Abstract: A brand new find out about exposed a up to now unknown mechanism in hair follicles that permits us to discover contact.Prior to now, sensation was once attributed most effective to nerve endings within the pores and skin, however this find out about unearths that cells inside hair follicles too can sense contact. Those cells liberate neurotransmitters, histamine and serotonin, according to contact.This discovery may result in a deeper figuring out of inflammatory pores and skin prerequisites like eczema.Key Details:Hair follicle cells, now not simply nerve endings within the pores and skin, can discover contact.When stimulated via contact, hair follicle cells liberate the neurotransmitters histamine and serotonin.This new figuring out may reshape how we view the function of histamine in inflammatory pores and skin illnesses corresponding to eczema.Supply: Imperial School LondonImperial researchers have came upon a hidden mechanism inside hair follicles that let us to really feel contact.Prior to now, contact was once regarded as detected most effective via nerve endings provide throughout the pores and skin and surrounding hair follicles. This new analysis from Imperial School London has discovered that that cells inside hair follicles – the constructions that encompass the hair fibre – also are in a position to discover the feeling in cellular cultures.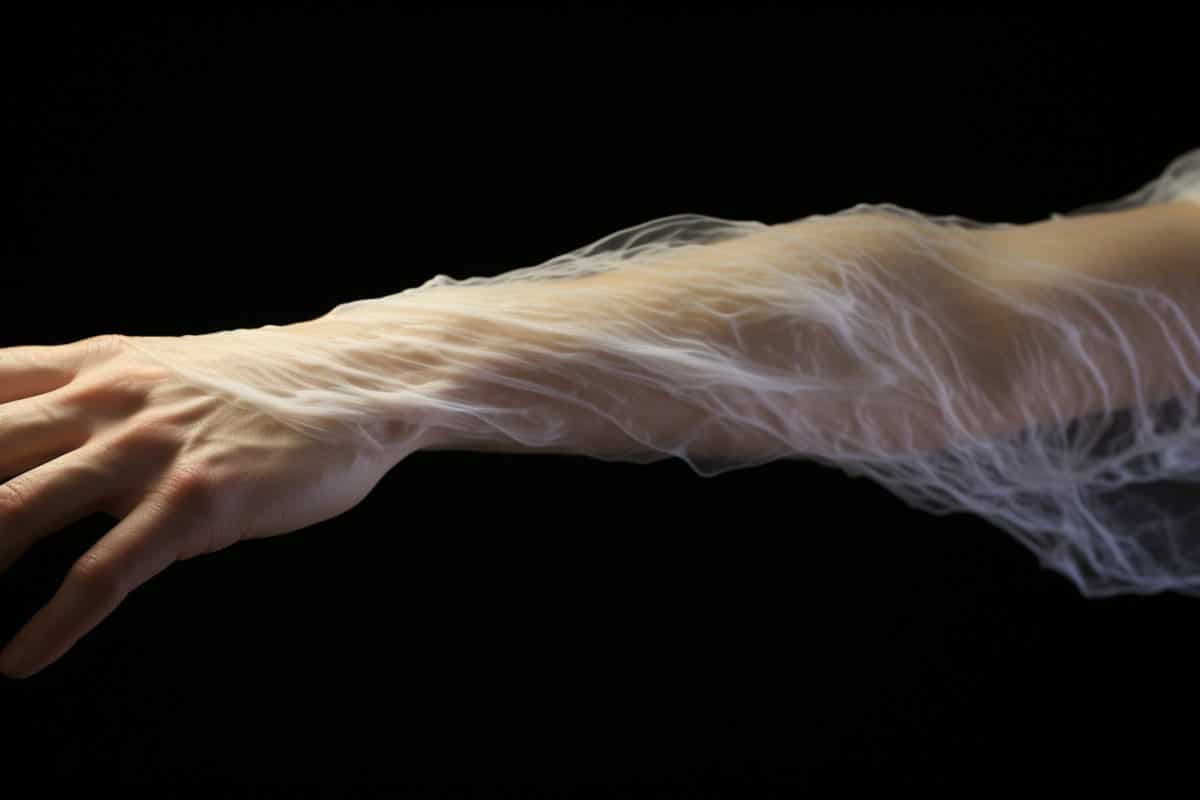  The cells answered to gentle contact via freeing histamine, however they didn’t liberate serotonin. Credit score: Neuroscience NewsThe researchers additionally discovered that those hair follicle cells liberate the neurotransmitters histamine and serotonin according to contact – findings that may assist us in long run to grasp histamine’s function in inflammatory pores and skin illnesses like eczema.Lead writer of the paper Dr Claire Higgins, from Imperial’s Division of Bioengineering, stated: “This can be a sudden discovering as we don’t but know why hair follicle cells have this function in processing gentle contact. Because the follicle accommodates many sensory nerve endings, we now wish to resolve if the hair follicle is activating particular kinds of sensory nerves for an unknown however distinctive mechanism.”A sensitive subjectWe really feel contact the use of a number of mechanisms: sensory nerve endings within the pores and skin discover contact and ship alerts to the mind; richly innervated hair follicles discover the motion of hair fibres; and sensory nerves referred to as C-LTMRs, which can be most effective present in furry pores and skin, procedure emotional, or ‘feel-good’ contact.Now, researchers will have exposed a brand new procedure in hair follicles. To hold out the find out about, the researchers analysed unmarried cellular RNA sequencing knowledge of human pores and skin and hair follicles and located that hair follicle cells contained a better share of touch-sensitive receptors than an identical cells within the pores and skin. They established co-cultures of human hair follicle cells and sensory nerves, then automatically stimulated the hair follicle cells, discovering that this resulted in activation of the adjoining sensory nerves.They then made up our minds to research how the hair follicle cells signalled to the sensory nerves. They tailored a method referred to as speedy scan cyclic voltammetry to analyse cells in tradition and located that the hair follicle cells have been freeing the neurotransmitters serotonin and histamine according to contact.Once they blocked the receptor for those neurotransmitters at the sensory