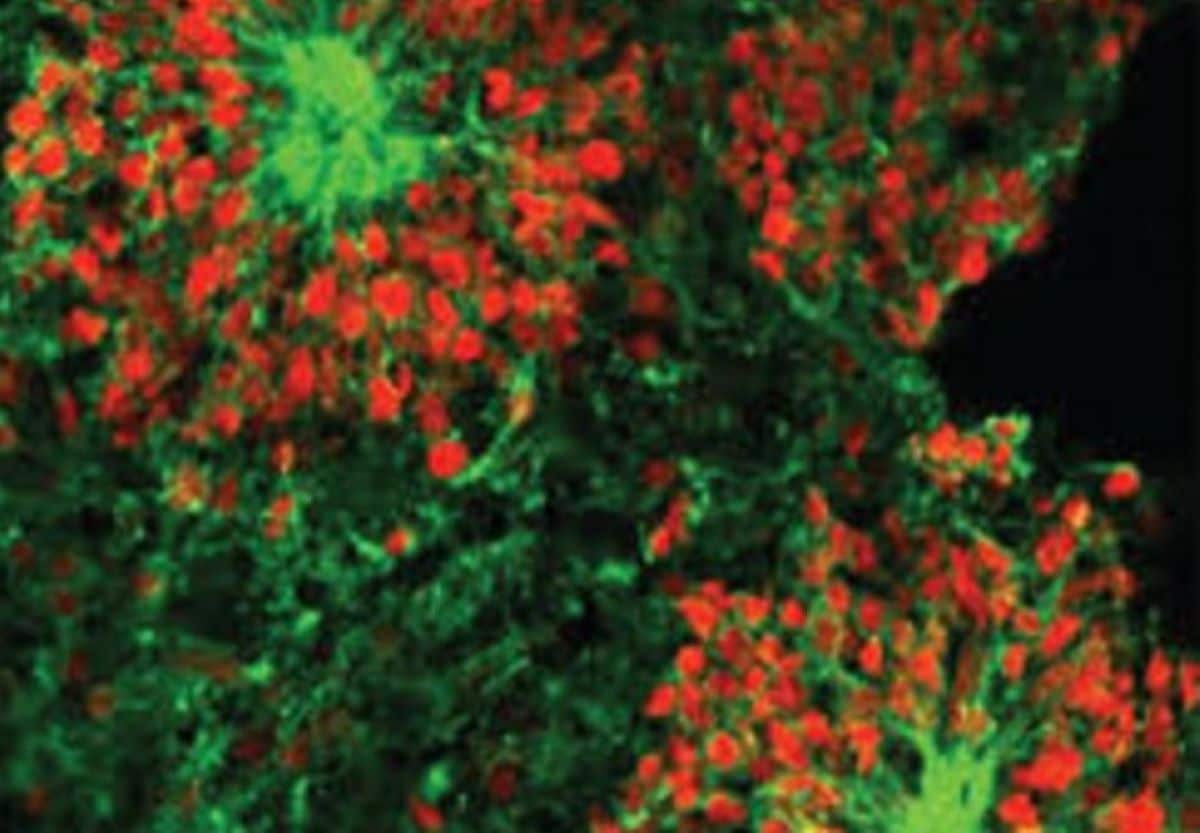
Abstract: Alcohol use dysfunction affects 283 million people globally, with restricted healing choices.Researchers found out a vital connection between the tension hormone, corticotropin-releasing issue (CRF), and alcohol-withdrawal complications. CRF turns on mast cells within the dura, triggering ache alerts right through alcohol withdrawal.This groundbreaking discovery may pave the best way for centered drug remedies, probably breaking the vicious cycle of dependancy.Key Details:CRF, a pressure hormone, performs a pivotal position in activating ache alerts right through alcohol withdrawal by way of binding to a selected mast cellular receptor, MrgprB2.Mast cells, unique to the MrgprB2 receptor, are integral in alcohol-withdrawal complications, inflicting dilation of blood vessels and sensitizing sensory neurons.Concentrated on the interplay between CRF and MrgprB2 may result in new healing methods for relieving ache right through alcohol withdrawal.Supply: UT San AntonioAbout 283 million other people international be afflicted by alcohol use dysfunction, a debilitating well being problem for which restricted healing choices are to be had. The fee to society is estimated at more than $2 trillion every year.“Other people attempt to rehabilitate, however it is rather difficult,” stated Yu Shin Kim, Ph.D., a neuroscience researcher at The College of Texas Well being Science Middle at San Antonio.“Headache is without doubt one of the serious withdrawal signs that pushes the rehabilitating affected person again to alcohol, as a result of other people know that, after ingesting, alcohol will if truth be told cut back the headache. It turns into a vicious cycle. That is how they increase alcohol dependence.”  Researchers knew that peripheral neural fibers will have to be associated with vessel dilation that happens with alcohol withdrawal. Credit score: Neuroscience NewsKim, affiliate professor of oral and maxillofacial surgical treatment within the well being science middle’s College of Dentistry, and co-workers discovered {that a} pressure hormone referred to as corticotropin-releasing issue (CRF) turns on immune cells referred to as mast cells within the dura—the skinny, clear membrane underneath the cranium.Dura subject comprises peripheral nerve fibers and peripheral blood vessels. CRF binds to a selected mast cellular receptor referred to as MrgprB2, Kim stated. That is the central discovering of the group’s find out about revealed Oct. 30 within the magazine Neuron.“After alcohol withdrawal, the CRF pressure hormone is launched from the hypothalamus, a mind area that controls many purposes,” Kim stated.“The CRF travels via peripheral blood vessels to dura subject, the place it’s launched from the vessels and binds to MrgprB2. This alerts the mast cells to degranulate, or open, and secrete chemical messengers that induce purposes together with blood vessel dilation (widening).“This additionally turns on peripheral nerve fibers extending from trigeminal ganglia neurons, which might be sensory neurons. This is how those neurons are sensitized and an individual has alcohol-withdrawal headache.”It’s this procedure that sends the ache alerts.Researchers knew that peripheral neural fibers will have to be associated with vessel dilation that happens with alcohol withdrawal. The lab’s new contribution is that CRF binds to the mast cellular receptor MrgprB2, Kim stated.“MrgprB2 is an overly particular receptor for mast cells. Simplest mast cells have those receptors,” Kim stated.This analysis could gain advantage additional research of quite a lot of substance use dysfunction mechanisms together with withdrawal, he stated. It can be imaginable to increase a small-molecule drug remedy to inhibit the CRF and MrgprB2 interplay, leading to fewer ache alerts right through alcohol withdrawal.About this AUD and hormone analysis newsAuthor: Yu Shin Kim
