Id of CH circumstances from WGS in ISL and UKBWe used WGS from 45,510 Icelanders and 130,709 British ancestry contributors from the UKB17,18. Moderate sequencing intensity used to be 33× for UKB and 38× for ISL. Members with prior diagnoses of hematological problems or grossly unusual hematology measurements on access had been excluded. We recognized other folks with CH in accordance with an evolution of our mutational barcode strategy1. Mosaic somatic mutation barcodes had been generated via modeling low variant allele fraction (VAF) series reads (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 1). To scale back contamination from low-VAF germline variants and recurrent sequencing mistakes, we used simplest indicator mutations that had been noticed as soon as in each and every cohort and limited in VAF vary to 0.10–0.25. Members with barcodes containing quite a few indicator mutations above a threshold had been thought to be to have CH. We recognized 16,306 other folks with CH, a occurrence over the 2 cohorts of 9.3%.As expected from earlier research, CH used to be unusual in beneath 45-year-olds, however greater dramatically in frequency thereafter, drawing near 50% via age 80. Each present and former smoking considerably greater menace of CH (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 1b,c). Pack years additional greater CH menace (P = 8.57 × 10−7), while years since stopped smoking had been protecting (P = 3.54 × 10−10; Supplementary Desk 1), indicating a dose-dependent dating between smoking and CH. Whilst the mechanisms in which age and smoking advertise CH are but to be elucidated, each elements obviously are attainable confounders in epidemiological analyses. Members with CH had been at considerably higher menace of all-cause mortality and of being identified due to this fact with a hematological dysfunction. Smoking used to be an impartial menace issue for mortality however now not for hematological problems (Supplementary Desk 2).Associations of CH with diseaseIn case–keep an eye on evaluation, CH had robust associations with each myeloid and lymphoid neoplasia (Desk 1 and Supplementary Desk 3). CH used to be additionally related to present or next diagnoses of persistent obstructive pulmonary illness (COPD), lung most cancers, peripheral artery illness (PAD), emphysema and alcohol abuse. Those nonhematological prerequisites are identified to be smoking-related, and their importance used to be considerably attenuated as soon as smoking used to be taken into consideration. This implies that the associations could also be because of residual confounding from quite a lot of facets of smoking habits. Hematological dysfunction associations weren’t in a similar fashion attenuated via smoking changes. Research limited to by no means people who smoke produced equivalent conclusions (Supplementary Desk 4).Desk 1 Associations between clonal hematopoiesis and illness in UKBCase–keep an eye on evaluation printed no indication of affiliation between CH and key CVD phenotypes, neither in UKB nor in ISL (Supplementary Desk 5). Unadjusted for smoking, no CVD phenotype handed Bonferroni importance and, as soon as adjusted, none used to be even nominally important. To inspect this additional, we carried out a time-to-CVD-event evaluation in UKB. We thought to be additionally whether or not CH explained via mutational barcodes differed on this admire from CH containing a CPLD mutation. Moreover, we tested CHIP as explained the use of the filtering technique advisable in ref. 19,20. In all 3 circumstances, we had been not able to measure any greater menace of CVD in other folks with CH. We did, even though, follow robust results from attainable confounders within the multivariable type (Desk 2). CH has additionally been implicated in pro-inflammatory phenomena, a steered foundation for its reported CVD association21,22. Accordingly, we seemed for CH associations with a panel of inflammatory prerequisites, however noticed none (Supplementary Desk 5). In UKB, CH used to be related to alcoholic liver illness (Desk 1) however now not fatty liver prerequisites, at variance with a contemporary report23.Desk 2 Time-to-event evaluation of 3 fashions of CH for heart problems endpointsaTo higher perceive the greater mortality price because of CH, we tested the main reason behind demise information in a meta-analysis of ISL and UKB. Members with CH had been at greater menace of demise from each myeloid and lymphoid hematological problems, in addition to lung most cancers, COPD and alcohol abuse (Supplementary Desk 6). As sooner than, the nonhematological dangers had been attenuated (however now not eradicated) via adjustment for smoking. Persistent ischemic center illness and center failure had nominally important danger ratios (HRs), however didn’t meet the Bonferroni threshold. Despite the fact that a considerable collection of deaths from acute myocardial infarction happened within the cohort, their frequency used to be now not increased in contributors with CH.Affiliation of mosaic somatic mutations with CHMost prior DNA sequence-based research recognized CH the use of a predefined checklist of CPLD mutations which might be already identified to happen in myeloid neoplasia4,13,14,15. Some research have examined mutated genes for statistical affiliation with CH or proof of sure variety in CH1,3,24,25. Our manner can determine CH regardless of whether or not a CPLD mutation is provide. Thus we will be able to seek in a relatively independent method for genes with mutations that force CH. We carried out a gene-based burden check for somatic mutations related to CH (Fig. 1a and Supplementary Desk 7). As expected from earlier studies1,3,4, mutations in DNMT3A, TET2 and ASXL1 had been essentially the most considerably related to CH. Many of the different genes are identified to be repeatedly mutated in myeloid illness. Some are implicated, moreover or uniquely, in lymphoid neoplasia26.Fig. 1: Affiliation of mosaic somatic mutations with CH.