Abstract: Whilst people proportion over 95% in their genome with chimpanzees, our brains are way more complicated because of variations in gene expression. Analysis displays that human mind cells, in particular glial cells, show off upper ranges of upregulated genes, improving neural plasticity and building.Oligodendrocytes, a glial cellular sort, play a key function by means of insulating neurons for sooner and extra environment friendly signaling. This learn about underscores that the evolution of human intelligence most probably concerned coordinated adjustments throughout all mind cellular varieties, now not simply neurons.Key Information:Gene Expression: Human mind cells display upper ranges of gene process in comparison to chimpanzees.Glial Cellular Position: Variations in oligodendrocyte gene expression might make stronger neural plasticity and potency.Evolutionary Perception: Human mind complexity advanced via specialised gene expression throughout cellular varieties.Supply: UC Santa BarbaraOur mind is arguably the organ that almost all distinguishes people from different primates. Its remarkable measurement, complexity and features some distance exceed the ones of another species on Earth. But people proportion upwards of 95% of our genome with chimpanzees, our closest dwelling family.UC Santa Barbara professor Soojin Yi, within the Division of Ecology, Evolution, and Marine Biology, her doctoral scholar Dennis Joshy and collaborator Gabriel Santepere, at Sanatorium del Mar Clinical Analysis Institute in Barcelona, aimed to decide how genes in various kinds of mind cells have advanced in comparison to the ones in chimpanzees. 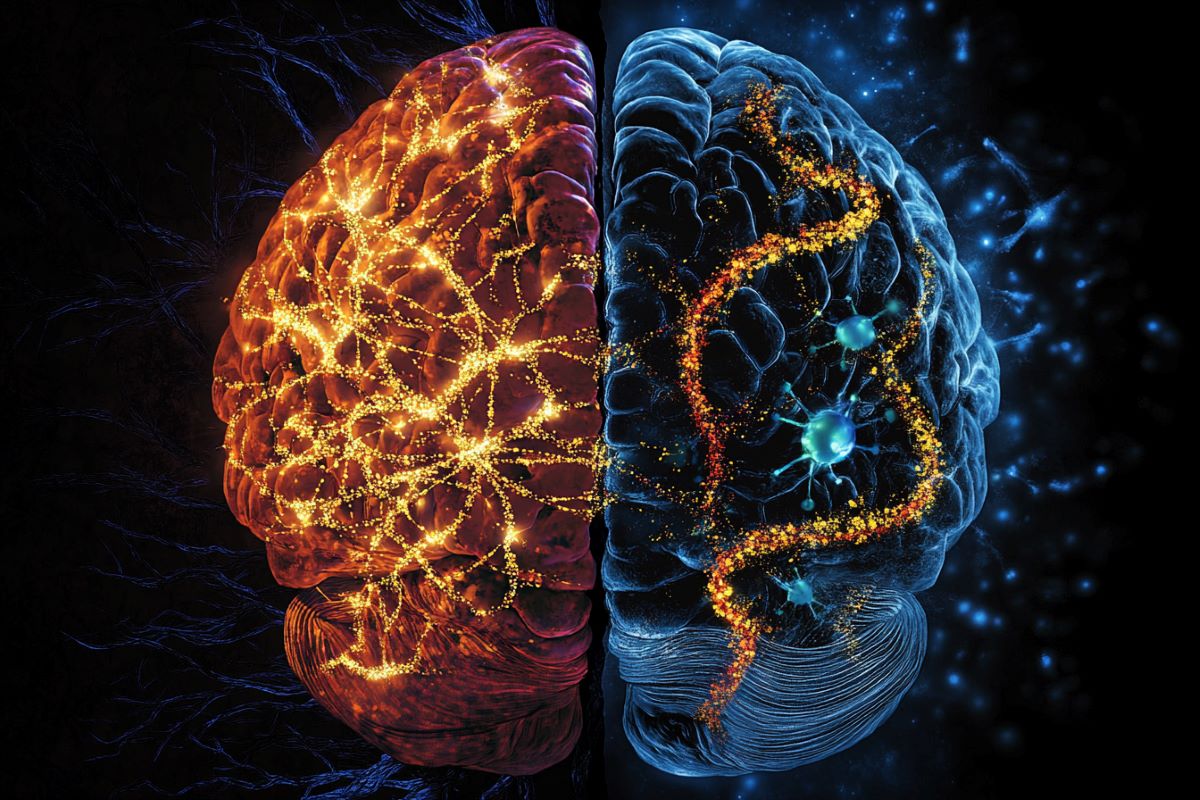 Human glial cells account for greater than part of the cells in our brains, a far higher share than in even chimpanzees. Credit score: Neuroscience NewsThey discovered that, whilst our genes code for just about the entire identical proteins as different apes, a lot of our genes are a lot more productive than the ones of different primates.Their effects, revealed within the Complaints of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences, spotlight the function of gene expression within the evolution and serve as of the human mind.Deciphering nature’s blueprintsEach gene tells a cellular to make a selected molecule, however this isn’t carried out by means of the DNA itself. As a substitute, the ideas is relayed to mobile equipment by means of a molecule referred to as messenger RNA. Researchers measure gene expression by means of looking at the quantity of mRNA a selected gene produces.As scientists started to know the function of the genome as lifestyles’s blueprint, they concept possibly the human genome may just provide an explanation for our distinctive characteristics. However an intensive comparability with chimpanzees in 2005 printed we proportion 99% p.c of our genes (although scientists have since revised this quantity).This showed previous research in accordance with small numbers of genes that had urged there was once just a small distinction between the human and chimpanzee genome.Now biologists suspect that gene expression might underlie those variations. Believe a monarch butterfly. The grownup has the similar genome as when it was once a caterpillar.The implausible variations between the 2 lifestyles levels all come all the way down to gene expression. Turning off and on other genes, or having them code for kind of mRNA, can greatly adjust an organism’s characteristics.Getting a clearer picturePrevious analysis has discovered variations in gene expression between people and chimpanzees, and that human cells have a tendency to have upper gene expression, however the image was once blurry.The mind is made up of many kinds of cells. Historically, scientists arranged mind cells into two primary varieties: neurons and glial cells. Neurons raise electrochemical alerts, somewhat just like the copper wiring in a construction.Glial cells carry out many of the different purposes, similar to insulating the wires, supporting the construction and clearing out particles.Till lately, scientists may just simplest learn about bulk tissue samples composed of many various kinds of cells. However inside the previous decade, it’s change into conceivable to assay cellular nuclei one after the other. This permits researchers to differentiate between cellular varieties, and frequently even subtypes.Yi, Joshy and Santepere used datasets generated from a tool with an excessively slender channel to split every nucleus into its personal chamber in an array. Then they grouped the cells by means of sort sooner than appearing statistical analysisThe group measured gene expression by means of looking at the quantity of mRNA a selected gene produced in people, chimpanzees and macaques. An upregulated gene produces extra mRNA in a given species in comparison to the others, whilst a downregulated gene produces much less.Evaluating chimpanzees and people to macaques enabled the researchers to inform when variations between the 2 apes had been because of adjustments in chimpanzees, adjustments in people, or each.The authors recorded variations within the expression of about 5-10% of the 25,000 genes within the learn about. Typically, human cells had extra upregulated genes in comparison to chimpanzees.This can be a a lot higher share than researchers discovered after they couldn’t spoil down the research by means of cellular sort. And the proportion grew to 12-15% when the authors started to imagine cellular subtypes.“Now we will be able to see that particular cellular varieties have their very own evolutionary trail, changing into truly specialised,” Yi stated.No longer simply neuronsThe intricacy of our neural pathways is unequalled within the animal kingdom, then again Yi suspects that our distinctive mind isn’t a results of this by itself.Human glial cells account for greater than part of the cells in our brains, a far higher share than in even chimpanzees.Amongst glial cells, oligodendrocytes confirmed the best variations in gene expression. Those cells create the insulation that coats neurons, enabling their electric alerts to go back and forth a lot more briefly and successfully.In a collaborative learn about revealed the former yr, the group seen that people have the next ratio of precursor as opposed to mature oligodendrocytes when compared with chimpanzees.Yi suspects this will relate to the superb neural plasticity and gradual building of human brains.“The greater complexity of our neural community almost certainly didn’t evolve on my own,” Yi stated.“It would now not come to life except some of these different cellular varieties additionally advanced and enabled the growth of the neuron variety, the choice of neurons and the complexity of the networks.”This learn about simplest thought to be cells from a couple of areas of the mind; then again, the cells in a single house of the mind might range from their opposite numbers in different spaces. Yi plans to check the mechanisms in the back of variations in gene expression and the way genes map to other characteristics.She additionally plans to track differential gene expression even previous in our evolutionary historical past by means of incorporating baselines from much more distantly comparable animals. And she or he’s fascinated with finding out genomic variations between us and different archaic people, like Neanderthals and Denisovans.Evolution is ready greater than simply converting genes. “Differential gene expression is truly how human brains advanced,” Yi stated.About this genetics and evolutionary neuroscience analysis newsAuthor: Harrison Tasoff
