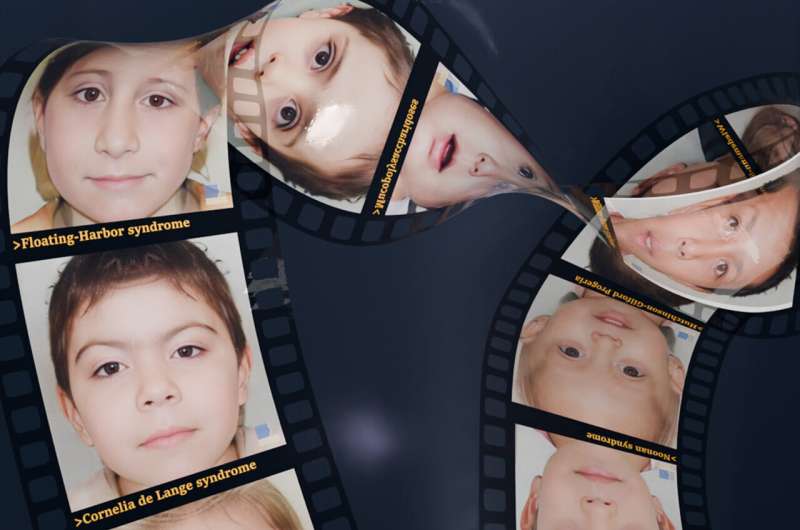
Photorealistic, artificial portraits of more than a few illnesses identified within the context of the learn about. The pictures had been generated with GestaltGAN and don’t permit any conclusions to be drawn concerning the folks. Credit score: Aron Kirchhoff, College Sanatorium Bonn (UKB)
Nearly all of infrequent illnesses have a genetic purpose. The underlying genetic alteration can also be discovered an increasing number of simply, for instance, by way of exome sequencing (ES), resulting in a molecular genetic prognosis. ES is an exam of all sections of our genetic subject matter (DNA) that code for proteins. As a part of a Germany-wide multicenter learn about, ES knowledge was once accrued from 1,577 sufferers and systematically evaluated.
This made it imaginable to diagnose a complete of 499 sufferers, with 34 sufferers appearing new, up to now unknown genetic illnesses. The learn about thus makes an important contribution to the preliminary description of recent illnesses. As well as, instrument in accordance with using synthetic intelligence (AI) was once used for the primary time on a wide scale to beef up scientific prognosis. ‘
The “GestaltMatcher” AI gadget can help within the review of facial options with reference to the classification of congenital genetic syndromes. The result of the learn about, wherein 16 college places had been concerned, had been printed in Nature Genetics.
Extremely-rare illnesses require each multidisciplinary scientific experience and complete genetic diagnostics for optimum care. The 3-year TRANSLATE NAMSE innovation fund venture started on the finish of 2017 with the purpose of bettering the care of the ones affected by way of fashionable diagnostic ideas.
Researchers from 16 college hospitals analyzed the ES knowledge of one,577 sufferers, together with 1,309 youngsters, who offered to infrequent illness facilities as a part of TRANSLATE NAMSE. The purpose of the venture was once to search out the reason for the illness in as many sufferers as imaginable the usage of cutting edge exam strategies.
A genetic explanation for the infrequent illness was once known in 499 sufferers, 425 of whom had been youngsters. In overall, the researchers discovered adjustments in 370 other genes.
“We’re specifically pleased with the invention of 34 new molecular illnesses, which is a brilliant instance of knowledge-generating affected person care at college hospitals,” says Dr. Theresa Brunet, one of the vital lead authors from the Institute of Human Genetics on the Klinikum rechts der Isar of the Technical College of Munich.
What occurs subsequent with the unsolved instances?
“We will be able to read about the affected sufferers for whom now we have now not but been in a position to discover a prognosis as a part of the type venture Genome Sequencing, or MVGenomSeq for brief,” says Dr. Tobias Haack, Deputy Director of the Institute of Clinical Genetics and Implemented Genomics on the College Sanatorium of Tübingen.