Researchers knew that peripheral neural fibers will have to be associated with vessel dilation that happens with alcohol withdrawal. Credit score: Neuroscience NewsKim, affiliate professor of oral and maxillofacial surgical treatment within the well being science middle’s College of Dentistry, and co-workers discovered {that a} pressure hormone referred to as corticotropin-releasing issue (CRF) turns on immune cells referred to as mast cells within the dura—the skinny, clear membrane underneath the cranium.Dura subject comprises peripheral nerve fibers and peripheral blood vessels. CRF binds to a selected mast cellular receptor referred to as MrgprB2, Kim stated. That is the central discovering of the group’s find out about revealed Oct. 30 within the magazine Neuron.“After alcohol withdrawal, the CRF pressure hormone is launched from the hypothalamus, a mind area that controls many purposes,” Kim stated.“The CRF travels via peripheral blood vessels to dura subject, the place it’s launched from the vessels and binds to MrgprB2. This alerts the mast cells to degranulate, or open, and secrete chemical messengers that induce purposes together with blood vessel dilation (widening).“This additionally turns on peripheral nerve fibers extending from trigeminal ganglia neurons, which might be sensory neurons. This is how those neurons are sensitized and an individual has alcohol-withdrawal headache.”It’s this procedure that sends the ache alerts.Researchers knew that peripheral neural fibers will have to be associated with vessel dilation that happens with alcohol withdrawal. The lab’s new contribution is that CRF binds to the mast cellular receptor MrgprB2, Kim stated.“MrgprB2 is an overly particular receptor for mast cells. Simplest mast cells have those receptors,” Kim stated.This analysis could gain advantage additional research of quite a lot of substance use dysfunction mechanisms together with withdrawal, he stated. It can be imaginable to increase a small-molecule drug remedy to inhibit the CRF and MrgprB2 interplay, leading to fewer ache alerts right through alcohol withdrawal.About this AUD and hormone analysis newsAuthor: Yu Shin Kim
Supply: UT San Antonio
Touch: Yu Shin Kim – UT San Antonio
Symbol: The picture is credited to Neuroscience NewsOriginal Analysis: Closed get admission to.
“Mast cell-specific receptor mediates alcohol withdrawal-associated headache in male mice” by way of Yu Shin Kim et al. NeuronAbstractMast cell-specific receptor mediates alcohol withdrawal-associated headache in male miceHighlightsAlcohol withdrawal reasons headache behaviors, relying at the presence of MrgprB2Alcohol-withdrawal-induced sensitization of TG is absent in MrgprB2-lacking miceMast cellular degranulation by way of MrgprB2 in dura mater induces alcohol-withdrawal headacheMrgprB2 receptor mediates the improvement of alcohol-withdrawal-associated headacheSummaryRehabilitation from alcohol dependancy or abuse is hampered by way of withdrawal signs together with serious complications, which steadily result in rehabilitation failure.There’s no suitable healing choice to be had for alcohol-withdrawal-induced complications. Right here, we display the position of the mast-cell-specific receptor MrgprB2 within the building of alcohol-withdrawal-induced headache.Taking flight alcohol from alcohol-acclimated mice induces headache behaviors, together with facial allodynia, facial ache expressions, and lowered motion, which might be signs steadily noticed in people. The ones behaviors had been absent in MrgprB2-deficient mice right through alcohol withdrawal.We noticed in vivo spontaneous activation and hypersensitization of trigeminal ganglia (TG) neurons in alcohol-withdrawal WT mice, however no longer in alcohol-withdrawal MrgprB2-deficient mice. Greater mast cellular degranulation by way of alcohol withdrawal in dura mater was once dependent at the presence of MrgprB2.The effects point out that alcohol withdrawal reasons headache by the use of MrgprB2 of mast cells in dura mater, suggesting that MrgprB2 is a possible goal for treating alcohol-withdrawal-related complications.
Hormonal Hyperlink in Alcohol Withdrawal Complications – Neuroscience Information






![Right here’s the entirety new in Android 16 Developer Preview 2 [Gallery] Right here’s the entirety new in Android 16 Developer Preview 2 [Gallery]](https://i0.wp.com/9to5google.com/wp-content/uploads/sites/4/2024/12/Android-16-DP2-Note-taking-4.jpg?ssl=1)




