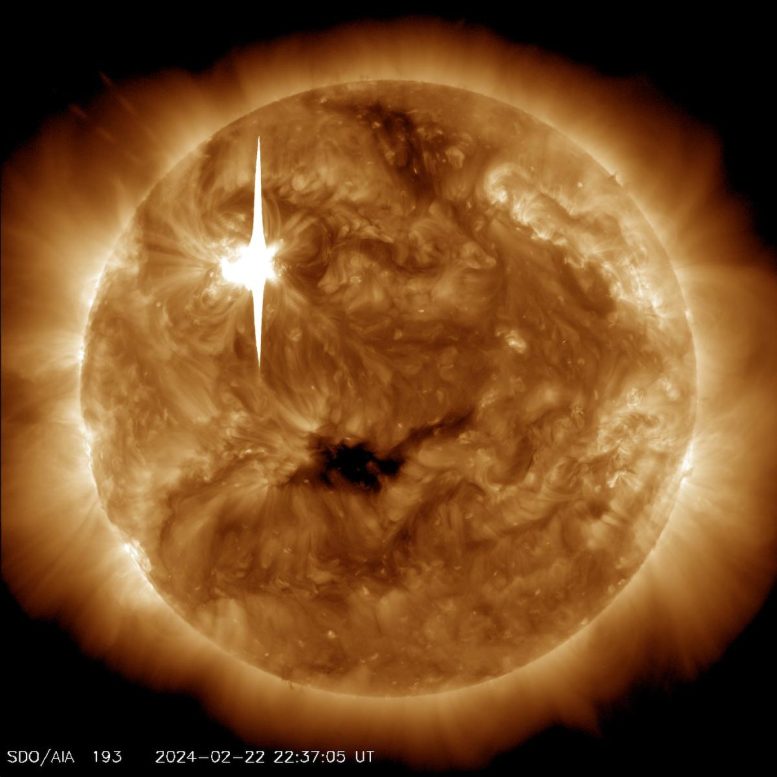
NASA’s Sun Dynamics Observatory captured this symbol of a sun flare – as observed within the vivid flash within the higher left of the Solar – on February 22, 2024. The picture presentations a subset of utmost ultraviolet gentle that highlights the extraordinarily sizzling subject material in flares and which is colorized in bronze. Credit score: NASA/SDOOn February 22, 2024, the Solar emitted a particularly sturdy sun flare. It reached its height at 5:34 p.m. EST. NASA’s Sun Dynamics Observatory, which watches the Solar repeatedly, captured a picture of the development.This actual sun flare has been categorised as an X6.3 flare. The “X-class” designation is reserved for essentially the most intense sun flares, with the numerical price providing additional element on its energy. An X6.3 flare represents a very potent match. It would be the most vital flare noticed since an X8.2 flare used to be recorded on September 10, 2017.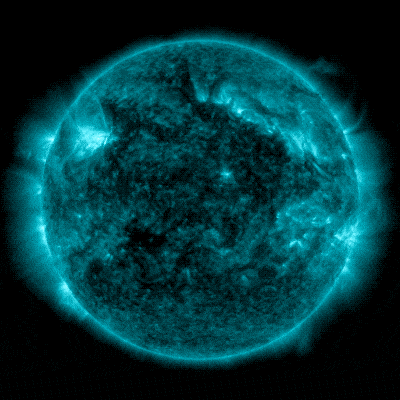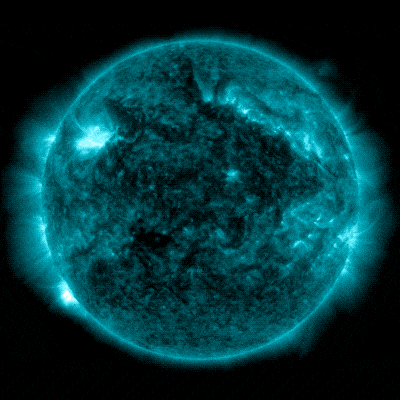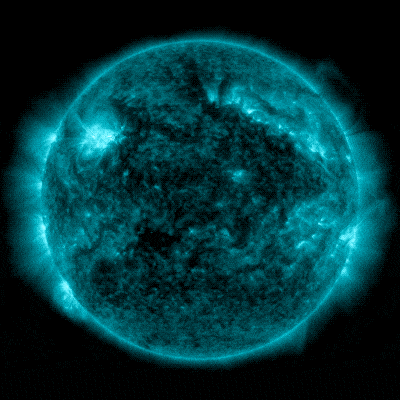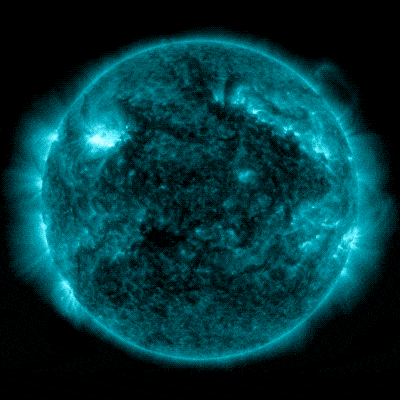 NASA’s Sun Dynamics Observatory captured those pictures of a sun flare – as observed within the vivid flashes within the higher left house of the Solar – on February 21 and 22, 2024. The photographs display a subset of utmost ultraviolet gentle that highlights the extraordinarily sizzling subject material in flares and which is colorized in teal. Credit score: NASA/SDOThat X6.3 flare used to be the 3rd important sun flare inside 24 hours. Previous the Solar emitted two sturdy sun flares, the primary one, categorised as an X1.8 flare, peaked at 6:07 p.m. EST on February 21, 2024. The second, categorised as an X1.7 flare, peaked at 1:32 a.m. EST on February 22, 2024.