Human glial cells account for greater than part of the cells in our brains, a far higher share than in even chimpanzees. Credit score: Neuroscience NewsThey discovered that, whilst our genes code for just about the entire identical proteins as different apes, a lot of our genes are a lot more productive than the ones of different primates.Their effects, revealed within the Complaints of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences, spotlight the function of gene expression within the evolution and serve as of the human mind.Deciphering nature’s blueprintsEach gene tells a cellular to make a selected molecule, however this isn’t carried out by means of the DNA itself. As a substitute, the ideas is relayed to mobile equipment by means of a molecule referred to as messenger RNA. Researchers measure gene expression by means of looking at the quantity of mRNA a selected gene produces.As scientists started to know the function of the genome as lifestyles’s blueprint, they concept possibly the human genome may just provide an explanation for our distinctive characteristics. However an intensive comparability with chimpanzees in 2005 printed we proportion 99% p.c of our genes (although scientists have since revised this quantity).This showed previous research in accordance with small numbers of genes that had urged there was once just a small distinction between the human and chimpanzee genome.Now biologists suspect that gene expression might underlie those variations. Believe a monarch butterfly. The grownup has the similar genome as when it was once a caterpillar.The implausible variations between the 2 lifestyles levels all come all the way down to gene expression. Turning off and on other genes, or having them code for kind of mRNA, can greatly adjust an organism’s characteristics.Getting a clearer picturePrevious analysis has discovered variations in gene expression between people and chimpanzees, and that human cells have a tendency to have upper gene expression, however the image was once blurry.The mind is made up of many kinds of cells. Historically, scientists arranged mind cells into two primary varieties: neurons and glial cells. Neurons raise electrochemical alerts, somewhat just like the copper wiring in a construction.Glial cells carry out many of the different purposes, similar to insulating the wires, supporting the construction and clearing out particles.Till lately, scientists may just simplest learn about bulk tissue samples composed of many various kinds of cells. However inside the previous decade, it’s change into conceivable to assay cellular nuclei one after the other. This permits researchers to differentiate between cellular varieties, and frequently even subtypes.Yi, Joshy and Santepere used datasets generated from a tool with an excessively slender channel to split every nucleus into its personal chamber in an array. Then they grouped the cells by means of sort sooner than appearing statistical analysisThe group measured gene expression by means of looking at the quantity of mRNA a selected gene produced in people, chimpanzees and macaques. An upregulated gene produces extra mRNA in a given species in comparison to the others, whilst a downregulated gene produces much less.Evaluating chimpanzees and people to macaques enabled the researchers to inform when variations between the 2 apes had been because of adjustments in chimpanzees, adjustments in people, or each.The authors recorded variations within the expression of about 5-10% of the 25,000 genes within the learn about. Typically, human cells had extra upregulated genes in comparison to chimpanzees.This can be a a lot higher share than researchers discovered after they couldn’t spoil down the research by means of cellular sort. And the proportion grew to 12-15% when the authors started to imagine cellular subtypes.“Now we will be able to see that particular cellular varieties have their very own evolutionary trail, changing into truly specialised,” Yi stated.No longer simply neuronsThe intricacy of our neural pathways is unequalled within the animal kingdom, then again Yi suspects that our distinctive mind isn’t a results of this by itself.Human glial cells account for greater than part of the cells in our brains, a far higher share than in even chimpanzees.Amongst glial cells, oligodendrocytes confirmed the best variations in gene expression. Those cells create the insulation that coats neurons, enabling their electric alerts to go back and forth a lot more briefly and successfully.In a collaborative learn about revealed the former yr, the group seen that people have the next ratio of precursor as opposed to mature oligodendrocytes when compared with chimpanzees.Yi suspects this will relate to the superb neural plasticity and gradual building of human brains.