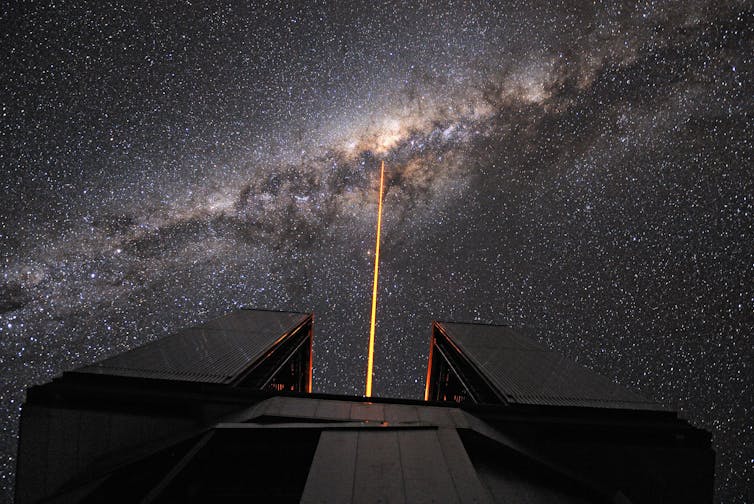
Researchers from Michigan State College (MSU) have made groundbreaking discoveries concerning the supermassive black hollow on the middle of the Milky Manner, referred to as Sagittarius A* (Sgr A*).
Using a decade’s value of X-ray knowledge from NASA’s NuSTAR telescope, those findings supply new insights into the enigmatic atmosphere surrounding this colossal cosmic entity.
Finding Hidden Flares and Echoes
Grace Sanger-Johnson, a postbaccalaureate researcher at MSU, came upon 9 up to now undetected X-ray flares from Sagittarius A* by means of meticulously inspecting ten years of knowledge. Those flares are high-energy bursts that remove darkness from the rapid neighborhood of the black hollow, a space normally shrouded in darkness because of the immense gravitational pull that even mild can’t break out.
“We’re sitting within the entrance row to watch those distinctive cosmic fireworks on the middle of our personal Milky Manner galaxy,” stated Shuo Zhang, Sanger-Johnson’s marketing consultant. The flares supply an extraordinary alternative to check the black hollow’s environment and higher perceive the extraordinary prerequisites provide there.
Whilst Sanger-Johnson targeted at the flares, Jack Uteg, an undergraduate researcher within the MSU Honors Faculty, studied X-ray echoes from a close-by molecular cloud referred to as “the Bridge.” Those echoes be offering a glimpse into Sgr A*’s task over the last centuries.
Through analyzing just about twenty years of knowledge from NuSTAR and the Eu Area Company’s X-ray Multi-Replicate (XMM) Newton observatory, Uteg discovered that the cloud’s brightness is most probably a not on time mirrored image of previous X-ray outbursts from the black hollow.

“The brightness we see is perhaps the not on time mirrored image of previous X-ray outbursts from Sgr A*,” Uteg defined. This research is helping reconstruct a timeline of the black hollow’s previous habits, revealing that Sgr A* was once considerably extra lively round 200 years in the past.

The Importance of Those Findings
Those discoveries are the most important for working out the dynamic atmosphere on the middle of our galaxy. Black holes are notoriously tough to check at once because of their intense gravitational fields, which distort mild and different alerts.
On the other hand, by means of analyzing the results of those fields on surrounding topic, scientists can infer necessary information about black hollow task. Sanger-Johnson and Uteg’s paintings exemplifies this means, losing mild on each the rapid and historic behaviors of Sgr A*.
“Grace and Jack’s contributions are a supply of immense satisfaction,” stated Shuo Zhang, assistant professor within the Division of Physics and Astronomy at MSU. “Their paintings exemplifies MSU’s dedication to pioneering analysis and fostering the following era of astronomers. This analysis is a first-rate instance of the way MSU scientists are unlocking the universe’s secrets and techniques, bringing us nearer to comprehending the character of black holes and the dynamic atmosphere on the middle of our galaxy.”
Figuring out Black Hollow Flares
The newly came upon flares are dramatic bursts of high-energy mild that happen when the black hollow ingests subject material, similar to fuel clouds or stars. Those flares supply precious knowledge concerning the bodily prerequisites close to the development horizon, the boundary past which not anything can break out the black hollow’s gravity. When a black hollow consumes topic, the fabric is heated to excessive temperatures because it speeds up and spirals inward, emitting intense X-rays and different radiation within the procedure. This radiation is what scientists follow as flares.
Flares are normally temporary, lasting from a couple of mins to a couple of hours, however they are able to unencumber a huge quantity of calories all the way through that point. The calories output of those flares may also be an identical to that of tens of millions of suns. Sanger-Johnson’s research, which concerned sifting thru knowledge from 2015 to 2024, printed the traits of those flares, serving to to construct a complete database for long run analysis. Every flare supplies a snapshot of the dynamic processes going on close to the black hollow, providing clues concerning the habits of the accreting subject material and the physics of the extraordinary atmosphere.
“We are hoping that by means of increase this financial institution of knowledge on Sgr A* flares, we and different astronomers can analyze the homes of those X-ray flares and infer the bodily prerequisites within the excessive atmosphere of the supermassive black hollow,” Sanger-Johnson stated. Through learning the timing, depth, and frequency of those flares, researchers can infer information about the velocity at which the black hollow is eating subject material and the character of the encircling accretion disk. This knowledge is the most important for creating fashions of black hollow expansion and task.