neurons, the neurons not answered to the hair follicle cellular stimulation. In a similar way, once they blocked synaptic vesicle manufacturing via hair follicle cells, they have been not in a position to sign to the sensory nerves.They due to this fact concluded that according to contact, hair follicle cells liberate that turn on within sight sensory neurons.The researchers additionally performed the similar experiments with cells from the surface as an alternative of the hair follicle. The cells answered to gentle contact via freeing histamine, however they didn’t liberate serotonin.Dr Higgins stated: “That is fascinating as histamine within the pores and skin contributes to inflammatory pores and skin prerequisites corresponding to eczema, and it has at all times been presumed that immune cells liberate the entire histamine. Our paintings uncovers a brand new function for pores and skin cells within the liberate of histamine, with attainable packages for eczema analysis.”The researchers observe that the analysis was once carried out in cellular cultures, and can wish to be replicated in dwelling organisms to substantiate the findings. The researchers additionally wish to resolve if the hair follicle is activating particular kinds of sensory nerves.Since C-LTMRs are most effective provide inside furry pores and skin, they’re to look if the hair follicle has a novel mechanism to sign to those nerves that we’ve got but to discover.Investment: This paintings was once funded via Engineering and Bodily Analysis Council (EPSRC, a part of UKRI), Proctor & Gamble, Wellcome Consider, and Biotechnology and Organic Sciences Analysis Council (BBSRC, a part of UKRI).About this tactile belief analysis newsAuthor: Caroline Brogan
The cells answered to gentle contact via freeing histamine, however they didn’t liberate serotonin. Credit score: Neuroscience NewsThe researchers additionally discovered that those hair follicle cells liberate the neurotransmitters histamine and serotonin according to contact – findings that may assist us in long run to grasp histamine’s function in inflammatory pores and skin illnesses like eczema.Lead writer of the paper Dr Claire Higgins, from Imperial’s Division of Bioengineering, stated: “This can be a sudden discovering as we don’t but know why hair follicle cells have this function in processing gentle contact. Because the follicle accommodates many sensory nerve endings, we now wish to resolve if the hair follicle is activating particular kinds of sensory nerves for an unknown however distinctive mechanism.”A sensitive subjectWe really feel contact the use of a number of mechanisms: sensory nerve endings within the pores and skin discover contact and ship alerts to the mind; richly innervated hair follicles discover the motion of hair fibres; and sensory nerves referred to as C-LTMRs, which can be most effective present in furry pores and skin, procedure emotional, or ‘feel-good’ contact.Now, researchers will have exposed a brand new procedure in hair follicles. To hold out the find out about, the researchers analysed unmarried cellular RNA sequencing knowledge of human pores and skin and hair follicles and located that hair follicle cells contained a better share of touch-sensitive receptors than an identical cells within the pores and skin. They established co-cultures of human hair follicle cells and sensory nerves, then automatically stimulated the hair follicle cells, discovering that this resulted in activation of the adjoining sensory nerves.They then made up our minds to research how the hair follicle cells signalled