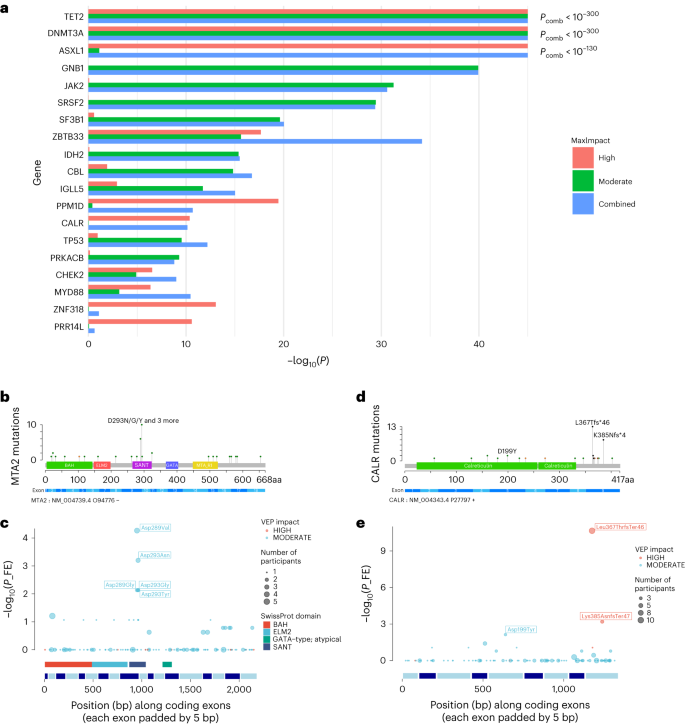 a, Effects (−log10(P)) of gene-based burden check the use of SKAT-O for affiliation of somatic mutations with CH. Knowledge are a meta-analysis of ISL and UKB. Separate burden assessments had been carried out to incorporate high-impact (crimson) or moderate-impact mutations (inexperienced; as assessed with the Ensembl VEP) and a mix of each varieties (blue) for the genes indicated. Pcomb is the P worth for blended high- and moderate-impact variants. The utmost influence (MaxImpact) VEP annotation used to be used to categorise each and every mutation. b, Lollipop plot appearing the counts of somatic mutations within the MTA2 gene detected in CH circumstances in UKB. Inexperienced lollipops are missense, black are frameshifts and orange are splice mutations. PFAM area and exon buildings are proven underneath. BAH, bromo-adjacent homology area; ELM2, Egl-27 and MTA1 homology 2 area; GATA, GATA zinc finger area; MTA_R1, metastasis-associated protein MTA1 R1 area; SANT, Swi3-Ada2-N-Cor and TFIIIB area. c, Fisher’s precise affiliation check ends up in UKB for particular person mutations in MTA2. Diameter of the circles signifies the full collection of contributors with the mutation (CH circumstances + controls). SwissProt domain names and exon construction of the gene are proven underneath. d,e, As in b and c however for the CALR gene. FE, Fisher’s precise.We additionally tested the intragenic distribution of the somatic mutations and used Fisher’s precise assessments to spot particular person mutations that force the sign from each and every gene (Fig. 1b–e and Supplementary Fig. 1). ASXL1 exhibited predominantly frameshift or nonsense mutations within the thirteenth (closing) exon. ASXL1 activation in myeloid neoplasia generally effects from gain-of-function mutations that produce C-terminally truncated proteins27. Alternatively, we additionally noticed protein truncation mutations in exon 12, specifically Arg404Ter and Arg417Ter, that related strongly with CH (P = 9.7 × 10−6 and a pair of.6 × 10−6, respectively, UKB, Fisher’s precise check). Those mutations are puzzling as a result of they might be anticipated to urge nonsense-mediated decay of the ASXL1 transcript28, which might obviate a gain-of-function impact. Additional investigation is warranted. The CH affiliation with GNB1 used to be totally because of Lys57Glu mutations (P = 1.4 × 10−46, UKB, Fisher’s precise check). GNB1 mutations affecting Lys57 predominate in myeloid neoplasia, while mutations at different positions are extra widespread in lymphoid malignancies29. In CALR, high-impact mutations clustered within the 9th (closing) exon, suggesting a gain-of-function analogous to that noticed in PPM1D and ASXL1 (Fig. 1d,e). Such mutations are found in very important thrombocythemia (ET) and number one myelofibrosis30; on the other hand, they’ve now not been persistently implicated as CH-defining mutations (Supplementary Desk 7). We acquired tough proof linking high-impact PRR14L mutations to CH (P = 3 × 10−11, UKB, SKAT-O). PRR14L isn’t normally known as a CH gene (Supplementary Desk 7); on the other hand, mutations had been noticed in persistent myelomonocytic leukemia and from time to time in CH participants31.We in the past reported a tentative affiliation between CH and MYD88 mutations in ISL1. We verify that discovering robustly right here (P = 1.9 × 10−10, UKB, SKAT-O), the most powerful sign coming from Leu252Pro. MYD88 Leu252Pro (previously Leu265Pro) mutations are specifically associated with lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma/Waldenström macroglobulinemia (LPL/WM), which might now not be anticipated to have a considerable bloodborne component26,32,33. Alternatively, MYD88 mutations additionally happen in an unusual minority of persistent lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and Leu252Pro has been noticed in standard B cells from sufferers with LPL/WM34,35. We additionally reported a CH affiliation with mutations in MTA2 (ref. 1) and make sure that discovering right here (P = 7.9 × 10−7, UKB, SKAT-O). For my part important missense mutations had been clustered inside the SANT area (Fig. 1b,c), which recruits histone deacetylase-1 to the nucleosome transforming and deacetylase (NuRD) complex36. Despite the fact that we had been in a position to display robust associations between the average CPLD genes and CH, maximum circumstances may now not be accounted for via an glaring driving force mutation (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 2). A number of elements would possibly give a contribution to this; a decrease sensitivity for CPLD mutation detection in WGS as opposed to entire exome or panel sequencing, driving force mutations positioned outdoor the coding sequences of identified CPLD genes, mosaic chromosomal alterations (mCA), clonally inherited epigenetic results and random glide in an HSC pool with an excessively low efficient inhabitants size1,2.Differential dangers of hematological disordersWe investigated the sorts of hematological problems bobbing up in contributors with CH. Additionally, we thought to be how the chance profile of CH explained via mutational barcodes (referred to herein as merely ‘CH’ or ‘barcode-CH’ when disambiguation is needed) differed from CH explained via the presence of a CPLD mutation (CPLD-CH) or via the absence of a CPLD mutation in a barcode sure case (CPLDneg-CH) (Supplementary Desk 8). As proven in Fig. 2a, HRs for each myeloid and lymphoid problems had been greater for all 3 CH categories. There have been, on the other hand, variations in nuance. Members with CPLD-CH had been much more likely to expand myeloid neoplasia than the ones with barcode-CH or CPLDneg-CH. Conversely, contributors with barcode-CH or CPLDneg-CH had been much more likely to expand lymphoid neoplasia than the ones with CPLD-CH. Inside myeloid subtypes, CPLDneg-CH contributors had been at demonstrable menace of persistent myeloid leukemia (CML), myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and myeloproliferative neoplasia (MPN). Alternatively, CPLD-CH contributors had been at upper menace of growing acute myeloblastic leukemia (AML), MDS and MPN (particularly, polycythemia vera (PCV)) than CPLDneg-CH contributors. Inside lymphoid subtypes, barcode-CH and CPLDneg-CH carried important dangers of CLL, while CPLD-CH didn’t. This implies that some barcode-CH circumstances can have incipient, undiagnosed CLL or high-count monoclonal B cellular lymphocytosis (MBL). Alternatively, as a result of B cells generally include a small share of the leukocyte inhabitants, even in MBL, B cellular clonal expansions are not going to move our CH detection threshold within the absence of an overt hematological abnormality. Accordingly, they’re not going to account for a considerable collection of barcode-CH circumstances. Additionally, associations with MPN and CLL might be pushed via undetected mCA accompanying the barcode-CH37,38.Fig. 2: Differential dangers of next hematological problems for barcode-CH, CPLD-CH and CPLDneg-CH.
