This newsletter has been reviewed in step with Science X’s editorial procedure
and insurance policies.
Editors have highlighted the next attributes whilst making sure the content material’s credibility:
fact-checked
relied on supply
proofread
Good enough!
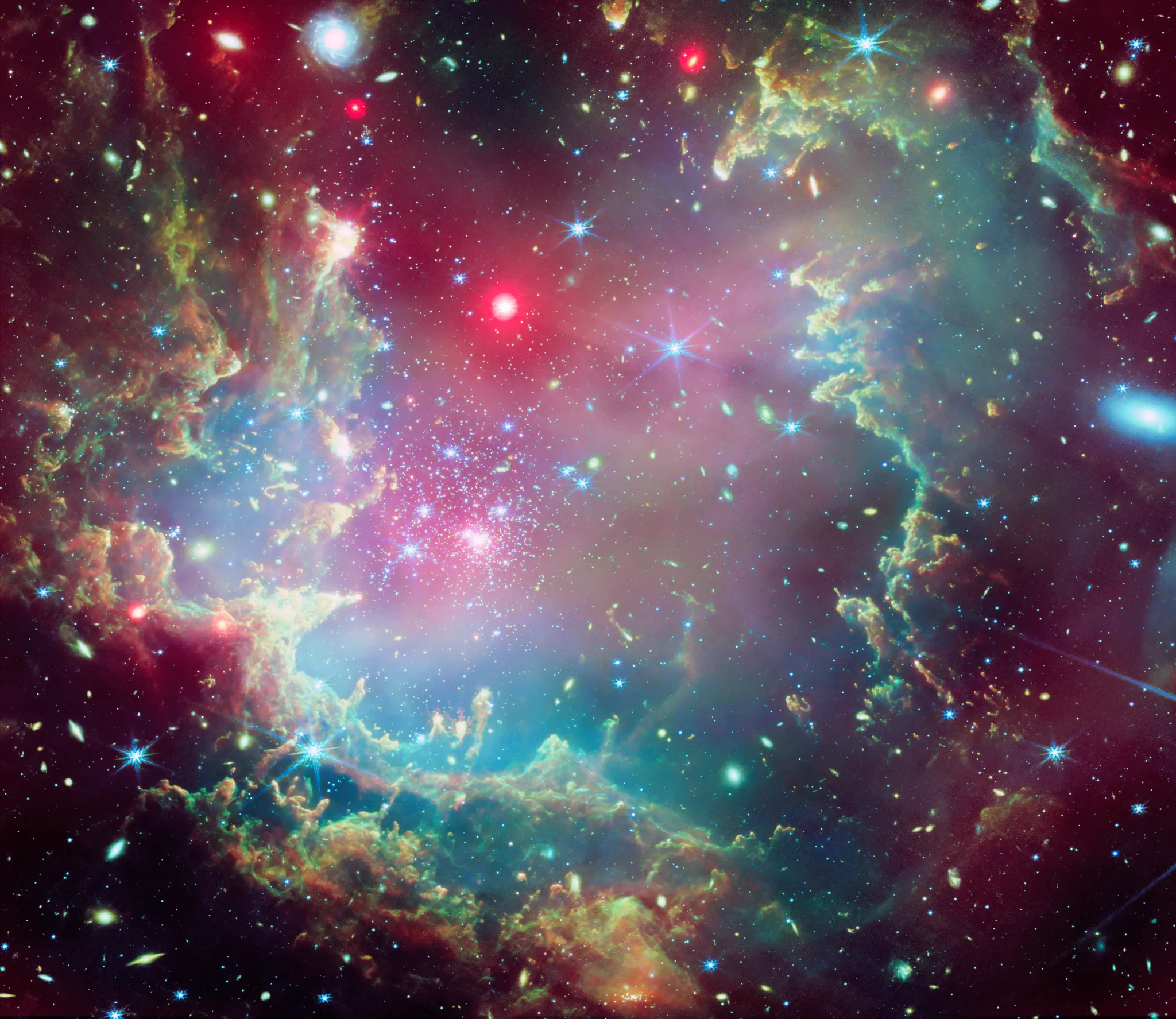
A deep-space symbol of the galaxy the place the supernova befell. Credit score: Legacy Surveys / D. Lang (Perimeter Institute) for Legacy Surveys layers and unWISE / NASA/JPL-Caltech / D. Lang (Perimeter Institute)
× shut
A deep-space symbol of the galaxy the place the supernova befell. Credit score: Legacy Surveys / D. Lang (Perimeter Institute) for Legacy Surveys layers and unWISE / NASA/JPL-Caltech / D. Lang (Perimeter Institute)
A completely computerized procedure, together with a brand-new synthetic intelligence (AI) software, has effectively detected, recognized and labeled its first supernova.
Evolved by means of a world collaboration led by means of Northwestern College, the brand new device automates all the seek for new supernovae around the evening sky—successfully eliminating people from the method. Now not simplest does this impulsively boost up the method of examining and classifying new supernova applicants, it additionally bypasses human error.