The MVGenomSeq builds at the luck of the TRANSLATE NAMSE venture and permits the research of scientific genomes at college hospitals all through Germany. Unsolved instances can be investigated in follow-up research the usage of new exam strategies, comparable to long-read sequencing, which permits for much longer DNA fragments to be analyzed.
“Lengthy-read sequencing permits us to search out genetic adjustments which might be tricky to hit upon and we think that we can make additional diagnoses the usage of this system,” says Dr. Nadja Ehmke, Head of Genome Diagnostics at Charité’s Institute of Clinical Genetics and Human Genetics and one of the vital ultimate authors.
As a part of the TRANSLATE NAMSE venture, standardized procedures for prolonged genetic diagnostics for suspected infrequent illnesses had been additionally established on the collaborating infrequent illness facilities, in accordance with interdisciplinary case meetings. Those had been integrated into usual care after the venture was once finished.
“The interdisciplinary case meetings play crucial function for the ones affected. This allows a complete scientific characterization, which is related for the phenotype-based analysis of the genetic knowledge. As well as, the detected variants can also be mentioned in an interdisciplinary context,” says Dr. Magdalena Danyel, one of the vital first authors, who works as a expert on the Institute of Clinical Genetics and Human Genetics and a fellow of the Clinician Scientist Program of the Berlin Institute of Well being (BIH) at Charité—Universitätsmedizin.
Uncommon genetic illnesses can once in a while be identified by way of the face
The researchers additionally investigated whether or not the supplementary use of device studying and synthetic intelligence (AI) equipment improves diagnostic effectiveness and potency.
To this finish, the “GestaltMatcher” instrument evolved by way of researchers in Bonn, which makes use of computer-assisted facial research to beef up the individual the usage of it within the prognosis of infrequent illnesses, was once examined on a wide scale for the primary time.
The learn about used the series and symbol knowledge of 224 individuals who had additionally consented to the computer-assisted research in their facial pictures, and it was once proven that the AI-supported generation supplies a scientific receive advantages.
The GestaltMatcher AI can acknowledge abnormalities within the face and assign them to express illnesses. Crucial query when assessing genetic knowledge is: Does the phenotype fit the genotype? The AI may give beef up right here.
“GestaltMatcher is like knowledgeable opinion that we will supply to any clinical skilled in an issue of seconds. Early prognosis is very important for the ones suffering from infrequent illnesses and their households. Supportive use of the instrument by way of pediatricians may already be helpful with regards to abnormalities throughout the U7 screening at 21 to 24 months or U7a at 34 to 36 months,” says corresponding creator Prof. Peter Krawitz, Director of the Institute for Genomic Statistics and Bioinformatics (IGSB) on the College Sanatorium Bonn (UKB), the place the GestaltMatcher AI is being evolved.
Prof. Krawitz could also be a member of the Cluster of Excellence ImmunoSensation2 and within the Transdisciplinary Analysis Spaces (TRA) “Modeling” and “Lifestyles & Well being” on the College of Bonn. The instrument and app can also be made to be had to all medical doctors throughout the non-profit group Arbeitsgemeinschaft für Gen-Diagnostik e.V. (AGD).
Additional info:
Axel Schmidt et al, Subsequent-generation phenotyping built-in in a countrywide framework for sufferers with ultrarare problems improves genetic diagnostics and yields new molecular findings, Nature Genetics (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41588-024-01836-1
Equipped by way of
College Sanatorium Bonn
Quotation:
Genetic diagnostics of ultra-rare illnesses: Massive multicenter learn about identifies 34 new genetic illnesses (2024, July 22)
retrieved 22 July 2024
from
This file is matter to copyright. With the exception of any honest dealing for the aim of personal learn about or analysis, no
section is also reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is equipped for info functions simplest.