a, Effects (−log10(P)) of gene-based burden check the use of SKAT-O for affiliation of somatic mutations with CH. Knowledge are a meta-analysis of ISL and UKB. Separate burden assessments had been carried out to incorporate high-impact (crimson) or moderate-impact mutations (inexperienced; as assessed with the Ensembl VEP) and a mix of each varieties (blue) for the genes indicated. Pcomb is the P worth for blended high- and moderate-impact variants. The utmost influence (MaxImpact) VEP annotation used to be used to categorise each and every mutation. b, Lollipop plot appearing the counts of somatic mutations within the MTA2 gene detected in CH circumstances in UKB. Inexperienced lollipops are missense, black are frameshifts and orange are splice mutations. PFAM area and exon buildings are proven underneath. BAH, bromo-adjacent homology area; ELM2, Egl-27 and MTA1 homology 2 area; GATA, GATA zinc finger area; MTA_R1, metastasis-associated protein MTA1 R1 area; SANT, Swi3-Ada2-N-Cor and TFIIIB area. c, Fisher’s precise affiliation check ends up in UKB for particular person mutations in MTA2. Diameter of the circles signifies the full collection of contributors with the mutation (CH circumstances + controls). SwissProt domain names and exon construction of the gene are proven underneath. d,e, As in b and c however for the CALR gene. FE, Fisher’s precise.We additionally tested the intragenic distribution of the somatic mutations and used Fisher’s precise assessments to spot particular person mutations that force the sign from each and every gene (Fig. 1b–e and Supplementary Fig. 1). ASXL1 exhibited predominantly frameshift or nonsense mutations within the thirteenth (closing) exon. ASXL1 activation in myeloid neoplasia generally effects from gain-of-function mutations that produce C-terminally truncated proteins27. Alternatively, we additionally noticed protein truncation mutations in exon 12, specifically Arg404Ter and Arg417Ter, that related strongly with CH (P = 9.7 × 10−6 and a pair of.6 × 10−6, respectively, UKB, Fisher’s precise check). Those mutations are puzzling as a result of they might be anticipated to urge nonsense-mediated decay of the ASXL1 transcript28, which might obviate a gain-of-function impact. Additional investigation is warranted. The CH affiliation with GNB1 used to be totally because of Lys57Glu mutations (P = 1.4 × 10−46, UKB, Fisher’s precise check). GNB1 mutations affecting Lys57 predominate in myeloid neoplasia, while mutations at different positions are extra widespread in lymphoid malignancies29. In CALR, high-impact mutations clustered within the 9th (closing) exon, suggesting a gain-of-function analogous to that noticed in PPM1D and ASXL1 (Fig. 1d,e). Such mutations are found in very important thrombocythemia (ET) and number one myelofibrosis30; on the other hand, they’ve now not been persistently implicated as CH-defining mutations (Supplementary Desk 7). We acquired tough proof linking high-impact PRR14L mutations to CH (P = 3 × 10−11, UKB, SKAT-O). PRR14L isn’t normally known as a CH gene (Supplementary Desk 7); on the other hand, mutations had been noticed in persistent myelomonocytic leukemia and from time to time in CH participants31.We in the past reported a tentative affiliation between CH and MYD88 mutations in ISL1. We verify that discovering robustly right here (P = 1.9 × 10−10, UKB, SKAT-O), the most powerful sign coming from Leu252Pro. MYD88 Leu252Pro (previously Leu265Pro) mutations are specifically associated with lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma/Waldenström macroglobulinemia (LPL/WM), which might now not be anticipated to have a considerable bloodborne component26,32,33. Alternatively, MYD88 mutations additionally happen in an unusual minority of persistent lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and Leu252Pro has been noticed in standard B cells from sufferers with LPL/WM34,35. We additionally reported a CH affiliation with mutations in MTA2 (ref. 1) and make sure that discovering right here (P = 7.9 × 10−7, UKB, SKAT-O). For my part important missense mutations had been clustered inside the SANT area (Fig. 1b,c), which recruits histone deacetylase-1 to the nucleosome transforming and deacetylase (NuRD) complex36. Despite the fact that we had been in a position to display robust associations between the average CPLD genes and CH, maximum circumstances may now not be accounted for via an glaring driving force mutation (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 2). A number of elements would possibly give a contribution to this; a decrease sensitivity for CPLD mutation detection in WGS as opposed to entire exome or panel sequencing, driving force mutations positioned outdoor the coding sequences of identified CPLD genes, mosaic chromosomal alterations (mCA), clonally inherited epigenetic results and random glide in an HSC pool with an excessively low efficient inhabitants size1,2.Differential dangers of hematological disordersWe investigated the sorts of hematological problems bobbing up in contributors with CH. Additionally, we thought to be how the chance profile of CH explained via mutational barcodes (referred to herein as merely ‘CH’ or ‘barcode-CH’ when disambiguation is needed) differed from CH explained via the presence of a CPLD mutation (CPLD-CH) or via the absence of a CPLD mutation in a barcode sure case (CPLDneg-CH) (Supplementary Desk 8). As proven in Fig. 2a, HRs for each myeloid and lymphoid problems had been greater for all 3 CH categories. There have been, on the other hand, variations in nuance. Members with CPLD-CH had been much more likely to expand myeloid neoplasia than the ones with barcode-CH or CPLDneg-CH. Conversely, contributors with barcode-CH or CPLDneg-CH had been much more likely to expand lymphoid neoplasia than the ones with CPLD-CH. Inside myeloid subtypes, CPLDneg-CH contributors had been at demonstrable menace of persistent myeloid leukemia (CML), myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and myeloproliferative neoplasia (MPN). Alternatively, CPLD-CH contributors had been at upper menace of growing acute myeloblastic leukemia (AML), MDS and MPN (particularly, polycythemia vera (PCV)) than CPLDneg-CH contributors. Inside lymphoid subtypes, barcode-CH and CPLDneg-CH carried important dangers of CLL, while CPLD-CH didn’t. This implies that some barcode-CH circumstances can have incipient, undiagnosed CLL or high-count monoclonal B cellular lymphocytosis (MBL). Alternatively, as a result of B cells generally include a small share of the leukocyte inhabitants, even in MBL, B cellular clonal expansions are not going to move our CH detection threshold within the absence of an overt hematological abnormality. Accordingly, they’re not going to account for a considerable collection of barcode-CH circumstances. Additionally, associations with MPN and CLL might be pushed via undetected mCA accompanying the barcode-CH37,38.Fig. 2: Differential dangers of next hematological problems for barcode-CH, CPLD-CH and CPLDneg-CH.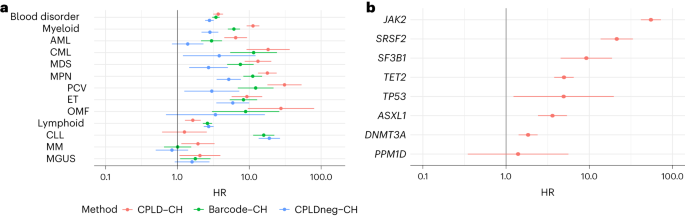 a, HR and 95% CI from Cox regressions for subtypes of hematological dysfunction, stratified via CPLD-CH, barcode-CH and CPLDneg-CH. Diagnoses had been incorporated in the event that they arose 6 months or extra after blood sampling for CH resolution. Knowledge are meta-analysis of UKB and ISL (n = 162,963 contributors general, 14,837 with barcode-CH, 5,288 with CPLD-CH and 11,692 with CPLDneg-CH). b, HR and 95% CI for next hematological dysfunction stratified via CPLD genes. MM, a couple of myeloma; MGUS, monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined importance; OMF, osteomyelofibrosis.We investigated whether or not, amongst CPLD-CH contributors, dangers of hematological problems differed via the precise CPLD gene concerned (Fig. 2b). Vital HRs had been noticed for ASXL1-CH, DNMT3A-CH, JAK2-CH, SF3B1-CH, SRSF2-CH, TET2-CH and TP53-CH however now not for PPM1D-CH. The danger from JAK2-CH used to be more than from every other of the CPLD genes. Whilst contributors with DNMT3A-CH had been at relatively greater menace, HR estimates for different CPLD-CH varieties together with ASXL1-CH and TET2-CH had been considerably upper.CH GWAS meta-analysis in ISL and UKBWe performed a GWAS meta-analysis for barcode-CH (designated the ‘CH GWAS’) in 130,709 UKB and 45,510 ISL contributors, the use of germline genotypes imputed from WGS coaching sets17,18. We recognized 25 loci with affiliation alerts of P < 5 × 10−8 (Fig. 3 and Supplementary Desk 9). An extra ten low-frequency, high-effect variants require affirmation and weren’t thought to be additional. All the sentinel variants had low variant impact predictor (VEP) affects. At chr22q12, the sentinel variant used to be in excessive linkage disequilibrium (LD) (r2 = 0.95 in UKB and 1.0 in ISL) with the well known oncogenic ‘1100delC’ CHEK2 frameshift mutation rs555607708_delG (Thr367MetfsTer15)39. Conditional evaluation recognized secondary alerts at chr3q25 (a splice area variant in SMC4), chr5p15 (TERT) and chr21q11 (an Arg448Gly missense in NRIP1; Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 3 and Supplementary Desk 9). Scanning at a extra comfy stringency (P < 5 × 10−7) for variants with reasonable or excessive VEP results recognized a low-frequency protecting Arg684Gln variant in RTEL1 (rs35640778_A; odds ratio (OR) = 0.80, P = 1.75 × 10−7) and a Thr343Ser missense in ELF1 (rs1056820_T; OR = 0.92, P = 1.71 × 10−7).Fig. 3: GWAS meta-analysis of barcode-CH in ISL and UKB.
