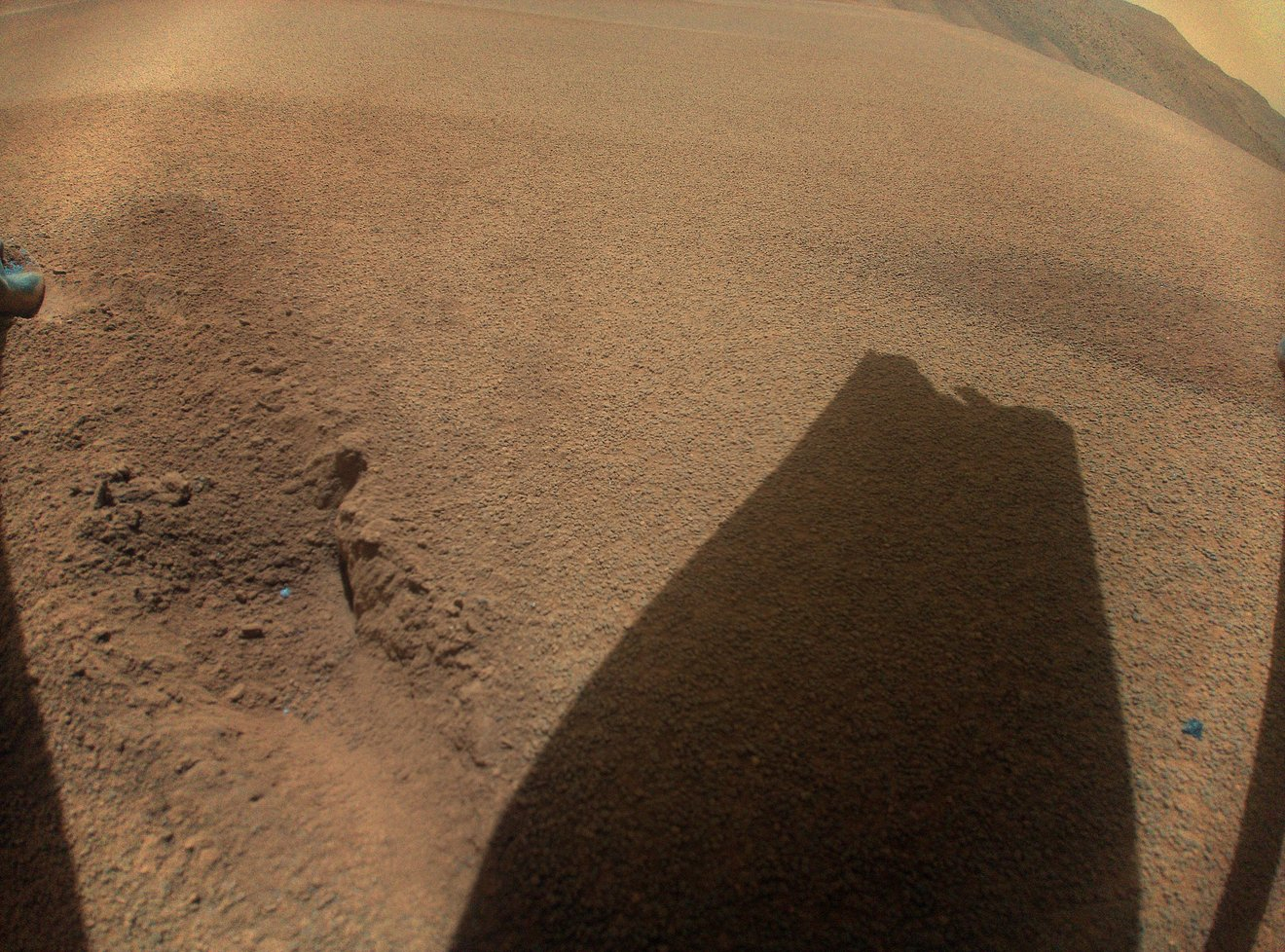
The seek for existence on Mars is going ever on.On a daily basis we inch nearer to learning whether or not or now not existence on Mars ever existed — and even may have existed. Maximum lately, scientists finding out information from NASA’s Interest rover have new perception into how Mars would possibly have modified from a probably liveable, water-rich planet to a completely uninhabitable barren region.As Interest traverses Gale Crater on Mars, it is appearing experiments on rocks. The usage of its Pattern Research at Mars (SAM) and Tunable Laser Spectrometer (TLS) tools, the rover has heated rock samples to research the gases produced. In appearing this process on carbon-rich minerals, or carbonates, which incessantly function local weather information, Interest published an isotopic composition that implies two conceivable climatic eventualities in Mars’ previous.Within the first, the carbonates would possibly had been shaped by way of repeated wet-dry cycles, suggesting excessive evaporation. In the second one, the carbonates would possibly had been shaped in extraordinarily salty, extraordinarily chilly water.”Those formation mechanisms constitute two other local weather regimes that can provide other habitability eventualities,” