Loads of tens of millions of years in the past, Earth plunged right into a deep-freeze that became the planet into an enormous ball of ice. Now, scientists have found out rocks marking this second on a far flung archipelago within the Inside Hebrides of Scotland.The rocks, courting to between 720 million and 662 million years in the past, supply an extraordinary whole report of the transition between a heat tropical setting and a “snowball Earth,” the place glaciers encased the globe.If showed, the Garvellachs rocks might be declared a “golden spike” — a marker appearing a transition to a brand new geological age. In particular, those rocks would display the purpose when Earth moved from the Tonian length (1 billion to 720 million years in the past) to the Cryogenian length (720 million to 635 million years in the past).”Maximum spaces of the sector are lacking this exceptional transition for the reason that historical glaciers scraped and eroded away the rocks beneath, however in Scotland by means of some miracle the transition can also be noticed,” find out about first writer Elias Rugen, a researcher at College School London’s Earth Sciences division, mentioned in a observation.Scientists imagine there have been two snowball Earth occasions right through the Cryogenian — the Sturtian glaciation and the Marinoan glaciation. The previous tournament used to be previous and extra serious, lasting for round 57 million years, whilst the latter, extra poorly constrained tournament, lasted between 15 and 20 million years.In a brand new find out about, printed Thursday (Aug. 15) within the Magazine of the Geological Society of London, researchers analyzed layers of rock 0.7 miles (1.1 kilometers) thick, at the side of any other 230-foot-thick (70 meters) layer sitting underneath.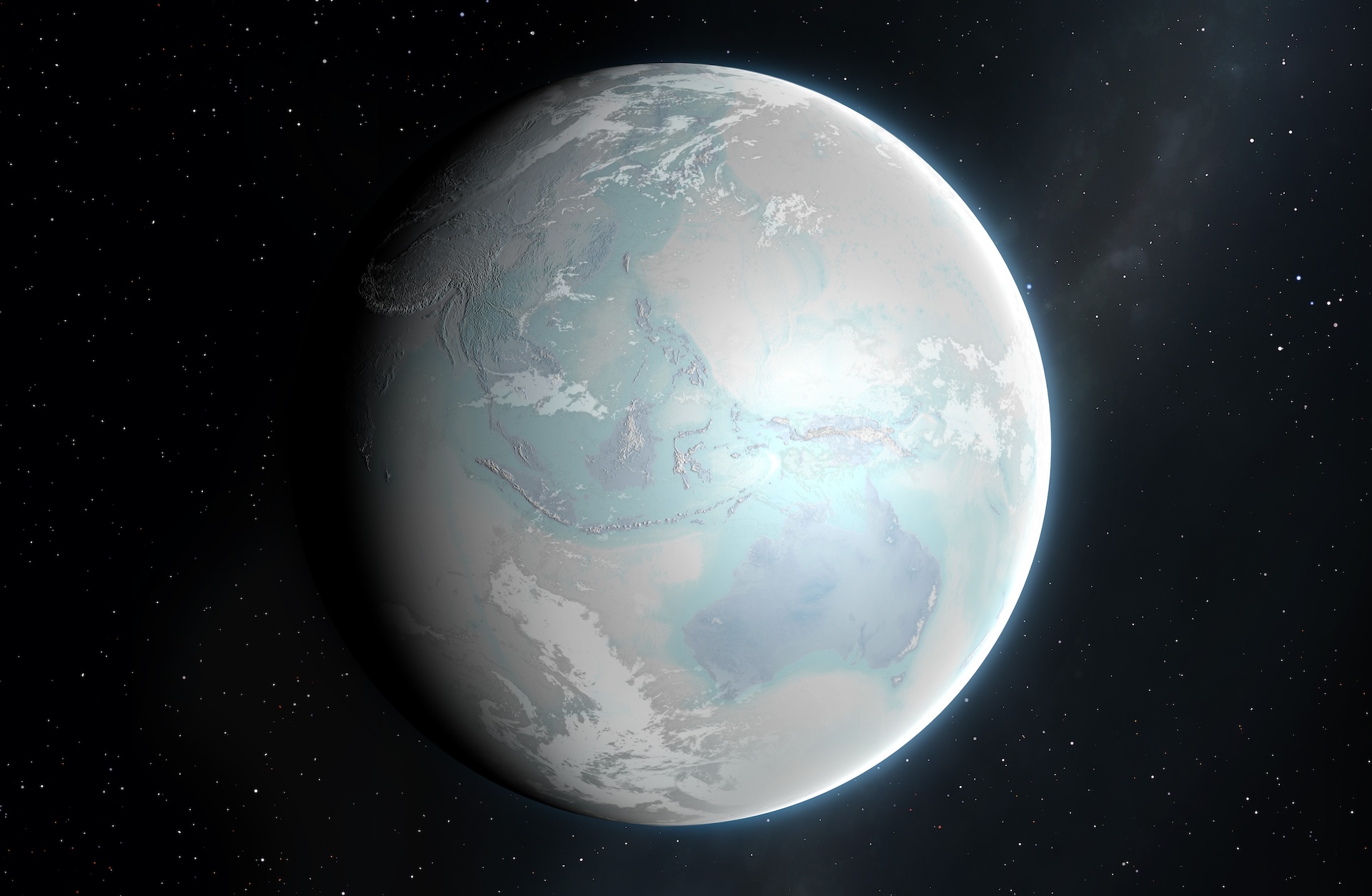 A demonstration of a “snowball earth”. (Symbol credit score: MARK GARLICK/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY Getty Photographs)The researchers amassed rock samples from two formations at the Garvellachs and analyzed tiny crystals known as zircons. Zircons comprise uranium, a radioactive part that slowly and ceaselessly decays into lead, so the staff used to be ready to resolve precisely when the rocks have been shaped. The researchers discovered that the decrease phase of rock shaped in tropical waters, when Earth used to be a lot hotter.Get the sector’s most attractive