a, HR and 95% CI from Cox regressions for subtypes of hematological dysfunction, stratified via CPLD-CH, barcode-CH and CPLDneg-CH. Diagnoses had been incorporated in the event that they arose 6 months or extra after blood sampling for CH resolution. Knowledge are meta-analysis of UKB and ISL (n = 162,963 contributors general, 14,837 with barcode-CH, 5,288 with CPLD-CH and 11,692 with CPLDneg-CH). b, HR and 95% CI for next hematological dysfunction stratified via CPLD genes. MM, a couple of myeloma; MGUS, monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined importance; OMF, osteomyelofibrosis.We investigated whether or not, amongst CPLD-CH contributors, dangers of hematological problems differed via the precise CPLD gene concerned (Fig. 2b). Vital HRs had been noticed for ASXL1-CH, DNMT3A-CH, JAK2-CH, SF3B1-CH, SRSF2-CH, TET2-CH and TP53-CH however now not for PPM1D-CH. The danger from JAK2-CH used to be more than from every other of the CPLD genes. Whilst contributors with DNMT3A-CH had been at relatively greater menace, HR estimates for different CPLD-CH varieties together with ASXL1-CH and TET2-CH had been considerably upper.CH GWAS meta-analysis in ISL and UKBWe performed a GWAS meta-analysis for barcode-CH (designated the ‘CH GWAS’) in 130,709 UKB and 45,510 ISL contributors, the use of germline genotypes imputed from WGS coaching sets17,18. We recognized 25 loci with affiliation alerts of P < 5 × 10−8 (Fig. 3 and Supplementary Desk 9). An extra ten low-frequency, high-effect variants require affirmation and weren’t thought to be additional. All the sentinel variants had low variant impact predictor (VEP) affects. At chr22q12, the sentinel variant used to be in excessive linkage disequilibrium (LD) (r2 = 0.95 in UKB and 1.0 in ISL) with the well known oncogenic ‘1100delC’ CHEK2 frameshift mutation rs555607708_delG (Thr367MetfsTer15)39. Conditional evaluation recognized secondary alerts at chr3q25 (a splice area variant in SMC4), chr5p15 (TERT) and chr21q11 (an Arg448Gly missense in NRIP1; Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 3 and Supplementary Desk 9). Scanning at a extra comfy stringency (P < 5 × 10−7) for variants with reasonable or excessive VEP results recognized a low-frequency protecting Arg684Gln variant in RTEL1 (rs35640778_A; odds ratio (OR) = 0.80, P = 1.75 × 10−7) and a Thr343Ser missense in ELF1 (rs1056820_T; OR = 0.92, P = 1.71 × 10−7).Fig. 3: GWAS meta-analysis of barcode-CH in ISL and UKB.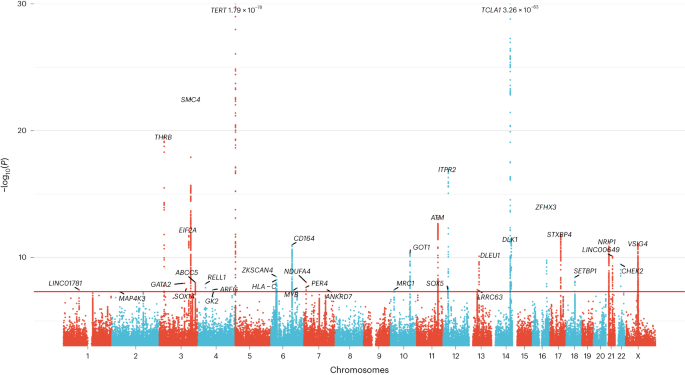 Long island plot appearing logistic regression GWAS effects (−log10(P) as opposed to chromosomal place) from 16,306 circumstances and 159,913 controls. The horizontal crimson line corresponds to a P worth of five × 10−8. Named loci have unconditional P values of <5 × 10−8. Loci are named via the closest gene or believable candidate. The TERT and TCL1A loci are offscale, and their P values are indicated at the plot. Detailed information for named loci are in Supplementary Desk 9. A number of high-effect, uncommon variants had been deemed to require additional affirmation and weren’t thought to be additional (indicated in Supplementary Desk 9).One CH GWAS variant, at TERT, used to be reported via us in the past in affiliation with barcode-CH in ISL1. We reproduced this affiliation; on the other hand, the sentinel TERT variant this time used to be rs7705526_A (OR = 1.28, P = 1.79 × 10−78), which is similar variant as due to this fact reported for CPLD-CH13. A number of different CH GWAS loci had been related to connected phenotypes, comparable to CPLD-CH13,14,15, mCA38,39, lack of Y chromosome (LoY)40,41,42 or MPN43,44. The LD between our CH GWAS variants and the ones alerts is detailed in Supplementary Desk 10. We discovered no earlier experiences for 19 of the CH GWAS loci.To realize additional perception into CH with out identified drivers, we repeated the GWAS the use of simplest CPLDneg-CH contributors as circumstances (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 4 and Supplementary Desk 11). Results had been widely very similar to the barcode-CH GWAS (m = 1.02, P = 1.47 × 10−18). Following two new loci had been detected: TERC and KDM6B. The protecting impact of chr14:TCL1A rs2887399_T used to be more potent in CPLDneg-CH, most likely because of the differing results of this allele in quite a lot of CPLD mutation backgrounds (see CPLD gene particular CH GWAS associations, underneath). CHEK2 and SMC4 variants had relatively higher results in barcode-CH.CPLD gene-specific CH GWAS associationsWe repeated the GWAS meta-analysis on CPLD-defined CH for driving force genes the place there used to be enough energy to take action. Taking into consideration all variants that had been considerably related to barcode-CH or any probably the most CPLD-CH varieties, we when put next their results on barcode-CH and quite a lot of sorts of CPLD-CH. There have been considerable variations in results between CPLD-CH varieties (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 5 and Supplementary Desk 12).Viewing the patterns general, maximum variants demonstrated no impact on ASXL1-CH. Whilst TET2-CH, as an example, confirmed a extremely important slope when regressed on barcode-CH (m = 0.94, P = 5.64 × 10−10), the slope for ASXL1-CH as opposed to barcode-CH used to be a lot shallower and of decrease importance (m = 0.41, P = 8.76 × 10−4). Additionally, PPM1D-CH produced no important regression towards barcode-CH. One imaginable rationalization is that environmental elements have a better affect on ASXL1-CH and PPM1D-CH than on different CPLD-CH varieties— menace of PPM1D-CH used to be considerably greater in sufferers who’ve gone through chemotherapy (OR = 7.9, P = 4.5 × 10−4; Supplementary Desk 13), whilst ASXL1-CH used to be extra strongly related to smoking than different CPLD-CH varieties (Supplementary Desk 14) in settlement with earlier reports9,45,46.CH GWAS variants impact blood characteristics, telomeres and