Fifty million years in the past, lush rainforests blanketed modern day Antarctica, Australia, New Zealand and the end of South The united states. Now, researchers have came upon new fossils that expose which plant species populated those forests and the way they tailored to existence close to the South Pole.Contemporary excavations in western Tasmania exposed quite a few plant fossils, together with the stays of 2 species of conifer up to now unknown to science that had been a part of a 53 million-year-old “polar wooded area.”The wooded area thrived all the way through the Eocene epoch (56 million to 33.9 million years in the past), when international floor temperatures averaged 80 levels Fahrenheit (27 levels Celsius) and the southern continents shaped one large landmass across the South Pole, in step with a find out about printed Aug. 27 within the American Magazine of Botany.”This discovery gives uncommon insights right into a time when international temperatures had been a lot upper than lately,” find out about writer Miriam Slodownik, a paleobotanist and up to date doctoral graduate from the College of Adelaide in Australia, mentioned in a remark. “Tasmania was once a lot nearer to the South Pole, however the heat international local weather allowed lush forests to thrive in those areas.”World temperatures spiked all the way through the Early Eocene Climatic Optimal (53 million to 49 million years in the past), a length predating the breakup of Australia from Antarctica between 45 million and 35 million years in the past. New fossils unearthed close to Tasmania’s Macquarie Harbor recommend tropical crops from the polar wooded area traveled north because the continents drifted aside, seeding rainforests that also exist lately.Similar: 390 million-year-old fossilized wooded area is the oldest ever discoveredResearchers excavated greater than 400 plant fossils and analyzed them within the lab the usage of complex microscopes and ultraviolet pictures. Those tactics printed well-preserved leaves and mobile buildings that helped the crew determine 12 other plant species. All these had been ancestors of plants nonetheless discovered lately in Australia, New Zealand and South The united states, in step with the remark. Those 3 landmasses stayed joined in combination after the breakup of the traditional supercontinent Gondwana and remained so till a minimum of 49 million years in the past.Get the sector’s most attractive discoveries delivered directly for your inbox.Of the 12 species, a minimum of 9 had been conifers, in step with the find out about. “Essentially the most impressive fossils are kin of the Kauri [Agathis], Bunja [Araucaria bidwillii] and Wollemi [Wollemia nobilis] pines that give clues concerning the evolution of those iconic Australian timber,” Slodownik mentioned.