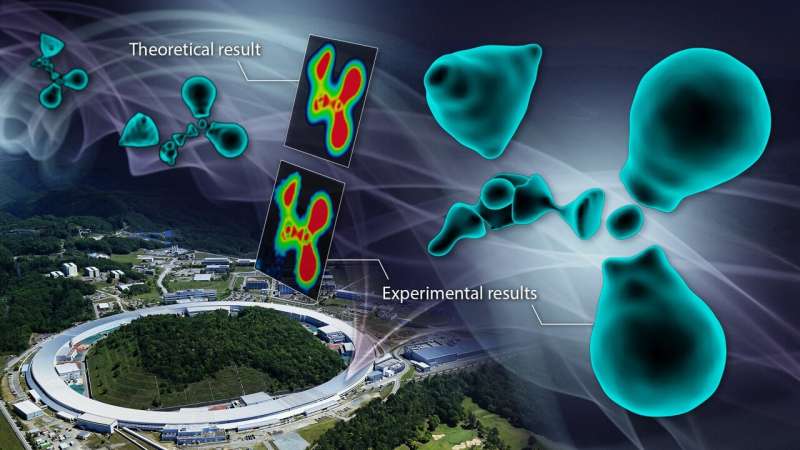
The distribution of outermost shell electrons, referred to as valence electrons, of natural molecules was once noticed for the primary time. Credit score: Reiko Matsushita / RIKEN
The distribution of outermost shell electrons, referred to as valence electrons, of natural molecules was once experimentally noticed for the primary time by way of a workforce led by way of Nagoya College in Japan. Because the interactions between atoms are ruled by way of the valence electrons, their findings shine gentle at the basic nature of chemical bonds, with implications for pharmacy and chemical engineering. The consequences had been revealed within the Magazine of the American Chemical Society.
The habits of the electrons in atoms is advanced, forming electron orbitals that experience other purposes relying on their closeness to the nucleus. The interior shell electrons, known as core electrons, are used for self-stabilization and don’t have interaction with different atoms. Then again, the outer electrons, or valence electrons, outline many of the subject material’s homes, particularly right through bonding with different atoms.
Working out a subject material’s homes calls for extracting details about its valence electrons. Then again, it’s been tough to experimentally isolate simplest the valence electron knowledge, resulting in researchers having to depend on theoretical fashions and spectroscopy to estimate it.
By way of engaging in world-class synchrotron X-ray diffraction experiments at SPring-8, the gang found out that it’s imaginable to selectively extract simplest the valence electron density of atoms in a crystal.
“We named this system the CDFS means. The use of this system, we noticed the electron state of the glycine molecule, a kind of amino acid,” corresponding creator Hiroshi Sawa stated. “Even supposing the process was once quite easy to accomplish, the end result was once spectacular. The noticed electron cloud didn’t showcase the sleek, enveloping form that many predicted, however fairly a fragmented, discrete state.”
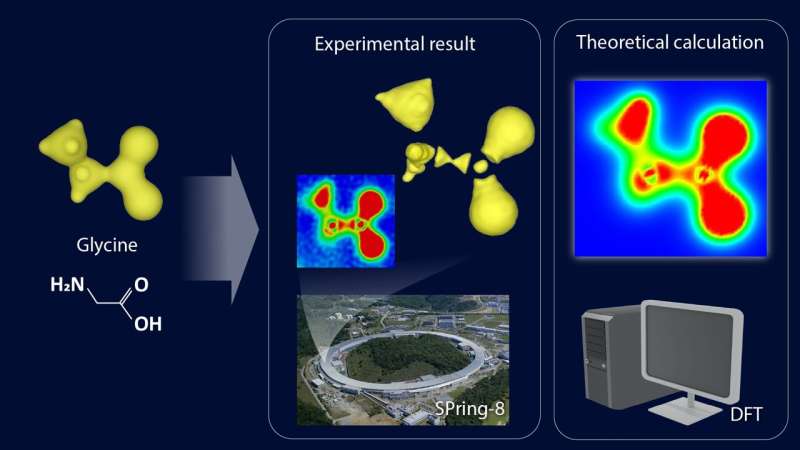
Direct commentary of valence electron density was once achieved by way of synchrotron radiation X-ray diffraction at SPring-8. Theoretical effects the usage of a quantum mechanical modelling means known as density practical principle (DFT) matched with the commentary. Credit score: Sawa lab, Nagoya College / RIKEN
To grasp the character of the consequences, the gang made a colour map in their observations. In chemistry, a colour map makes use of colours to show diversifications in datasets throughout a selected vary. Such maps are steadily used together with spectroscopic tactics, imaging, and chemical research to supply an intuitive method to interpret advanced datasets.
The map of the cross-sectional view within the enlarged diagram obviously confirmed interruptions within the electron distribution surrounding the carbon atoms.
“When carbon bureaucracy bonds with surrounding atoms, it reconstructs its electron cloud to create hybridized orbitals. On this case, the outermost L-shell electrons have nodes in line with their wave nature referred to as wave purposes,” Sawa defined. “Which means that because of the wave nature of electrons, there are portions of the hybrid orbitals the place electrons are absent, a lot other to the picture that many of us have of a continual ‘cloud’ of electrons.”
The fragmented electron cloud distribution noticed within the experiment demonstrates the quantum mechanical wave nature of electrons, as predicted by way of physics. To substantiate whether or not the noticed electron cloud appropriately captures the actual state, they performed complex quantum chemical calculations in collaboration with Hokkaido College that showed that the experimental and theoretical effects matched completely.
Sawa believes that the consequences display the advantages of interdisciplinary analysis. “I consider it’s been useful in offering a transparent conclusion to the ambiguous figuring out of bonding states that has at a loss for words researchers for the reason that nineteenth century,” Sawa stated.
“Visualizing electron habits is a difficult enterprise, but the consequences can also be elegantly understood as electrons appearing in keeping with wave purposes. I consider our findings have astonished many researchers and validated the style proposed by way of quantum chemistry.”
With an actual figuring out of the valence electron density distribution forming this molecule, the gang performed an identical experiments and calculations on cytidine, a fairly extra advanced molecule. They effectively extracted the electrons inside the carbon double bonds and obviously noticed variations between the carbon-carbon and carbon-nitrogen bonds.
“This learn about has made it imaginable to immediately visualize the essence of chemical bonds, probably contributing to the design of practical fabrics and the figuring out of response mechanisms. It is because it aids in discussing the digital states of molecules, which can be tough to deduce from simply the chemical structural formulation,” Sawa stated.
“It’ll, as an example, provide an explanation for why some drugs paintings and others do not. Fields the place interactions affect capability and structural steadiness, comparable to natural semiconductors and analysis at the construction of DNA double helixes, are prone to get advantages maximum from our analysis.”
Additional info:
Hara, T. et al. Unveiling the Nature of Chemical Bonds in Actual House, Magazine of the American Chemical Society (2024). DOI: 10.1021/jacs.4c05673
Supplied by way of
Nagoya College
Quotation:
First visualization of valence electrons unearths basic nature of chemical bonding (2024, August 21)
retrieved 21 August 2024
from
This report is matter to copyright. Except any truthful dealing for the aim of personal learn about or analysis, no
phase could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is equipped for info functions simplest.












