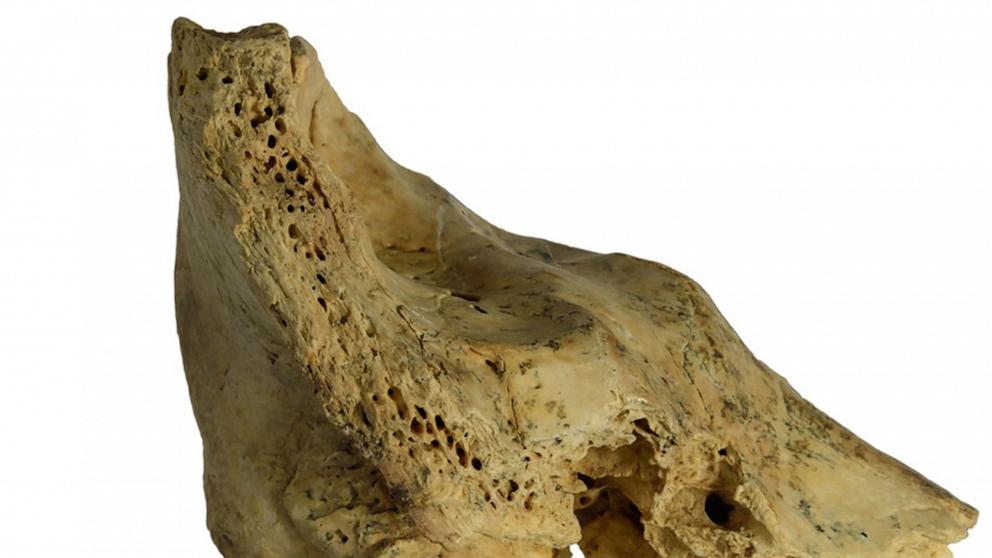
The kid’s survival to age 6 is also because of altruism throughout the neighborhood.June 26, 2024, 2:00 PM ET• 6 min readFossils from the cranium of a Neanderthal kid that most likely had Down syndrome shed gentle into the collaborative and communal caregiving that most likely helped the kid continue to exist to the age of 6, in line with new analysis.The fossil fragments, excavated from the Cova Negra archaeological web page in Valencia, Spain, had been decided to be from a Neanderthal kid’s ear. The kid most likely lived 273,000 years in the past and confirmed congenital malformations in step with Down syndrome, in line with a learn about, which used to be printed Wednesday in Science Advances.When researchers did a CT scan of the small fragment of the temporal lobe, the bone the place the interior ear is positioned, they reconstructed the interior ear that confirmed 5 abnormalities related to Down syndrome, which had by no means been detected earlier than in a Neanderthal, Mercedes Conde-Valverde, a paleoanthropologist on the College of Alcala in Spain, informed ABC Information.”The one syndrome this is appropriate with all the set of malformations found in [the remains] is Down syndrome,” Conde-Valverde wrote.Fossilized fragments from a Neanderthal kid’s ear endure congenital malformations which are in step with Down Syndrome, researchers say.Science AdvancesWhat makes the fossil much more outstanding is that the feminine kid would have wanted a large number of help to maintain her well being difficulties, Conde-Valverde stated.Neanderthals would care for individuals who had been in a position to returning the desire or serving to them in differently. However this Neanderthal woman — who suffered from well being problems reminiscent of listening to loss, imbalance issues and vertigo — most likely may now not go back the desire, so her survival seems to be based totally purely at the altruism of the adults round her, Conde-Valverde stated.This negates the speculation that caregiving emerged simply as a self-interested pact between individuals who may reciprocate the habits and that Neanderthals had been in a position to exhibiting altruism, the researchers stated.Fossilized fragments from a Neanderthal kid’s ear endure congenital malformations which are in step with Down Syndrome, researchers say.Science AdvancesThe kid’s mom would have struggled to offer care whilst concurrently maintaining with the day by day demanding situations of a foraging way of life within the Paleolithic technology, in line with the paper.Prehistoric youngsters with congenital sicknesses had an unsure trail to survival to maturity and may now not be counted on for reciprocation, in line with the paper.The findings recommend that hominin caregiving emerged because of compassion moderately than reciprocation, the researchers concluded.An image displays the rebuilt cranium and a bodily reconstruction of the face and head, of a 75,000-year-old Neanderthal lady, named Shanidar Z, after the collapse Iraqi Kurdistan the place her cranium used to be present in 2018, on the College of Cambridge, japanese England, April 25, 2024. Justin Tallis/AFP by way of Getty ImagesNeanderthals, or Homo neanderthalensis, lived right through the Paleolithic duration lived between 430,000 and 40,000 years in the past. They had been “suave other folks” with large brains and buried their useless, Conde-Valverde stated. The largest distinction to homo sapiens are the morphology of the cranium.”I believe they’re in point of fact humankind,” she stated. “…with extra analysis and extra fossils, we will be able to know that they had been in point of fact very similar to us.”
Fossilized cranium of Neanderthal kid with Down syndrome unearths communal caregiving amongst species