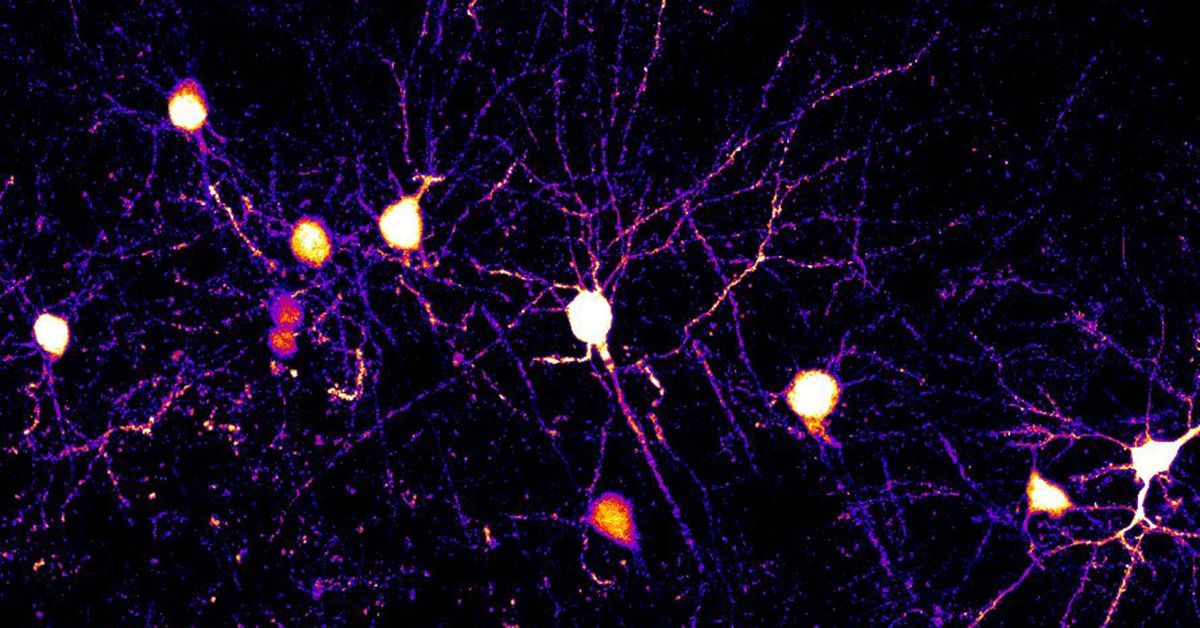
Studying is one thing everybody does day-to-day—mastering new abilities at paintings, remembering track lyrics, or following instructions to new puts. However at the back of those on a regular basis duties lies a fancy organic procedure referred to as synaptic plasticity, a phenomenon crucial in your mind’s talent to conform and retailer new knowledge. Just lately, neuroscientists have found out sudden new information about how your mind makes a decision which synapses—the tiny connections between nerve cells—get more potent or weaker as you be told. Those insights problem previous concepts, revealing that your mind applies more than one regulations concurrently to reshape its connections throughout finding out.The Thriller of Synaptic PlasticityYour mind is composed of billions of nerve cells, or neurons, interconnected through synapses. Whilst you be told, particular synapses develop more potent, whilst others change into weaker, adapting your mind’s circuitry to new duties or knowledge. As mice realized a brand new conduct, researchers intently tracked synaptic connections (depicted right here as small protrusions) at the dendrites of neurons. (CREDIT: UCSD) Till lately, scientists concept that neurons used uniform regulations for synaptic adjustments. But, exactly how every neuron selects the synapses for strengthening or weakening remained a systematic puzzle—referred to as the “credit score task downside.” Working out this puzzle is a very powerful as it determines how your mind information and remembers realized knowledge.William “Jake” Wright, Nathan Hedrick, and Takaki Komiyama, neurobiologists on the College of California San Diego, tackled this puzzle head-on. The usage of complicated mind imaging strategies, their groundbreaking analysis published that neurons do not practice a unmarried rule when finding out. As a substitute, neurons use more than one other regulations concurrently. Their findings, printed within the magazine Science, have profound implications for neuroscience, drugs, or even synthetic intelligence.A Nearer Glance into the Mind’s Studying RulesTo discover those new insights, the researchers seen how synapses behaved throughout motor finding out duties in mice. The usage of two-photon imaging—an impressive manner permitting scientists to visualise mind process in real-time—they tracked person synapses inside layer 2/3 pyramidal neurons within the motor cortex. Those neurons have complicated buildings, branching into apical dendrites (extending upward) and basal dendrites (extending sideways or downward). Unusually, every dendrite kind adopted other regulations for synaptic strengthening throughout finding out.In particular, the staff discovered that synapses on apical dendrites turned into more potent when activated along neighboring synapses. Those synapses reply jointly to native process patterns, strengthening connections in keeping with what is going down within reach. However, basal dendrite synapses reinforced when their process coincided with motion potentials—transient electric alerts touring down neurons. In brief, the apical synapses replied to community process, whilst basal synapses trusted exact timing with neuron alerts.“We in most cases bring to mind synaptic plasticity as uniform during the mind,” defined Wright, lead writer of the learn about. “However now we see obviously that neurons use distinct regulations for synaptic plasticity in numerous portions in their dendritic branches.”Instance pictures throughout 2 days of apical dendrites from keep watch over and Kir2.1 mice. Blue and purple arrows denote spines present process sLTP and sLTD, respectively. (CREDIT: Science) This discovery got here abruptly, prompting scientists to rethink earlier assumptions. Till now, analysis most commonly indicated that synapses throughout neurons adopted a unmarried, uniform rule—usually known as Hebbian plasticity—the place connections reinforce if either side of a synapse turn on concurrently. Whilst Hebbian plasticity explains many finding out processes, scientists have lengthy suspected further, extra nuanced mechanisms exist. This learn about showed the ones suspicions, revealing how neurons concurrently observe more than