining traits of the herbal atmosphere within the Arctic Ocean, which is that it’s lined through sea ice and snow year-round, via greenhouse gasoline emissions.”
The quantity of sea ice within the Arctic and Antarctic naturally shrinks and grows right through the process the 12 months. The utmost and minimal extents had been monitored since November 1978 to trace the results of local weather alternate.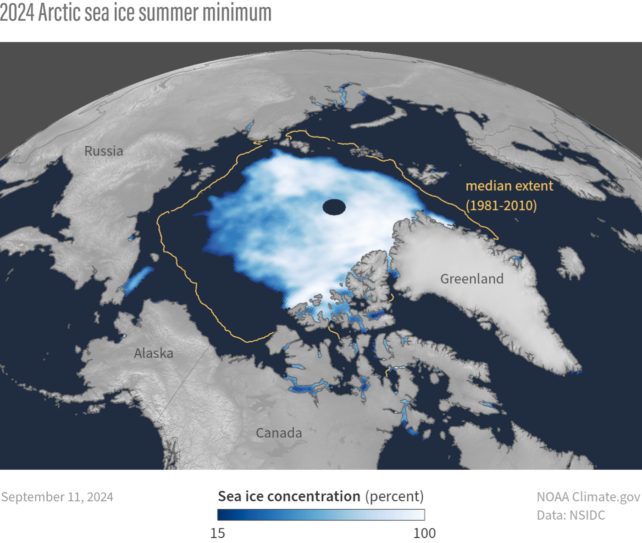 The Arctic sea ice minimal for 2024 (blue space), as recorded on Sep 11, in comparison to the median minimal extent for the length 1981-2010 (yellow define). (NOAA Local weather.gov/Information: NSIDC)This 12 months, as an example, the minimal sea ice space was once recorded on Sep 11, at 4.28 million sq. kilometers. That makes it the 7th smallest space on document, with the loss appearing a downward development of 12.4 p.c in line with decade.
The Arctic sea ice minimal for 2024 (blue space), as recorded on Sep 11, in comparison to the median minimal extent for the length 1981-2010 (yellow define). (NOAA Local weather.gov/Information: NSIDC)This 12 months, as an example, the minimal sea ice space was once recorded on Sep 11, at 4.28 million sq. kilometers. That makes it the 7th smallest space on document, with the loss appearing a downward development of 12.4 p.c in line with decade.
Projecting forwards, scientists have in the past estimated when the Arctic would possibly turn out to be ice-free for massive chunks of its summertime. For the brand new find out about, the researchers investigated an overpassed stepping stone on that trail: when the primary ice-free day would possibly happen.
In all 9 of the worst-case situation simulations, sea ice was once preconditioned for a couple of years ahead of the primary ice-free day took place. In the ones years, atmospheric cooling arrives later in autumn, and heat spells seem as past due as December.
Throughout the ‘ultimate’ wintry weather ahead of, temperatures linger above -20 °C (-4 °F) for prolonged classes, lowering the volume of recent ice shaped.
Spring might arrive as much as one month previous than standard, or see fewer chilly spells. Heatwaves of over 0 °C turn out to be not unusual. And after all, the summer time that includes that fateful day may be very heat, with temperatures over 10 °C. Storms presently can additional tension sea ice. Arctic sea ice is melting on account of local weather alternate. (Céline Heuzé/College of Gothenburg)In combination, those stipulations can cause the primary ice-free day to reach in August or September. After that first day, the Arctic stays ice-free for between 11 and 53 days in the ones 9 fast transition simulations.
Arctic sea ice is melting on account of local weather alternate. (Céline Heuzé/College of Gothenburg)In combination, those stipulations can cause the primary ice-free day to reach in August or September. After that first day, the Arctic stays ice-free for between 11 and 53 days in the ones 9 fast transition simulations.
The researchers don’t seem to be investigating this simply to bum other folks out. The find out about discovered that ice-free days in all fast transition circumstances took place in years the place international warming exceeded 1.5 °C above the pre-industrial baseline – the objective of the Paris Settlement.
If nations can stick with the tips set out in that settlement, an ice-free Arctic might be behind schedule, the crew says. Sadly, 2024 is not off course to be the primary 12 months above 1.5 °C of warming, so we could be heading down a destructive trail faster somewhat than later.The analysis was once printed within the magazine Nature Communications.
First Ice-Unfastened Day in Arctic Ocean May Arrive This Decade, Learn about Unearths