NASA’s Sun Dynamics Observatory captured those pictures of a sun flare – as observed within the vivid flashes within the higher left house of the Solar – on February 21 and 22, 2024. The photographs display a subset of utmost ultraviolet gentle that highlights the extraordinarily sizzling subject material in flares and which is colorized in teal. Credit score: NASA/SDOThat X6.3 flare used to be the 3rd important sun flare inside 24 hours. Previous the Solar emitted two sturdy sun flares, the primary one, categorised as an X1.8 flare, peaked at 6:07 p.m. EST on February 21, 2024. The second, categorised as an X1.7 flare, peaked at 1:32 a.m. EST on February 22, 2024. Every other X-class flare from Area 3590 peaked at roughly 1734 EST on February 22, 2024. The X6.3 flare used to be the biggest of the 3 X-class flares that took place previously 24 hours, and the most powerful of this sun cycle. Whilst spectacular, this match nonetheless poses no important risk to most people. Credit score: NOAANASA’s Sun Dynamics ObservatoryNASA’s Sun Dynamics Observatory (SDO), which captured the pictures in this web page, used to be introduced in February 2010. Its project is designed to look at the Solar and its sun actions comprehensively. Located in a geosynchronous orbit about 22,000 miles above Earth, SDO supplies remarkable insights into sun phenomena, together with sun flares, sunspots, and coronal mass ejections (CMEs).SDO’s number one purpose is to know the Solar’s affect on Earth and near-Earth area through learning the sun surroundings in lots of wavelengths concurrently. It’s supplied with a collection of tools that permit scientists to observe the Solar’s magnetic box, its floor, and atmospheric actions in prime solution. Probably the most key tools, the Atmospheric Imaging Meeting (AIA), captures pictures of the sun surroundings in 10 other wavelengths each and every 12 seconds, offering a dynamic view of the Solar’s conduct. Thru its steady commentary, SDO performs a vital position in making improvements to our skill to forecast area climate occasions that may have an effect on existence and era on Earth.