MPNTo acquire perception into the capability and pleiotropic results of the CH GWAS variants, we tested revealed GWAS associations for them and variants in LD (Supplementary Desk 15). Despite the fact that contributors with grossly unusual hematology were excluded from the learn about, many scientific hematology parameters47 confirmed associations with the CH phenotype. Additionally, many CH GWAS loci had related scientific hematology characteristics within the GWAS Catalog or UKB information (Supplementary Tables 15 and 16 and Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 6).A number of CH GWAS variants had been reportedly related to leukocyte telomere size (LTL) within the GWAS Catalog. To analyze this intimately, we tested the connection between CH and LTL, the use of UKB samples that had been contemporaneously assessed for each CH (on this learn about) and LTL (in ref. 48). CH, along side age and prior or present smoking, used to be strongly related to shorter LTL (β = −0.129, P < 2 × 10−16; Supplementary Desk 17) as noticed in the past in ISL1. Additionally, maximum CH GWAS variants related to shorter telomeres, consistent with the CH:LTL phenotype affiliation. Alternatively, the 2 chr5:TERT variants and a variant on chr6p22 (close to the MHC) had been considerably related to longer telomeres (Fig. 4a and Supplementary Desk 18). Because of this discordance, no important regression parameters might be acquired and, in consequence, a Mendelian randomization (MR) evaluation used to be now not thought to be prudent. For a complementary exam of the results of LTL GWAS variants at the CH phenotype, we carried out a brand new GWAS for LTL within the UKB, the use of our present WGS-based imputation. We discovered 191 LTL variants (Supplementary Desk 19). Their results on LTL and CH are plotted in Fig. 4b. We discovered proof of a large discordance of results, with some longer LTL alleles related to greater CH menace and others related to diminished menace (indicated as ‘cloud 1’ and ‘cloud 2,’ respectively, in Fig. 4b). Right here once more, MR evaluation used to be now not thought to be really helpful.Fig. 4: Results CH GWAS variants and LTL GWAS variants on CH, LTL and MPN results.
Long island plot appearing logistic regression GWAS effects (−log10(P) as opposed to chromosomal place) from 16,306 circumstances and 159,913 controls. The horizontal crimson line corresponds to a P worth of five × 10−8. Named loci have unconditional P values of <5 × 10−8. Loci are named via the closest gene or believable candidate. The TERT and TCL1A loci are offscale, and their P values are indicated at the plot. Detailed information for named loci are in Supplementary Desk 9. A number of high-effect, uncommon variants had been deemed to require additional affirmation and weren’t thought to be additional (indicated in Supplementary Desk 9).One CH GWAS variant, at TERT, used to be reported via us in the past in affiliation with barcode-CH in ISL1. We reproduced this affiliation; on the other hand, the sentinel TERT variant this time used to be rs7705526_A (OR = 1.28, P = 1.79 × 10−78), which is similar variant as due to this fact reported for CPLD-CH13. A number of different CH GWAS loci had been related to connected phenotypes, comparable to CPLD-CH13,14,15, mCA38,39, lack of Y chromosome (LoY)40,41,42 or MPN43,44. The LD between our CH GWAS variants and the ones alerts is detailed in Supplementary Desk 10. We discovered no earlier experiences for 19 of the CH GWAS loci.To realize additional perception into CH with out identified drivers, we repeated the GWAS the use of simplest CPLDneg-CH contributors as circumstances (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 4 and Supplementary Desk 11). Results had been widely very similar to the barcode-CH GWAS (m = 1.02, P = 1.47 × 10−18). Following two new loci had been detected: TERC and KDM6B. The protecting impact of chr14:TCL1A rs2887399_T used to be more potent in CPLDneg-CH, most likely because of the differing results of this allele in quite a lot of CPLD mutation backgrounds (see CPLD gene particular CH GWAS associations, underneath). CHEK2 and SMC4 variants had relatively higher results in barcode-CH.CPLD gene-specific CH GWAS associationsWe repeated the GWAS meta-analysis on CPLD-defined CH for driving force genes the place there used to be enough energy to take action. Taking into consideration all variants that had been considerably related to barcode-CH or any probably the most CPLD-CH varieties, we when put next their results on barcode-CH and quite a lot of sorts of CPLD-CH. There have been considerable variations in results between CPLD-CH varieties (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 5 and Supplementary Desk 12).Viewing the patterns general, maximum variants demonstrated no impact on ASXL1-CH. Whilst TET2-CH, as an example, confirmed a extremely important slope when regressed on barcode-CH (m = 0.94, P = 5.64 × 10−10), the slope for ASXL1-CH as opposed to barcode-CH used to be a lot shallower and of decrease importance (m = 0.41, P = 8.76 × 10−4). Additionally, PPM1D-CH produced no important regression towards barcode-CH. One imaginable rationalization is that environmental elements have a better affect on ASXL1-CH and PPM1D-CH than on different CPLD-CH varieties— menace of PPM1D-CH used to be considerably greater in sufferers who’ve gone through chemotherapy (OR = 7.9, P = 4.5 × 10−4; Supplementary Desk 13), whilst ASXL1-CH used to be extra strongly related to smoking than different CPLD-CH varieties (Supplementary Desk 14) in settlement with earlier reports9,45,46.CH GWAS variants impact blood characteristics, telomeres and MPNTo acquire perception into the capability and pleiotropic results of the CH GWAS variants, we tested revealed GWAS associations for them and variants in LD (Supplementary Desk 15). Despite the fact that contributors with grossly unusual hematology were excluded from the learn about, many