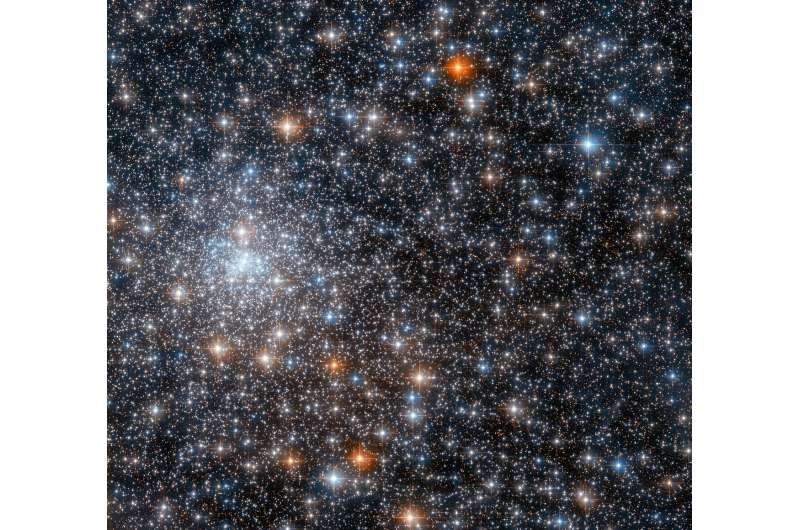
The globular cluster NGC 6558 imaged by means of the Hubble Area Telescope. Credit score: ESA/Hubble & NASA, R. Cohen.
The usage of the Gemini Observatory and the Hubble Area Telescope (HST), a global workforce of astronomers has investigated a Galactic globular cluster referred to as NGC 6558. Result of the brand new learn about, revealed July 22 at the pre-print server arXiv, ship necessary insights into the houses of this cluster.
Globular clusters (GCs) are collections of tightly certain stars orbiting galaxies. Astronomers understand them as herbal laboratories enabling research at the evolution of stars and galaxies. Particularly, globular clusters may lend a hand researchers to raised perceive the formation historical past and evolution of early-type galaxies, because the starting place of GCs appears to be intently related to sessions of intense superstar formation.
NGC 6558 (often referred to as GCL 89 or ESO 456-SC62) is a Galactic bulge globular cluster situated some 24,100 gentle years away within the constellation Sagittarius, with an angular dimension of about 5.4 x 5.4 arcminutes. Earlier observations have discovered that NGC 6558 has a metallicity at a degree of -1.32 dex and advised that it can be one of the most oldest gadgets within the Milky Approach.
Then again, because of top reddening, the area of NGC 6558 gifts demanding situations in deriving correct parameters. A gaggle of astronomers led by means of Stefano Souza of the College of São Paulo in Brazil, has now carried out near-infrared and optical photometry of this cluster. For this goal, they hired Gemini Observatory’s Gemini-South telescope and HST’s Complex Digital camera for Surveys (ACS).
“We purpose to refine the elemental parameters of NGC 6558, using top quality Gemini-South/GSAOI and HST/ACS photometries. Moreover, we intend to analyze its function within the formation of the Galactic bulge,” the researchers provide an explanation for.
The accrued top quality photometric knowledge allowed the workforce to derive elementary parameters of NGC 6558. Through taking away up to imaginable of the Galactic bulge box superstar contamination, the astronomers have been in a position to acquire probably the most correct effects than ever sooner than.
The observations discovered that NGC 6558 is situated about 27,400 gentle years away. That is farther than distances received by means of earlier research, which advised between 20,500 and 26,900 gentle years.
The reddening of NGC 6558 used to be measured to be at a degree of 0.34. The astronomers underline that that is the bottom worth relative to the to be had literature, received with the differential reddening correction according to reference stars much less infected by means of box stars.
In line with the received knowledge, the authors of the paper estimate that NGC 6558 is a few 13 billion years previous. They observe that this age is appropriate with different clusters with an identical metallicity and a blue horizontal department within the Galactic bulge.
Summing up the consequences, the researchers conclude that NGC 6558, mixed with different quite metal-poor GCs, recommend that the formation time of this inhabitants is as past due as 13.62 billion years and with a chemical enrichment 10-times quicker than the remainder of the Milky Approach.
Additional information:
S. O. Souza et al, Mixed Gemini-South and HST photometric research of the globular cluster NGC 6558. The age of the metal-poor inhabitants of the Galactic Bulge, arXiv (2024). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2407.15918
Magazine knowledge:
arXiv
© 2024 Science X Community
Quotation:
Globular cluster NGC 6558 explored with Gemini Observatory and Hubble Area Telescope (2024, July 29)
retrieved 30 July 2024
from
This file is matter to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal learn about or analysis, no
phase could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is equipped for info functions most effective.