Every other X-class flare from Area 3590 peaked at roughly 1734 EST on February 22, 2024. The X6.3 flare used to be the biggest of the 3 X-class flares that took place previously 24 hours, and the most powerful of this sun cycle. Whilst spectacular, this match nonetheless poses no important risk to most people. Credit score: NOAANASA’s Sun Dynamics ObservatoryNASA’s Sun Dynamics Observatory (SDO), which captured the pictures in this web page, used to be introduced in February 2010. Its project is designed to look at the Solar and its sun actions comprehensively. Located in a geosynchronous orbit about 22,000 miles above Earth, SDO supplies remarkable insights into sun phenomena, together with sun flares, sunspots, and coronal mass ejections (CMEs).SDO’s number one purpose is to know the Solar’s affect on Earth and near-Earth area through learning the sun surroundings in lots of wavelengths concurrently. It’s supplied with a collection of tools that permit scientists to observe the Solar’s magnetic box, its floor, and atmospheric actions in prime solution. Probably the most key tools, the Atmospheric Imaging Meeting (AIA), captures pictures of the sun surroundings in 10 other wavelengths each and every 12 seconds, offering a dynamic view of the Solar’s conduct. Thru its steady commentary, SDO performs a vital position in making improvements to our skill to forecast area climate occasions that may have an effect on existence and era on Earth. Coronal mass ejections and sun flares. Credit score: NASA’s Goddard Area Flight Heart/Mary Pat Hrybyk-KeithSolar FlaresSolar flares are intense bursts of radiation that originate from the discharge of magnetic power at the Solar’s floor. Those lively phenomena can emit gentle throughout all the electromagnetic spectrum — from radio waves to gamma rays. The power launched through a sun flare may also be enormous, rivaling billions of megatons of TNT in relation to explosive energy.The classification of sun flares is according to their brightness in X-ray wavelengths, as noticed through satellites orbiting Earth. The program categorizes flares into 3 primary categories: C, M, and X. Every category represents a tenfold building up in power output in comparison to the previous one, with C-class flares being the least intense, M-class flares extra intense, and X-class flares essentially the most intense.Inside those categories, flares are additional ranked through a numerical price from 1 to 9, which signifies their particular energy inside their category. Alternatively, X-class flares can exceed 9, reflecting their excessive depth. As an example, an M1 flare is ten occasions much less intense than an X1 flare, highlighting the numerous leap in energy between those categories. In a similar fashion, an M2 flare is two times as intense as an M1 flare, demonstrating the logarithmic scale inside each and every category.An X-class flare, such because the X6.3, indicates a particularly tough sun match, able to inflicting important disturbances in Earth’s surroundings, affecting communications, navigation programs, or even energy grids. The numerical price following the category letter supplies a extra actual indication of the flare’s depth, with upper numbers representing more potent flares.Via tracking and classifying sun flares, scientists can higher perceive the Solar’s conduct and are expecting attainable affects on area climate, which is an important for safeguarding satellites, astronauts, and era on Earth. NASA’s Sun Dynamics Observatory and different tools play a key position in looking at those sun actions, enabling well timed forecasts and mitigating the consequences of area climate on our planet.
Coronal mass ejections and sun flares. Credit score: NASA’s Goddard Area Flight Heart/Mary Pat Hrybyk-KeithSolar FlaresSolar flares are intense bursts of radiation that originate from the discharge of magnetic power at the Solar’s floor. Those lively phenomena can emit gentle throughout all the electromagnetic spectrum — from radio waves to gamma rays. The power launched through a sun flare may also be enormous, rivaling billions of megatons of TNT in relation to explosive energy.The classification of sun flares is according to their brightness in X-ray wavelengths, as noticed through satellites orbiting Earth. The program categorizes flares into 3 primary categories: C, M, and X. Every category represents a tenfold building up in power output in comparison to the previous one, with C-class flares being the least intense, M-class flares extra intense, and X-class flares essentially the most intense.Inside those categories, flares are additional ranked through a numerical price from 1 to 9, which signifies their particular energy inside their category. Alternatively, X-class flares can exceed 9, reflecting their excessive depth. As an example, an M1 flare is ten occasions much less intense than an X1 flare, highlighting the numerous leap in energy between those categories. In a similar fashion, an M2 flare is two times as intense as an M1 flare, demonstrating the logarithmic scale inside each and every category.An X-class flare, such because the X6.3, indicates a particularly tough sun match, able to inflicting important disturbances in Earth’s surroundings, affecting communications, navigation programs, or even energy grids. The numerical price following the category letter supplies a extra actual indication of the flare’s depth, with upper numbers representing more potent flares.Via tracking and classifying sun flares, scientists can higher perceive the Solar’s conduct and are expecting attainable affects on area climate, which is an important for safeguarding satellites, astronauts, and era on Earth. NASA’s Sun Dynamics Observatory and different tools play a key position in looking at those sun actions, enabling well timed forecasts and mitigating the consequences of area climate on our planet.











-Abstract-Background-SOURCE-Amazon.jpg)