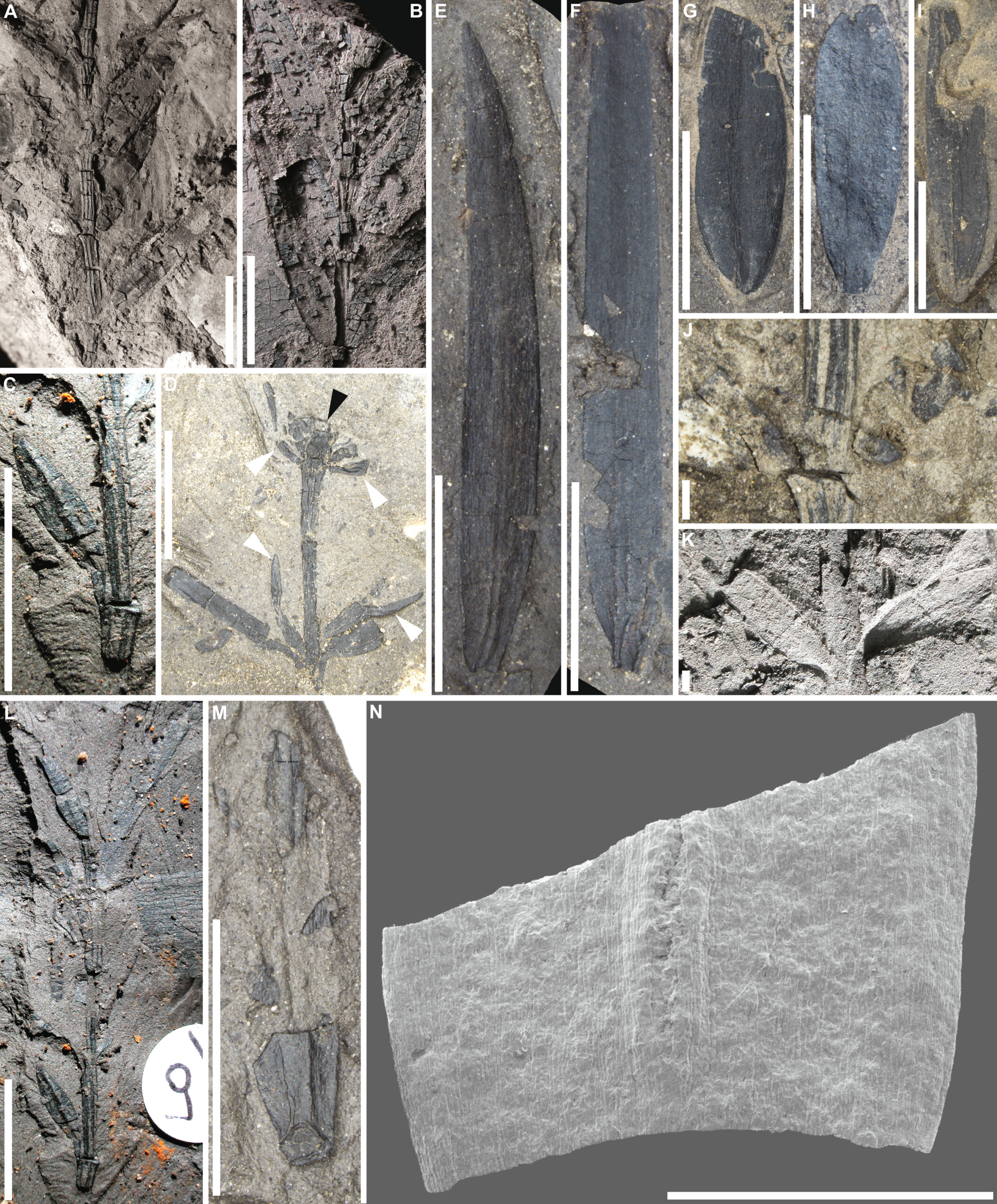 Plant fossils came upon close to Macquarie Harbor in western Tasmania. (Symbol credit score: © 2024 The Writer(s). American Magazine of Botany printed by way of Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Botanical Society of The united states.)The researchers, in collaboration with the Tasmanian Aboriginal Centre, additionally recognized ferns, a cycad and two newfound, extinct tree species, which they named Podocarpus paralungatikensis and Araucaria timkarikensis. “Paralungatik” is the unique identify of Macquarie Harbor and “Timkarik” that of the encompassing space within the Aboriginal language of Tasmania, in step with the remark.The analyses printed that the fossilized crops tailored to the polar setting, which might have skilled the similar excessive seasonal mild regime 53 million years in the past because it does lately. The crops developed huge leaves to maximise mild absorption in the summertime and deciduousness to maintain sources in low-light prerequisites all the way through the wintry weather, in step with the find out about.”The analyses confirmed how those crops tailored and thrived around the Southern Hemisphere in heat, ice-free prerequisites, even with the extraordinary seasonal adjustments close to the polar circle,” Slodownik mentioned.However the brand new fossils expose main points of even wider adjustments. “Those crops inform the tale of giant adjustments in local weather and the transferring tectonic plates over hundreds of thousands of years,” Soldownik mentioned.
Plant fossils came upon close to Macquarie Harbor in western Tasmania. (Symbol credit score: © 2024 The Writer(s). American Magazine of Botany printed by way of Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Botanical Society of The united states.)The researchers, in collaboration with the Tasmanian Aboriginal Centre, additionally recognized ferns, a cycad and two newfound, extinct tree species, which they named Podocarpus paralungatikensis and Araucaria timkarikensis. “Paralungatik” is the unique identify of Macquarie Harbor and “Timkarik” that of the encompassing space within the Aboriginal language of Tasmania, in step with the remark.The analyses printed that the fossilized crops tailored to the polar setting, which might have skilled the similar excessive seasonal mild regime 53 million years in the past because it does lately. The crops developed huge leaves to maximise mild absorption in the summertime and deciduousness to maintain sources in low-light prerequisites all the way through the wintry weather, in step with the find out about.”The analyses confirmed how those crops tailored and thrived around the Southern Hemisphere in heat, ice-free prerequisites, even with the extraordinary seasonal adjustments close to the polar circle,” Slodownik mentioned.However the brand new fossils expose main points of even wider adjustments. “Those crops inform the tale of giant adjustments in local weather and the transferring tectonic plates over hundreds of thousands of years,” Soldownik mentioned.