Paleolithic delicacies was once the rest however lean and inexperienced, in line with a learn about at the diets of our Pleistocene ancestors.For a excellent 2 million years, Homo sapiens and their ancestors ditched the salad and dined closely on meat, placing them on the best of the meals chain.
It isn’t rather the balanced vitamin of berries, grains, and steak we would possibly image after we bring to mind ‘paleo’ meals.
However in line with a learn about from 2021 via anthropologists from Israel’s Tel Aviv College and the College of Minho in Portugal, trendy hunter-gatherers have given us the improper influence of what we as soon as ate.
“This comparability is futile, on the other hand, as a result of 2 million years in the past hunter-gatherer societies may hunt and devour elephants and different huge animals – whilst as of late’s hunter gatherers do not need get entry to to such bounty,” researcher Miki Ben‐Dor from Israel’s Tel Aviv College defined when the analysis was once printed.
A glance thru loads of earlier research – on the whole lot from trendy human anatomy and body structure to measures of the isotopes inside of historical human bones and enamel – suggests we had been essentially apex predators till more or less 12,000 years in the past.
Reconstructing the grocery listing of hominids who lived way back to 2.5 million years in the past is made all that a lot more tough via the truth plant stays do not keep as simply as animal bones, enamel, and shells.
Different research have used chemical research of bones and teeth tooth to search out localized examples of diets heavy in plant subject matter. However extrapolating this to humanity as a complete is not so immediately ahead.
We will be able to in finding considerable proof of recreation looking within the fossil file, however to decide what we amassed, anthropologists have historically grew to become to modern day ethnography in keeping with the idea that little has modified.
In keeping with Ben-Dor and his colleagues, it is a large mistake.
“All the ecosystem has modified, and prerequisites can’t be when put next,” stated Ben‐Dor.
The Pleistocene epoch was once a defining time in Earth’s historical past for us people. Through the top of it, we had been marching our manner into the a long way corners of the globe, outliving each and every different hominid on our department of the circle of relatives tree.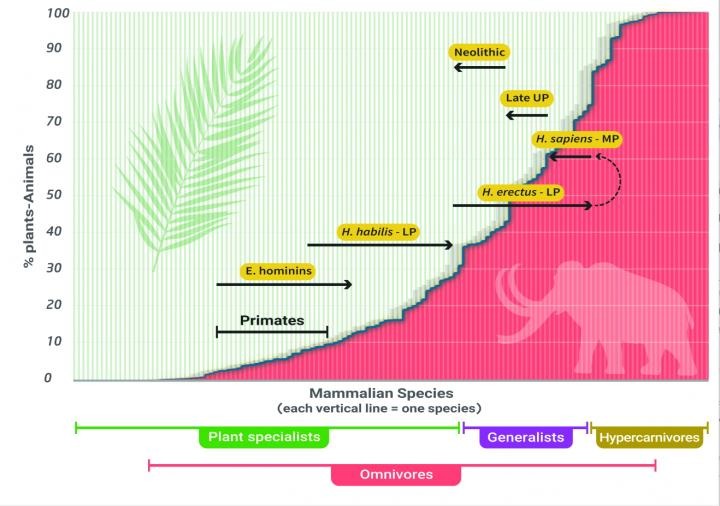 Graph appearing the place Homo sapiens sat at the spectrum of carnivore to herbivore all through the Pleistocene and Higher Pleistocene (UP). (Dr Miki Ben Dor)Ruled via the closing nice ice age, maximum of what’s as of late Europe and North The united states was once frequently buried underneath thick glaciers.
Graph appearing the place Homo sapiens sat at the spectrum of carnivore to herbivore all through the Pleistocene and Higher Pleistocene (UP). (Dr Miki Ben Dor)Ruled via the closing nice ice age, maximum of what’s as of late Europe and North The united states was once frequently buried underneath thick glaciers.
With such a lot water locked up as ice, ecosystems world wide had been massively other to what we see as of late. Massive beasts roamed the panorama, together with mammoths, mastodons, and massive sloths – in a long way higher numbers than we see as of late.
In fact it is no secret that Homo sapiens used their ingenuity and uncanny staying power to seek down those large meal-tickets. However the frequency with which they preyed on those herbivores hasn’t been really easy to determine.
Relatively than depend only at the fossil file, or make tenuous comparisons with pre-agricultural cultures, the researchers grew to become to the proof embedded in our personal our bodies and when put next it with our closest cousins.
“We determined to make use of different find out how to reconstruct the vitamin of stone-age people: to inspect the reminiscence preserved in our personal our bodies, our metabolism, genetics and bodily construct,” stated Ben‐Dor.
“Human conduct adjustments hastily, however evolution is sluggish. The frame recalls.”
For instance, when put next with different primates, our our bodies want extra calories in line with unit of frame mass. Particularly in the case of our energy-hungry brains. Our social time, reminiscent of in the case of elevating youngsters, additionally limits the period of time we will be able to spend in search of meals.
We now have upper fats reserves, and will employ them via hastily turning fat into ketones when the desire arises. In contrast to different omnivores, the place fats cells are few however huge, ours are small and a lot of, echoing the ones of a predator.
Our digestive methods also are suspiciously like that of animals upper up the meals chain. Having strangely robust abdomen acid is simply the article we would possibly want for breaking down proteins and killing damaging micro organism you’ll anticipate finding on a week-old mammoth chop. Mammoth chops, any individual? (Thomas Quine/Flickr/CC-BY-2.0)Even our genomes level to a heavier reliance on a meat-rich vitamin than a sugar-rich one.
Mammoth chops, any individual? (Thomas Quine/Flickr/CC-BY-2.0)Even our genomes level to a heavier reliance on a meat-rich vitamin than a sugar-rich one.
“For instance, geneticists have concluded that spaces of the human genome had been closed off to permit a fat-rich vitamin, whilst in chimpanzees, spaces of the genome had been opened to permit a sugar-rich vitamin,” stated Ben‐Dor.
The staff’s argument is intensive, touching upon proof in instrument use, indicators of hint parts and nitrogen isotopes in Paleolithic stays, and dental put on.
All of it tells a tale the place our genus’ trophic stage – Homo’s place within the meals internet – changed into extremely carnivorous for us and our cousins, Homo erectus, more or less 2.5 million years in the past, and remained that manner till the higher Paleolithic round 11,700 years in the past.
From there, research on trendy hunter-gatherer communities transform slightly extra helpful as a decline in populations of enormous animals and fragmentation of cultures world wide noticed to extra plant intake, culminating within the Neolithic revolution of farming and agriculture.
None of that is to mention we should consume extra meat. Our evolutionary previous is not an instruction information on human well being, and because the researchers emphasize, our international is not what it was once.
However figuring out the place our ancestors sat within the meals internet has a large have an effect on on figuring out the whole lot from our personal well being and body structure, to our affect over the surroundings in instances long past via.
This analysis was once printed within the American Magazine of Bodily Anthropology.An previous model of this text was once printed in April 2021.
Historical People Have been Apex Predators For two Million Years, Learn about Discovers













