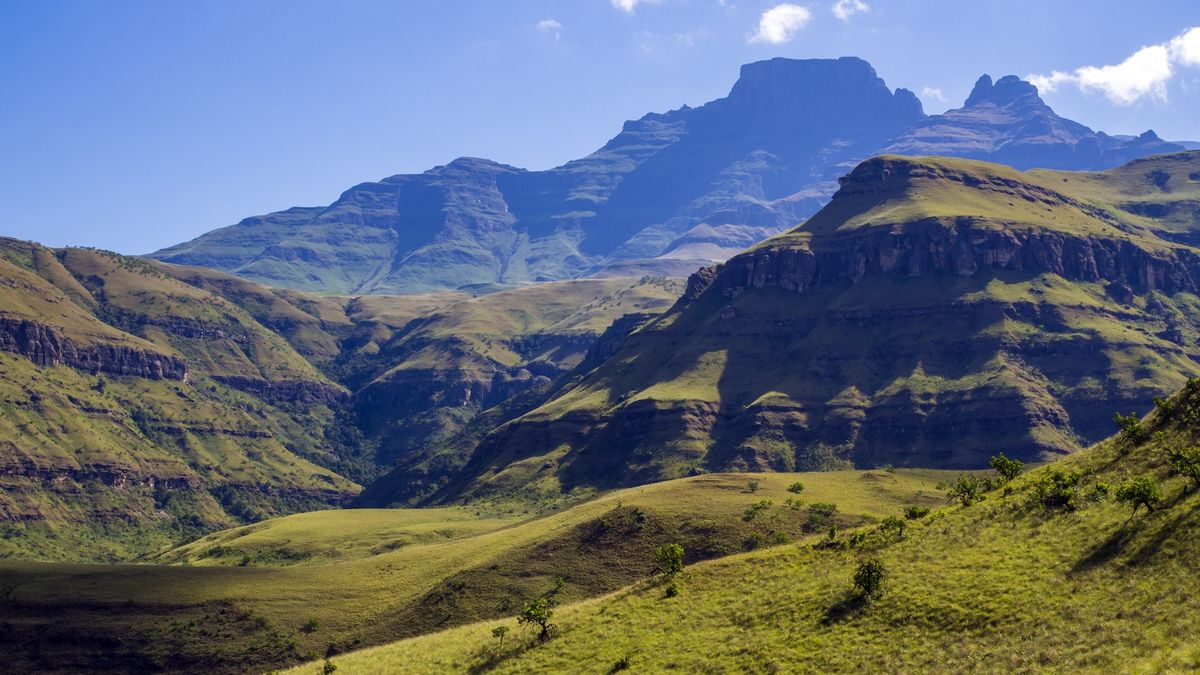
Prime plateaus upward push within the inner of continents due to churning deep within Earth loads of miles from the place they sooner or later spring up, new analysis suggests.As continents get a divorce, huge cliff partitions would possibly upward push close to the limits the place the crust is pulling aside. That breakup units off a wave in Earth’s center layer, the mantle, that slowly rolls inward over tens of tens of millions of years, fueling the upward push of plateaus, the brand new learn about discovered.Comparable: Fountains of diamonds that erupt from Earth’s heart are revealing the misplaced historical past of supercontinentsScientists have lengthy identified that continental rifts brought about the upward push of big escarpments, just like the cliff partitions that separate the East African Rift Valley from the Ethiopian plateau, stated lead creator Thomas Gernon, a geoscientist on the College of Southampton within the U.Okay. And those steep cliffs occasionally fringe inland plateaus that upward push from the sturdy, strong cores of continents, referred to as cratons.However as a result of those two panorama options typically shape tens of tens of millions to as much as 100 million years aside, many scientists idea the other formations have been pushed through other processes, Gernon advised Are living Science in an e-mail.Within the new learn about, revealed Aug. 7 within the magazine Nature, Gernon and co-workers studied 3 iconic coastal escarpments that shaped throughout the breakup of Earth’s remaining supercontinent, Gondwana. One, alongside India’s coast, fringes the Western Ghats for roughly 1,200 miles (2,000 kilometers); every other, in Brazil, rings the Highland plateau for roughly 1,900 miles (3,000 km); and the Nice Escarpment of South Africa encircles the Central Plateau and spans a staggering 3,700 miles (6,000 km), in keeping with the learn about. The internal plateaus in those areas can upward push a kilometer or extra, Gernon stated.The staff used topographic maps to turn the escarpments aligned with the continental limitations, which prompt that rifting created them. Pc simulations confirmed that the continental rifts disturb the mantle, triggering deep waves that roll inward towards the continent’s center.Get the arena’s most attractive discoveries delivered directly on your inbox.Subsequent, they analyzed present mineral information to turn that uplift and erosion at the plateau migrated inland at more or less the similar time and pace because the mantle wave churned miles beneath. This confirmed the 2 panorama options have been most probably brought about through the similar continental breakup procedure.With regards to the 3 escarpments within the present learn about, the churn was once achingly gradual, progressing at simply 9 to twelve miles (15 to twenty km) each million years, the learn about discovered. But this slow-motion mantle wave dramatically reshaped the panorama. Because it marched inward, it steadily peeled off the sturdy roots that anchor continents on the crust-mantle boundary. With out those anchors, the cratons was extra buoyant and subsequently rose.Wind and rain over the eons then whittled them away additional, making them lighter and extra buoyant nonetheless. This procedure culminated within the strong, top plateaus we see nowadays.In principle, the similar procedure would possibly give an explanation for different escarpment/plateau areas, corresponding to one in North and South Carolina or one south of Cameroon, Gernon stated. The cliffs and plateaus within the Carolinas are much less dramatic than the 3 studied within the paper, most probably as a result of they shaped as much as 100 million years previous than the 3 Gernon’s staff tested. That gave erosion tens of tens of millions of years to erase strains of each mantle churn and uplift.”Escarpments from a lot previous breakup occasions are not going to be preserved within the geologic document,” Gernon stated.The similar supercontinent breakup and mantle wave is a catalyst for different geologic processes, together with the eruption of diamonds from Earth’s heart, Gernon’s staff prior to now discovered.”It’s interesting to assume {that a} diamond worn on an engagement ring is also simply one of the crucial result of the similar geological processes that shape a few of Earth’s maximum dramatic landforms,” Gernon stated.