Dec 02, 2023
(Nanowerk Information) It first seemed as a sparkling blob from ground-based telescopes after which vanished utterly in pictures from the Hubble House Telescope. Now, the ghostly object has reappeared as a faint, but distinct galaxy in a picture from the James Webb House Telescope (JWST).
Astronomers with the COSMOS-Internet collaboration have known the article AzTECC71 as a dusty star-forming galaxy. Or, in different phrases, a galaxy that’s busy forming many new stars however is shrouded in a dusty veil that’s laborious to look via — from just about 1 billion years after the Large Bang. Those galaxies had been as soon as considered extraordinarily uncommon within the early universe, however this discovery, plus greater than a dozen further applicants within the first part of COSMOS-Internet knowledge that experience but to be described within the clinical literature, suggests they could be 3 to ten occasions as commonplace as anticipated.
“This factor is an actual monster,” mentioned Jed McKinney, a postdoctoral researcher at The College of Texas at Austin. “Even if it looks as if slightly blob, it’s in reality forming masses of recent stars annually. And the truth that even one thing that excessive is just visual in essentially the most touchy imaging from our latest telescope is so thrilling to me. It’s probably telling us there’s a complete inhabitants of galaxies which have been hiding from us.”
If that conclusion is showed, it suggests the early universe was once a lot dustier than prior to now idea.
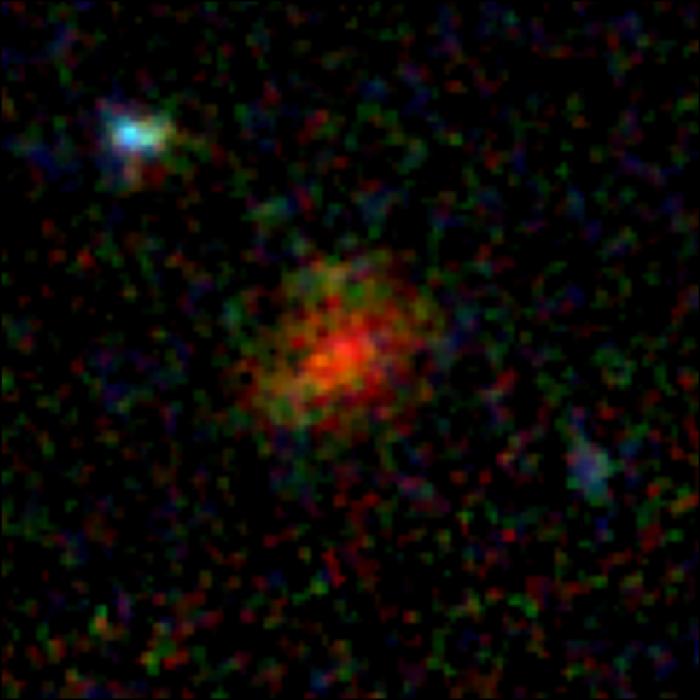

Colour composite of galaxy AzTECC71 from a couple of colour filters within the NIRCam device at the James Webb House Telescope. Credit score: J. McKinney/M. Franco/C. Casey/College of Texas at Austin. (Symbol: J. McKinney/M. Franco/C. Casey/College of Texas at Austin)
The workforce printed its findings in The Astrophysical Magazine (“A Close to-infrared-faint, A ways-infrared-luminous Dusty Galaxy at z ∼ 5 in COSMOS-Internet”).
The COSMOS-Internet mission — the most important preliminary JWST analysis initiative, co-led by way of Caitlin Casey, an affiliate professor at UT Austin — objectives to map as much as 1 million galaxies from part of the sky the dimensions of 3 complete moons. The function partly is to check the earliest buildings of the universe. The workforce of greater than 50 researchers was once awarded 250 hours of staring at time in JWST’s first yr and gained a primary batch of information in December 2022, with extra coming in via January 2024.
A dusty star-forming galaxy is difficult to look in optical gentle as a result of a lot of the sunshine from its stars is absorbed by way of a veil of filth after which re-emitted at redder (or longer) wavelengths. Earlier than JWST, astronomers occasionally referred to them as “Hubble-dark galaxies,” in connection with the prior to now most-sensitive area telescope.
“Till now, the one means we’ve been ready to look galaxies within the early universe is from an optical standpoint with Hubble,” McKinney mentioned. “That implies our working out of the historical past of galaxy evolution is biased as a result of we’re most effective seeing the unobscured, much less dusty galaxies.”
This galaxy, AzTECC71, was once first detected as an vague blob of filth emission by way of a digital camera at the James Clerk Maxwell Telescope in Hawaii that sees in wavelengths between a ways infrared and microwave. The COSMOS-Internet workforce subsequent noticed the article in knowledge accrued by way of some other workforce the use of the ALMA telescope in Chile, which has upper spatial solution and will see in infrared. That allowed them to slender down the positioning of the supply. Once they appeared within the JWST knowledge within the infrared at a wavelength of four.44 microns, they discovered a faint galaxy in precisely the similar position. In shorter wavelengths of sunshine, underneath 2.7 microns, it was once invisible.
Now, the workforce is operating to discover extra of those JWST-faint galaxies.
“With JWST, we will be able to learn about for the primary time the optical and infrared homes of this closely dust-obscured, hidden inhabitants of galaxies,” McKinney mentioned, “as it’s so touchy that now not most effective can it stare again into the farthest reaches of the universe, however it might additionally pierce the thickest of dusty veils.”
The workforce estimates that the galaxy is being considered at a redshift of about 6, which interprets to about 900 million years after the Large Bang.