discoveries delivered instantly on your inbox.”Those layers report a tropical marine setting with flourishing cyanobacterial lifestyles that step by step changed into cooler, marking the top of one billion years or so of a temperate local weather on Earth,” Rugen mentioned.The zircon courting confirmed the rocks have been deposited between 720 million and 662 million years in the past — a length that encompassed the transition between the geological classes, from the temperate Tonian and into the Sturtian glaciation and Cryogenian length.In July, representatives from the Global Fee on Stratigraphy, which is a part of the Global Union of Geological Sciences, went to the Garvellachs to evaluate whether or not the web page is a geological marker. Whether it is ratified, the web page will probably be marked with a golden spike.”The layers of rock uncovered at the Garvellachs are globally distinctive,” Rugen mentioned.
A demonstration of a “snowball earth”. (Symbol credit score: MARK GARLICK/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY Getty Photographs)The researchers amassed rock samples from two formations at the Garvellachs and analyzed tiny crystals known as zircons. Zircons comprise uranium, a radioactive part that slowly and ceaselessly decays into lead, so the staff used to be ready to resolve precisely when the rocks have been shaped. The researchers discovered that the decrease phase of rock shaped in tropical waters, when Earth used to be a lot hotter.Get the sector’s most attractive discoveries delivered instantly on your inbox.”Those layers report a tropical marine setting with flourishing cyanobacterial lifestyles that step by step changed into cooler, marking the top of one billion years or so of a temperate local weather on Earth,” Rugen mentioned.The zircon courting confirmed the rocks have been deposited between 720 million and 662 million years in the past — a length that encompassed the transition between the geological classes, from the temperate Tonian and into the Sturtian glaciation and Cryogenian length.In July, representatives from the Global Fee on Stratigraphy, which is a part of the Global Union of Geological Sciences, went to the Garvellachs to evaluate whether or not the web page is a geological marker. Whether it is ratified, the web page will probably be marked with a golden spike.”The layers of rock uncovered at the Garvellachs are globally distinctive,” Rugen mentioned.