A learn about in Nature Geosciences unearths that oceanic anoxia considerably contributed to marine extinctions right through the Triassic–Jurassic duration, with recent ranges of deoxygenation mirroring the ones of the previous. This discovery highlights the sensitivity of marine ecosystems to native and international environmental adjustments.
A learn about in Nature Geosciences unearths that oceanic anoxia considerably contributed to marine extinctions right through the Triassic–Jurassic duration, with recent ranges of deoxygenation mirroring the ones of the previous. This discovery highlights the sensitivity of marine ecosystems to native and international environmental adjustments.
Scientists have came upon a pivotal position of oceanic anoxia within the Triassic–Jurassic mass extinction, indicating that even localized deoxygenation may end up in in style ecosystem cave in. This analysis emphasizes the significance of figuring out recent marine ecosystem fragility within the face of accelerating deoxygenation.
Scientists have made a shocking discovery that sheds new gentle at the position that oceanic deoxygenation (anoxia) performed in probably the most devastating extinction occasions in Earth’s historical past. Their discovering has implications for current-day ecosystems – and serves as a caution that marine environments are most probably extra fragile than obvious.
New analysis, revealed on November 27 in a number one world magazine, Nature Geosciences, means that oceanic anoxia performed crucial position in ecosystem disruption and extinctions in marine environments right through the Triassic–Jurassic mass extinction, a significant extinction match that came about round 200 million years in the past.
Unusually, then again, the learn about displays that the worldwide extent of euxinia (an excessive type of de-oxygenated stipulations) was once very similar to the existing day.
 Sampling of the Carnduff cores (right here studied), which have been drilled within the Larne Basin, Northern Eire. Credit score: Prof. Micha Ruhl, Trinity Faculty Dublin
Sampling of the Carnduff cores (right here studied), which have been drilled within the Larne Basin, Northern Eire. Credit score: Prof. Micha Ruhl, Trinity Faculty Dublin
Ancient Context of Mass Extinctions
Earth’s historical past has been marked via a handful of primary mass extinctions, right through which international ecosystems collapsed and species went extinct. All previous extinction occasions seem to have coincided with international climatic and environmental perturbance that recurrently ended in ocean deoxygenation. On account of this, oceanic anoxia has been proposed as a most probably reason for marine extinctions at the ones instances, with the idea that the extra in style incidence of deoxygenation would have ended in a bigger extinction match.
Analysis Technique and Findings
The use of chemical information from historical mudstone deposits got from drill cores in Northern Eire and Germany, a global analysis staff led via scientists from Royal Holloway (UK), and together with scientists from Trinity Faculty Dublin’s College of Herbal Sciences (Eire) in addition to from Utrecht College (Netherlands), was once in a position to hyperlink two key facets related to the Triassic–Jurassic mass extinction.
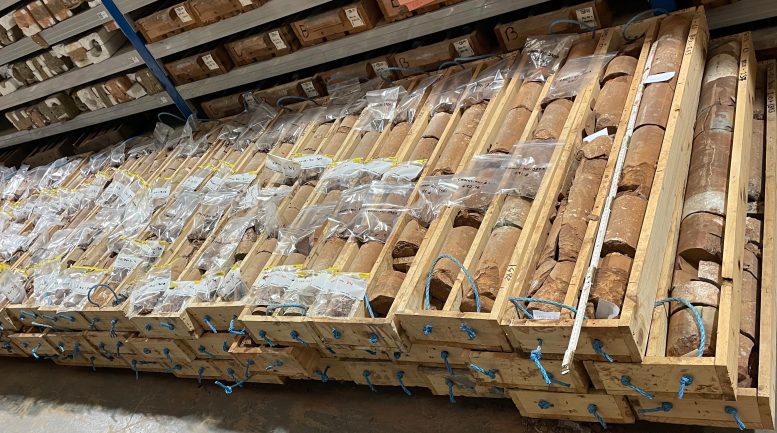
 A core pattern of ~201 million-year-old sediments got from the Carnduff-2 core, drilled within the Larne Basin (Northern Eire), appearing the shell of an animal that lived at the seabed in a while after the Triassic–Jurassic international mass extinction. Credit score: Prof. Micha Ruhl, Trinity Faculty Dublin
A core pattern of ~201 million-year-old sediments got from the Carnduff-2 core, drilled within the Larne Basin (Northern Eire), appearing the shell of an animal that lived at the seabed in a while after the Triassic–Jurassic international mass extinction. Credit score: Prof. Micha Ruhl, Trinity Faculty Dublin
The staff came upon that pulses in deoxygenation in shallow marine environments alongside the margins of the Eu continent at the moment immediately coincided with larger extinction ranges in the ones puts.
On additional investigation – and extra importantly – the staff additionally discovered that the worldwide extent of utmost deoxygenation was once quite restricted, and very similar to the existing day.
Micha Ruhl, Assistant Professor in Trinity’s College of Herbal Sciences, and analysis staff member, stated:
“Scientists have lengthy suspected that ocean deoxygenation performs crucial position within the disturbance of marine ecosystems, which can result in the extinction of species in marine environments. The learn about of previous time durations of utmost environmental exchange certainly displays this to be the case, which teaches us essential courses about doable tipping issues in native, in addition to international ecosystems in accordance with climatic forcing.
“Crucially then again, the present findings display that even if the worldwide extent of deoxygenation is very similar to the existing day, the native building of anoxic stipulations and next in the community larger extinction charges can cascade in in style or international ecosystem cave in and extinctions, even in spaces the place deoxygenation didn’t happen.”
 Professor Micha Ruhl within the lab. Credit score: Prof. Micha Ruhl, Trinity Faculty Dublin
Professor Micha Ruhl within the lab. Credit score: Prof. Micha Ruhl, Trinity Faculty Dublin
Ruhl defined, “It displays that international marine ecosystems change into inclined, even if simplest native environments alongside the perimeters of the continents are disturbed. Working out such processes is of paramount significance for assessing present-day ecosystem steadiness, and related meals provide, particularly in a global the place marine deoxygenation is projected to noticeably building up in accordance with international warming and larger nutrient run-off from continents.”
The learn about of previous international exchange occasions, such because the transition between the Triassic and Jurassic classes, permits scientists to disentangle the results of world climatic and environmental exchange and constrain basic Earth device processes that keep watch over tipping issues in Earth’s ecosystems.
Reference: “Globally restricted however serious shallow-shelf euxinia right through the end-Triassic extinction” via Andrew D. Bond, Alexander J. Dickson, Micha Ruhl, Remco Bos and Bas van de Schootbrugge, 27 November 2023, Nature Geoscience.
DOI: 10.1038/s41561-023-01303-2