to the sensory nerves. They tailored a method referred to as speedy scan cyclic voltammetry to analyse cells in tradition and located that the hair follicle cells have been freeing the neurotransmitters serotonin and histamine according to contact.Once they blocked the receptor for those neurotransmitters at the sensory neurons, the neurons not answered to the hair follicle cellular stimulation. In a similar way, once they blocked synaptic vesicle manufacturing via hair follicle cells, they have been not in a position to sign to the sensory nerves.They due to this fact concluded that according to contact, hair follicle cells liberate that turn on within sight sensory neurons.The researchers additionally performed the similar experiments with cells from the surface as an alternative of the hair follicle. The cells answered to gentle contact via freeing histamine, however they didn’t liberate serotonin.Dr Higgins stated: “That is fascinating as histamine within the pores and skin contributes to inflammatory pores and skin prerequisites corresponding to eczema, and it has at all times been presumed that immune cells liberate the entire histamine. Our paintings uncovers a brand new function for pores and skin cells within the liberate of histamine, with attainable packages for eczema analysis.”The researchers observe that the analysis was once carried out in cellular cultures, and can wish to be replicated in dwelling organisms to substantiate the findings. The researchers additionally wish to resolve if the hair follicle is activating particular kinds of sensory nerves.Since C-LTMRs are most effective provide inside furry pores and skin, they’re to look if the hair follicle has a novel mechanism to sign to those nerves that we’ve got but to discover.Investment: This paintings was once funded via Engineering and Bodily Analysis Council (EPSRC, a part of UKRI), Proctor & Gamble, Wellcome Consider, and Biotechnology and Organic Sciences Analysis Council (BBSRC, a part of UKRI).About this tactile belief analysis newsAuthor: Caroline Brogan
Supply: Imperial School London
Touch: Caroline Brogan – Imperial School London
Symbol: The picture is credited to Neuroscience NewsOriginal Analysis: Open get admission to.
“Mechanical stimulation of human hair follicle outer root sheath cultures turns on adjoining sensory neurons” via Claire Higgins et al. Science AdvancesAbstractMechanical stimulation of human hair follicle outer root sheath cultures turns on adjoining sensory neuronsMechanical stimuli, corresponding to stroking or urgent at the pores and skin, turn on mechanoreceptors transmitting data to the sensory fearful gadget and mind.It’s smartly approved that deflection of the hair fiber that happens with a mild breeze or contact immediately turns on the sensory neurons surrounding the hair follicle, facilitating transmission of mechanical data.Right here, we hypothesized that hair follicle outer root sheath cells act as transducers of mechanical stimuli to sensory neurons surrounding the hair follicle.The usage of electrochemical research on human hair follicle arrangements in vitro, we have been in a position to turn that outer root sheath cells liberate ATP and the neurotransmitters serotonin and histamine according to mechanical stimulation.The usage of calcium imaging blended with pharmacology in a coculture of outer root sheath cells with sensory neurons, we discovered that the discharge of those 3 molecules from hair follicle cells ends up in activation of sensory neurons.
Hair Follicles’ Hidden Position in Contact Sensation – Neuroscience Information