scientific hematology parameters47 confirmed associations with the CH phenotype. Additionally, many CH GWAS loci had related scientific hematology characteristics within the GWAS Catalog or UKB information (Supplementary Tables 15 and 16 and Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 6).A number of CH GWAS variants had been reportedly related to leukocyte telomere size (LTL) within the GWAS Catalog. To analyze this intimately, we tested the connection between CH and LTL, the use of UKB samples that had been contemporaneously assessed for each CH (on this learn about) and LTL (in ref. 48). CH, along side age and prior or present smoking, used to be strongly related to shorter LTL (β = −0.129, P < 2 × 10−16; Supplementary Desk 17) as noticed in the past in ISL1. Additionally, maximum CH GWAS variants related to shorter telomeres, consistent with the CH:LTL phenotype affiliation. Alternatively, the 2 chr5:TERT variants and a variant on chr6p22 (close to the MHC) had been considerably related to longer telomeres (Fig. 4a and Supplementary Desk 18). Because of this discordance, no important regression parameters might be acquired and, in consequence, a Mendelian randomization (MR) evaluation used to be now not thought to be prudent. For a complementary exam of the results of LTL GWAS variants at the CH phenotype, we carried out a brand new GWAS for LTL within the UKB, the use of our present WGS-based imputation. We discovered 191 LTL variants (Supplementary Desk 19). Their results on LTL and CH are plotted in Fig. 4b. We discovered proof of a large discordance of results, with some longer LTL alleles related to greater CH menace and others related to diminished menace (indicated as ‘cloud 1’ and ‘cloud 2,’ respectively, in Fig. 4b). Right here once more, MR evaluation used to be now not thought to be really helpful.Fig. 4: Results CH GWAS variants and LTL GWAS variants on CH, LTL and MPN results.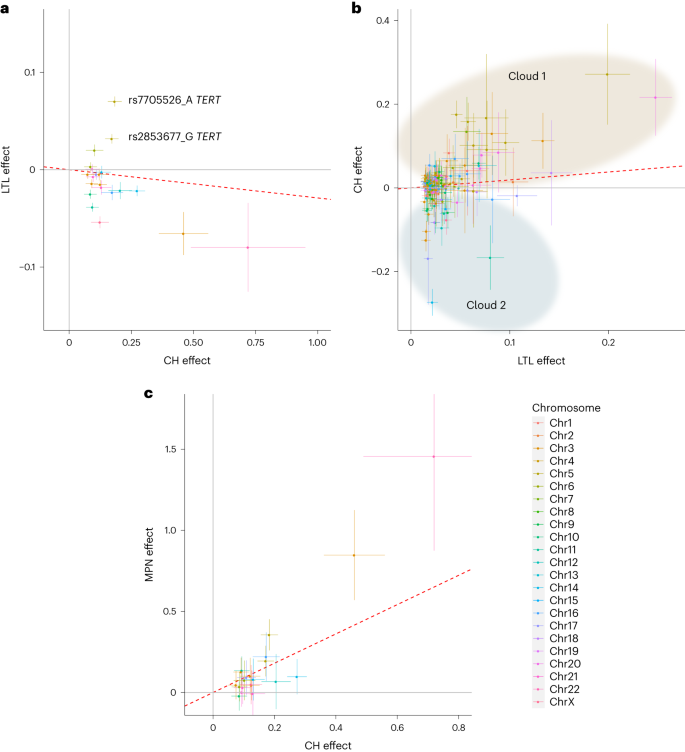 a, Results of CH GWAS variants on CH (x axis) and LTL (y axis) results. LTL information are from UKB (n = 418,251). The 2 discordant TERT variants discussed within the textual content are indicated. b, Results of LTL GWAS variants on LTL (x axis) and CH (y axis) results. Variants are grouped into ‘cloud 1’ (shaded brown) and ‘cloud 2’ (shaded blue) in keeping with their route of impact on CH (see textual content). c, Results of CH GWAS variants on CH (x axis) and MPN (y axis) results. MPN results had been acquired from meta-analysis of ISL and UKB information (ncase = 1,124 and ncontrol = 747,154). In all panels, simplest variants with MAF > 1% are plotted. The plotted issues are affiliation impact estimates from logistic/linear regression and the bars point out 95% CI. The crimson dotted strains point out the IVW regressions. The chromosomal location of each and every plotted variant is indicated via colour as indicated within the colour key, decrease proper.Seen LTL is measured in blood that can include CH expansions. So, any variant that promotes CH however does indirectly impact telomeres would seem to trigger shorter telomeres, as a result of the affiliation between CH and contemporaneously noticed quick telomeres. By means of the similar token, such CH-promoting variants could be recognized as LTL-associated variants in an LTL GWAS. To inspect this, we repeated the GWAS for LTL, the use of simplest contributors with out confirmed CH. There used to be no obvious distinction within the results of LTL GWAS variants between the 2 subgroups (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 7).As used to be proven in Fig. 2a, CH related strongly with next diagnoses of MPN consistent with its proposed standing as a scientific precursor to MPN49. Nearly all of CH GWAS variants additionally conferred menace of MPN (Fig. 4c and Supplementary Desk 18). MR evaluation used to be in keeping with CH having a causative impact on MPN (inverse-variance weighted (IVW), P = 7.86 × 10−6; Supplementary Desk 20).CH GWAS variants are eager about expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL), splicing quantitative trait loci (sQTL) and protein quantitative trait loci (pQTL)We thought to be whether or not the CH GWAS variants impact RNA abundance or splicing of within sight genes. For each and every sentinel variant, we recognized all variants in LD (r2 ≥ 0.8) after which queried public RNA-seq eQTL and sQTL databases, that specialize in blood or blood-related cellular varieties. Variants with considerable cis results had been investigated additional in ISL RNA-seq information from 17,848 peripheral blood samples (Supplementary Desk 21). eQTL at ABCC5 and TRIM59/SMC4 are described in Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 8, whilst different salient examples are mentioned underneath:CD164 is, biologically, a just right candidate for a task in CH pathogenesis. It’s expressed on early HSC and will impact their proliferation, differentiation, adhesion to bone marrow stromal components, migration and retention in HSC niches50,51,52. Public resources printed a CD164 sQTL in blood, lymphoblastoid B-cell strains (LCL) and a number of other nonhematological tissues. The highest reported sQTL in entire blood has r2 = 0.81 with our sentinel CH GWAS hit (rs3056655), whilst the highest sQTL in LCL has r2 = 0.86. The usage of ISL blood RNA-seq, we ascertained that the sQTL impacts the 2 primary isoforms of CD164, which fluctuate via the presence (CD164-202) or absence (CD164-203) of exon 5. The latter isoform lacks the full-length CD164 protein’s glycosaminoglycan attachment website online. Higher exon 5 skipping used to be strongly related to the rs3056655_A CH menace allele (P = 3.04 × 10−302, β = 0.44). Protection plots of ISL RNA-seq information from CD8+ T cells and monocytes printed a lower in general CD164 gene expression related to the CH menace allele rs3056655_A (Fig. 5).Fig. 5: CH GWAS variants are related to splicing and expression of CD164.