The staff alerted the astronomical group to the release and good fortune of the brand new software, known as the Vibrant Brief Survey Bot (BTSbot), this week. Prior to now six years, people have spent an estimated overall of two,200 hours visually analyzing and classifying supernova applicants. With the brand new software now formally on-line, researchers can redirect this treasured time towards different duties with a purpose to boost up the tempo of discovery.
“For the primary time ever, a chain of robots and AI algorithms has seen, then recognized, then communicated with every other telescope to in any case verify the invention of a supernova,” mentioned Northwestern’s Adam Miller, who led the paintings. “This represents a very powerful step ahead as additional refinement of fashions will permit the robots to isolate explicit subtypes of stellar explosions. In the long run, eliminating people from the loop supplies extra time for the analysis staff to research their observations and increase new hypotheses to provide an explanation for the starting place of the cosmic explosions that we follow.”
“We accomplished the sector’s first totally automated detection, identity and classification of a supernova,” added Northwestern’s Nabeel Rehemtulla, who co-led the generation construction with Miller. “This considerably streamlines massive research of supernovae, serving to us higher perceive the existence cycles of stars and the starting place of components supernovae create, like carbon, iron and gold.”
Miller is an assistant professor of physics and astronomy at Northwestern’s Weinberg School of Arts and Sciences and a member of the Middle for Interdisciplinary Exploration and Analysis in Astrophysics (CIERA). Rehemtulla is an astronomy graduate scholar in Miller’s analysis team.
Reducing out the intermediary
To stumble on and analyze supernovae, people lately paintings hand in hand with robot methods. First, robot telescopes time and again symbol the similar sections of the evening sky, looking for new assets that weren’t found in earlier pictures. Then, when those telescopes stumble on one thing new, people take over.
“Automatic instrument items a listing of candidate explosions to people, who spend time verifying the applicants and executing spectroscopic observations,” Miller mentioned. “We will be able to simplest definitively know {that a} candidate is in point of fact a supernova by means of amassing its spectrum—the supply’s dispersed gentle, which finds components provide within the explosion. There are current robot telescopes that may acquire spectra, however this could also be frequently executed by means of people running telescopes with spectrographs.”
A ahead of (left) and after symbol of the galaxy the place SN2023tyk befell. The higher left area of the galaxy (proper) seems bulbous and misshapen, the place the big name exploded. Credit score: Legacy Surveys / D. Lang (Perimeter Institute) for Legacy Surveys layers and unWISE / NASA/JPL-Caltech / D. Lang (Perimeter Institute)
× shut
A ahead of (left) and after symbol of the galaxy the place SN2023tyk befell. The higher left area of the galaxy (proper) seems bulbous and misshapen, the place the big name exploded. Credit score: Legacy Surveys / D. Lang (Perimeter Institute) for Legacy Surveys layers and unWISE / NASA/JPL-Caltech / D. Lang (Perimeter Institute)
The researchers evolved the BTSbot to chop out this human intermediary. To increase the AI software, Rehemtulla skilled a machine-learning set of rules with greater than 1.4 million ancient pictures from just about 16,000 assets, together with showed supernovae, quickly flaring stars, periodically variable stars and flaring galaxies.
“The Zwicky Brief Facility (ZTF) has been running for the previous six years, and, throughout that point, I and others have spent greater than 2,000 hours visually analyzing applicants and figuring out which to watch with spectroscopy,” mentioned Christoffer Fremling, an astronomer on the California Institute of Generation (Caltech) who evolved every other AI software known as SNIascore and contributed to the improvement of BTSbot. “Including BTSbot to our workflow will get rid of the will for us to spend time analyzing those applicants.”
Early good fortune, and a wave of reduction
To check the BTSbot, the researchers appeared to a newly found out supernova candidate dubbed SN2023tyk. The ZTF, a robot observatory that pictures the evening sky in a seek for supernovae, first detected the supply on Oct. 3. Sifting via ZTF’s information in genuine time, BTSbot discovered SN2023tyk on Oct. 5.
From there, BTSbot routinely asked the possible supernova’s spectrum from Palomar Observatory, the place every other robot telescope (SED Gadget) carried out in-depth observations to procure the supply’s spectrum. The SED Gadget then despatched this spectrum to Caltech’s SNIascore to decide the supernova’s sort: Both a thermonuclear explosion of a white dwarf or the cave in of a large big name’s core.
After figuring out that the candidate was once a Kind Ia supernova (a stellar explosion during which a white dwarf in a binary big name device totally explodes), the automatic device publicly shared the invention with the astronomical group on Oct. 7.
Within the first days of operating BTSbot, Rehemtulla felt a mixture of nerves and pleasure.
“The simulated efficiency was once superb, however you by no means in reality understand how that interprets to the real-world till you if truth be told take a look at it,” he mentioned. “As soon as the observations from SEDM and the automatic classification got here in from SNIascore, we felt an enormous wave of reduction. The wonderful thing about it’s that, as soon as the whole thing is became on and dealing correctly, we do not if truth be told do anything else. We fall asleep at evening, and, within the morning, we see that BTSbot, and those different AIs unwaveringly do their jobs.”
Led by means of Northwestern, the collaboration integrated astronomers from Caltech, College of Minnesota, Liverpool John Moores College in England and Stockholm College in Sweden.