“The greater complexity of our neural community almost certainly didn’t evolve on my own,” Yi stated.“It would now not come to life except some of these different cellular varieties additionally advanced and enabled the growth of the neuron variety, the choice of neurons and the complexity of the networks.”This learn about simplest thought to be cells from a couple of areas of the mind; then again, the cells in a single house of the mind might range from their opposite numbers in different spaces. Yi plans to check the mechanisms in the back of variations in gene expression and the way genes map to other characteristics.She additionally plans to track differential gene expression even previous in our evolutionary historical past by means of incorporating baselines from much more distantly comparable animals. And she or he’s fascinated with finding out genomic variations between us and different archaic people, like Neanderthals and Denisovans.Evolution is ready greater than simply converting genes. “Differential gene expression is truly how human brains advanced,” Yi stated.About this genetics and evolutionary neuroscience analysis newsAuthor: Harrison Tasoff
Supply: UC Santa Barbara
Touch: Harrison Tasoff – UC Santa Barbara
Symbol: The picture is credited to Neuroscience NewsOriginal Analysis: Open get admission to.
“Sped up cell-type-specific regulatory evolution of the human mind” by means of Soojin Yi et al. PNASAbstractAccelerated cell-type-specific regulatory evolution of the human brainThe molecular foundation of human mind evolution is a key piece in working out the evolution of human-specific cognitive and behavioral characteristics.Comparative research have urged that human mind evolution was once accompanied by means of speeded up adjustments of gene expression (known as “regulatory evolution”), particularly the ones resulting in an build up of gene merchandise excited by power manufacturing and metabolism.Alternatively, the alerts of speeded up regulatory evolution weren’t all the time constant throughout research. One confounding issue is the range of unique cellular varieties within the human mind.Right here, we leveraged single-cell human and nonhuman primate transcriptomic information to analyze regulatory evolution at cell-type solution.We trusted six well-established primary cellular varieties: excitatory and inhibitory neurons, astrocytes, microglia, oligodendrocytes, and oligodendrocyte precursor cells.We discovered pervasive signatures of speeded up regulatory evolution within the human brains in comparison to the chimpanzee brains within the primary six cellular varieties, in addition to throughout more than one neuronal subtypes.Additionally, regulatory evolution is very cellular sort particular moderately than shared between cellular varieties and strongly related to cellular-level epigenomic options.Evolutionarily differentially expressed genes (DEGs) show off better cell-type specificity than different genes, suggesting their function within the practical specialization of person cellular varieties within the human mind.As we proceed to spread the mobile complexity of the mind, the real scope of DEGs within the human mind seems to be a lot broader than up to now estimated.Our learn about helps the acceleration of cell-type-specific practical systems as crucial function of human mind evolution.
Gene Expression Drives Evolution of Human Mind Complexity – Neuroscience Information







:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():focal(746x727:748x729)/Pregnant-California-Teacher-Dies-Hiking-Trip-Greece-010425-01-536f5e95c7244fb6b5d26a10fa4dac38.jpg)