a, Results of CH GWAS variants on CH (x axis) and LTL (y axis) results. LTL information are from UKB (n = 418,251). The 2 discordant TERT variants discussed within the textual content are indicated. b, Results of LTL GWAS variants on LTL (x axis) and CH (y axis) results. Variants are grouped into ‘cloud 1’ (shaded brown) and ‘cloud 2’ (shaded blue) in keeping with their route of impact on CH (see textual content). c, Results of CH GWAS variants on CH (x axis) and MPN (y axis) results. MPN results had been acquired from meta-analysis of ISL and UKB information (ncase = 1,124 and ncontrol = 747,154). In all panels, simplest variants with MAF > 1% are plotted. The plotted issues are affiliation impact estimates from logistic/linear regression and the bars point out 95% CI. The crimson dotted strains point out the IVW regressions. The chromosomal location of each and every plotted variant is indicated via colour as indicated within the colour key, decrease proper.Seen LTL is measured in blood that can include CH expansions. So, any variant that promotes CH however does indirectly impact telomeres would seem to trigger shorter telomeres, as a result of the affiliation between CH and contemporaneously noticed quick telomeres. By means of the similar token, such CH-promoting variants could be recognized as LTL-associated variants in an LTL GWAS. To inspect this, we repeated the GWAS for LTL, the use of simplest contributors with out confirmed CH. There used to be no obvious distinction within the results of LTL GWAS variants between the 2 subgroups (Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 7).As used to be proven in Fig. 2a, CH related strongly with next diagnoses of MPN consistent with its proposed standing as a scientific precursor to MPN49. Nearly all of CH GWAS variants additionally conferred menace of MPN (Fig. 4c and Supplementary Desk 18). MR evaluation used to be in keeping with CH having a causative impact on MPN (inverse-variance weighted (IVW), P = 7.86 × 10−6; Supplementary Desk 20).CH GWAS variants are eager about expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL), splicing quantitative trait loci (sQTL) and protein quantitative trait loci (pQTL)We thought to be whether or not the CH GWAS variants impact RNA abundance or splicing of within sight genes. For each and every sentinel variant, we recognized all variants in LD (r2 ≥ 0.8) after which queried public RNA-seq eQTL and sQTL databases, that specialize in blood or blood-related cellular varieties. Variants with considerable cis results had been investigated additional in ISL RNA-seq information from 17,848 peripheral blood samples (Supplementary Desk 21). eQTL at ABCC5 and TRIM59/SMC4 are described in Prolonged Knowledge Fig. 8, whilst different salient examples are mentioned underneath:CD164 is, biologically, a just right candidate for a task in CH pathogenesis. It’s expressed on early HSC and will impact their proliferation, differentiation, adhesion to bone marrow stromal components, migration and retention in HSC niches50,51,52. Public resources printed a CD164 sQTL in blood, lymphoblastoid B-cell strains (LCL) and a number of other nonhematological tissues. The highest reported sQTL in entire blood has r2 = 0.81 with our sentinel CH GWAS hit (rs3056655), whilst the highest sQTL in LCL has r2 = 0.86. The usage of ISL blood RNA-seq, we ascertained that the sQTL impacts the 2 primary isoforms of CD164, which fluctuate via the presence (CD164-202) or absence (CD164-203) of exon 5. The latter isoform lacks the full-length CD164 protein’s glycosaminoglycan attachment website online. Higher exon 5 skipping used to be strongly related to the rs3056655_A CH menace allele (P = 3.04 × 10−302, β = 0.44). Protection plots of ISL RNA-seq information from CD8+ T cells and monocytes printed a lower in general CD164 gene expression related to the CH menace allele rs3056655_A (Fig. 5).Fig. 5: CH GWAS variants are related to splicing and expression of CD164.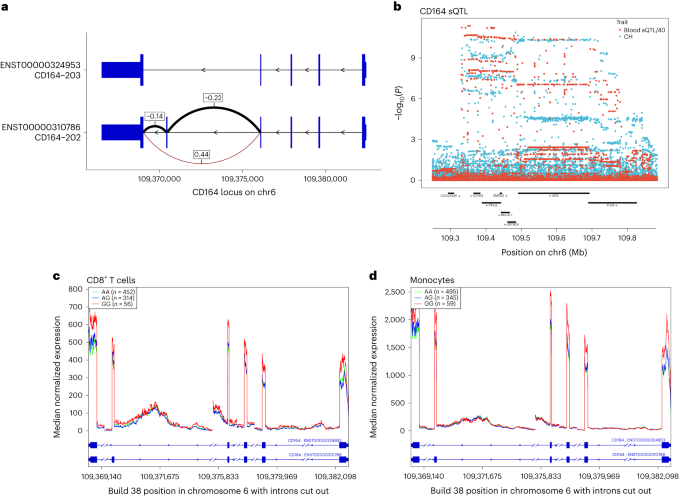 a, Splice diagram of the 2 primary CD164 mRNA isoforms from entire blood RNA-seq information. Blue bars depict exons and are wider in coding areas. Introns are depicted as black arrowed strains. The sQTL impacts skipping or inclusion of exon 5. Results (β in s.d. devices) from linear regression of the CH menace rs3056655_A allele are as follows: E4 to E6 (β = 0.44, P = 3.04 × 10−302; E4 to E5 (β = −0.22, P = 3.29 × 10−72); E5 to E6 (β = −0.14, P = 4.16 × 10−32). Thickness of the arcs signifies the whole utilization of the other splice junctions. Black arcs point out a discount in utilization in affiliation with rs3056655_A, whilst the brown arc signifies an build up. b, Colocalization plot of the CD164 locus appearing affiliation from logistic/linear regression of rs3056655 with CH (blue) and with the E4 to E6 splice occasion in entire blood (crimson, −log10(P) is split via 40 for scaling). c, RNA-seq protection plot of CD164 from 822 CD8+ cytotoxic T cellular samples, stratified via rs3056655 allele, appearing diminished ranges of expression in rs3056655_A (CH at-risk) heterozygotes and homozygotes. Be aware that rs3056655 is multi-allelic, however simplest the rs3056655_A (CH at-risk) and _G (CH protecting) alleles had been noticed within the RNA-seq samples. d, As c, however RNA-seq from 899 monocyte samples.We performed a proteomic evaluation of plasma samples from 12,636 UKB contributors for whom we had CH standing data, the use of the Olink platform to interrogate ranges of one,472 proteins and check them for affiliation with CH. A number of proteins of related organic pastime ranked extremely (via importance), together with the hematopoietic progenitor cellular expansion elements FLT3LG and CLEC11A, thrombopoietin THPO, pro-inflammatory cytokines CCL5 and TNFSF12 and smoking marker ALPP (Supplementary Desk 22). 2nd within the score used to be TCL1A, an oncoprotein in T cellular leukemias, lymphomas, CLL and a number of other nonhematological cancers53. Upper TCL1A ranges had been related to CH (P = 2.05 × 10−13, β = 0.21), and this replicated ISL SomaScan proteomic information (P = 2.86 × 10−3, β = 0.06) (ref. 54). TCL1A is of explicit pastime as a result of a CH GWAS variant is positioned 162 bp upstream of the gene’s transcription get started website online (Fig. 6a). The minor allele, rs2887399_T (minor allele frequency (MAF) ∼20%), is protecting towards CH in our information. It’s been implicated (with various route of impact) in CPLD-CH, mCA and LoY (see above and refs. 13,41,55). The rs2887399_T allele is reported to suppress ectopic expression of TCL1A in CPLD mutant HSC56. A seek for cis-pQTL the use of UKB Olink and ISL SomaScan recognized two conditionally impartial LD categories of variant, each with minor alleles appearing to scale back TCL1A expression. One LD magnificence of pQTL used to be correlated with rs2887399_T (r2 ∼0.67), while a 2nd LD magnificence pQTL, typified via rs78986913_A used to be now not (r2 ∼0.092, MAF ∼4%; Fig. 6b,c). Interestingly, rs78986913_A didn’t display an impartial sign in GWAS for CH predisposition in conditional evaluation (Padj = 0.78).Fig. 6: CH menace variants, pQTL and eQTL on the TCL1A locus.