one plasticity regulations in a compartment-specific means.Implications Past NeuroscienceThe implications of those findings achieve a long way past fundamental mind science. The invention essentially adjustments how researchers perceive the “credit score task downside.” Every synapse operates like a person employee in an infinite manufacturing facility, contributing with out seeing the larger image. But, neurons arrange to coordinate 1000’s of those employees concurrently, the use of other regulations relying on location inside the neuron. This complicated device may provide an explanation for the mind’s exceptional flexibility in finding out quite a lot of duties concurrently.In keeping with senior writer Komiyama, those findings considerably advance the figuring out of mind serve as. “This discovery essentially adjustments the way in which we know how the mind solves the credit score task downside,” stated Komiyama. “Particular person neurons carry out distinct computations in parallel, the use of other regulations inside other mobile compartments.”Past biology, this analysis provides a very powerful insights for synthetic intelligence. Present AI programs use neural networks impressed through mind construction however in most cases observe uniform regulations throughout their whole community. Working out how your mind employs more than one regulations concurrently may encourage new, extra tough AI designs. Scientists envision developing neural networks with larger flexibility and finding out potency through mimicking the mind’s process of compartment-specific plasticity.Instance lines appearing backbone process coinciding with dendritic process for spines present process other kinds of plasticity in apical dendrites. Backbone-dendrite coincident process is marked through grey bars with asterisks. (CREDIT: Science) Hope for Well being and Illness TreatmentThe researchers emphasize the prospective well being affects of figuring out synaptic plasticity higher. Many neurological and mental problems, akin to Alzheimer’s illness, habit, autism, and PTSD, contain dysfunctions in synaptic communique. Realizing how wholesome brains selectively reinforce or weaken synapses would possibly lead scientists towards focused remedies for those stipulations.“Our analysis supplies a clearer figuring out of the way synapses are changed throughout finding out,” Wright defined. “This can have vital well being implications since many illnesses contain synaptic disorder.”Scientists hope this foundational wisdom will help in figuring out exactly what is going on flawed on the synaptic degree throughout problems like autism or Alzheimer’s. It will result in treatments that right kind particular synaptic imbalances, providing advanced remedies for other folks dwelling with those difficult stipulations.(Best) Instance pictures of the similar dendrite throughout 2 days. Inexperienced and purple arrows point out spines present process sLTP and sLTD, respectively. (Backside) Instance spines present process sLTP (left) and sLTD (proper) from the dendrite proven above marked with an asterisk. (CREDIT: Science) What is Subsequent for Neuroscientists?Following this discovery, the analysis staff plans to discover additional how neurons can concurrently observe more than one regulations. Long run research will delve deeper into the biochemical and molecular processes at the back of compartment-specific plasticity. Researchers additionally intention to spot why the use of more than one regulations supplies a bonus in finding out new knowledge or behaviors.In the long run, their objective is to liberate extra profound wisdom about mind capability, supporting developments in drugs, schooling, and era. By way of figuring out how neurons arrange complicated computations without difficulty, scientists can open doorways to thrilling new chances in treating mind illnesses, creating subtle synthetic intelligence, and embellishing total figuring out of human conduct.“Our findings have supplied a basis for exploring how the mind most often works,” Wright concluded. “Now, we need to perceive precisely how neurons have the benefit of the use of other regulations concurrently.”
Groundbreaking learn about solves the thriller of the way our mind learns