a, Splice diagram of the 2 primary CD164 mRNA isoforms from entire blood RNA-seq information. Blue bars depict exons and are wider in coding areas. Introns are depicted as black arrowed strains. The sQTL impacts skipping or inclusion of exon 5. Results (β in s.d. devices) from linear regression of the CH menace rs3056655_A allele are as follows: E4 to E6 (β = 0.44, P = 3.04 × 10−302; E4 to E5 (β = −0.22, P = 3.29 × 10−72); E5 to E6 (β = −0.14, P = 4.16 × 10−32). Thickness of the arcs signifies the whole utilization of the other splice junctions. Black arcs point out a discount in utilization in affiliation with rs3056655_A, whilst the brown arc signifies an build up. b, Colocalization plot of the CD164 locus appearing affiliation from logistic/linear regression of rs3056655 with CH (blue) and with the E4 to E6 splice occasion in entire blood (crimson, −log10(P) is split via 40 for scaling). c, RNA-seq protection plot of CD164 from 822 CD8+ cytotoxic T cellular samples, stratified via rs3056655 allele, appearing diminished ranges of expression in rs3056655_A (CH at-risk) heterozygotes and homozygotes. Be aware that rs3056655 is multi-allelic, however simplest the rs3056655_A (CH at-risk) and _G (CH protecting) alleles had been noticed within the RNA-seq samples. d, As c, however RNA-seq from 899 monocyte samples.We performed a proteomic evaluation of plasma samples from 12,636 UKB contributors for whom we had CH standing data, the use of the Olink platform to interrogate ranges of one,472 proteins and check them for affiliation with CH. A number of proteins of related organic pastime ranked extremely (via importance), together with the hematopoietic progenitor cellular expansion elements FLT3LG and CLEC11A, thrombopoietin THPO, pro-inflammatory cytokines CCL5 and TNFSF12 and smoking marker ALPP (Supplementary Desk 22). 2nd within the score used to be TCL1A, an oncoprotein in T cellular leukemias, lymphomas, CLL and a number of other nonhematological cancers53. Upper TCL1A ranges had been related to CH (P = 2.05 × 10−13, β = 0.21), and this replicated ISL SomaScan proteomic information (P = 2.86 × 10−3, β = 0.06) (ref. 54). TCL1A is of explicit pastime as a result of a CH GWAS variant is positioned 162 bp upstream of the gene’s transcription get started website online (Fig. 6a). The minor allele, rs2887399_T (minor allele frequency (MAF) ∼20%), is protecting towards CH in our information. It’s been implicated (with various route of impact) in CPLD-CH, mCA and LoY (see above and refs. 13,41,55). The rs2887399_T allele is reported to suppress ectopic expression of TCL1A in CPLD mutant HSC56. A seek for cis-pQTL the use of UKB Olink and ISL SomaScan recognized two conditionally impartial LD categories of variant, each with minor alleles appearing to scale back TCL1A expression. One LD magnificence of pQTL used to be correlated with rs2887399_T (r2 ∼0.67), while a 2nd LD magnificence pQTL, typified via rs78986913_A used to be now not (r2 ∼0.092, MAF ∼4%; Fig. 6b,c). Interestingly, rs78986913_A didn’t display an impartial sign in GWAS for CH predisposition in conditional evaluation (Padj = 0.78).Fig. 6: CH menace variants, pQTL and eQTL on the TCL1A locus.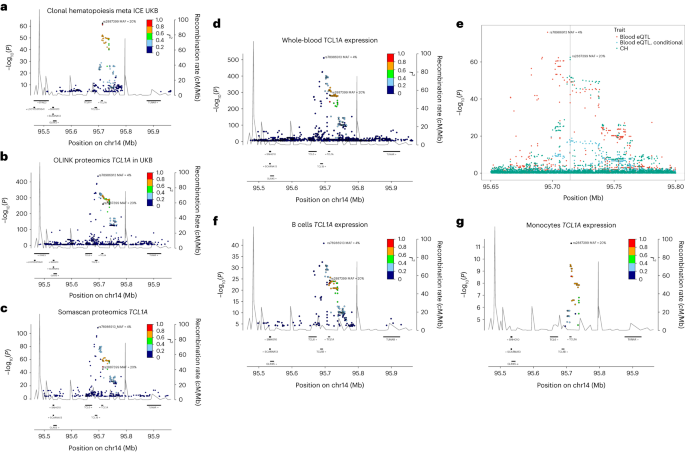 a, Locus zoom of CH GWAS effects at TCL1A. b, Cis-pQTL evaluation of variants affecting plasma protein ranges of TCL1A in 47,133 UKB contributors. c, As b, however from 35,559 ISL contributors. d, RNA-seq cis-eQTL evaluation of TCL1A in entire blood. e, Colocalization evaluation of CH GWAS and blood eQTL alerts on the TCL1A locus. The CH GWAS (inexperienced) and unadjusted eQTL alerts (crimson) don’t coincide. Alternatively, when the eQTL sign is adjusted for the 4% MAF rs78986913 variant (Padj values proven in blue), then the peaks overlap with a PP.H4 = 85% likelihood that they correspond to the similar sign. The location of the CH GWAS sentinel variant rs2887399 is indicated via the grey vertical line. f, TCL1A eQTL from 758 B cellular RNA samples. g, TCL1A eQTL from 884 monocyte samples. In all panels with the exception of e, the r2 focal point is on rs2887399.To analyze this additional, we looked for RNA-seq cis-eQTL for TCL1A. In entire blood, each the 4% MAF rs78986913_A and the 20% MAF rs2887399_T variant categories diminished expression of TCL1A. Conditioning the eQTL sign on rs78986913, COLOC57 printed an 85% likelihood of top identification between the rs2887399 eQTL and the CH GWAS top. Each the 4% MAF and 20% MAF variants categories affected expression in B cells. Alternatively, in monocytes simplest the 20% MAF rs2887399_T variant used to be related to TCL1A RNA expression and a 4% MAF rs78986913_A top used to be now not in proof (Fig. 6d–g). It seems that that, on this case, the eQTL and pQTL of relevance to CH could also be limited to the myeloid lineage.
a, Locus zoom of CH GWAS effects at TCL1A. b, Cis-pQTL evaluation of variants affecting plasma protein ranges of TCL1A in 47,133 UKB contributors. c, As b, however from 35,559 ISL contributors. d, RNA-seq cis-eQTL evaluation of TCL1A in entire blood. e, Colocalization evaluation of CH GWAS and blood eQTL alerts on the TCL1A locus. The CH GWAS (inexperienced) and unadjusted eQTL alerts (crimson) don’t coincide. Alternatively, when the eQTL sign is adjusted for the 4% MAF rs78986913 variant (Padj values proven in blue), then the peaks overlap with a PP.H4 = 85% likelihood that they correspond to the similar sign. The location of the CH GWAS sentinel variant rs2887399 is indicated via the grey vertical line. f, TCL1A eQTL from 758 B cellular RNA samples. g, TCL1A eQTL from 884 monocyte samples. In all panels with the exception of e, the r2 focal point is on rs2887399.To analyze this additional, we looked for RNA-seq cis-eQTL for TCL1A. In entire blood, each the 4% MAF rs78986913_A and the 20% MAF rs2887399_T variant categories diminished expression of TCL1A. Conditioning the eQTL sign on rs78986913, COLOC57 printed an 85% likelihood of top identification between the rs2887399 eQTL and the CH GWAS top. Each the 4% MAF and 20% MAF variants categories affected expression in B cells. Alternatively, in monocytes simplest the 20% MAF rs2887399_T variant used to be related to TCL1A RNA expression and a 4% MAF rs78986913_A top used to be now not in proof (Fig. 6d–g). It seems that that, on this case, the eQTL and pQTL of relevance to CH could also be limited to the myeloid lineage.
Genetics and epidemiology of mutational barcode-defined clonal hematopoiesis – Nature Genetics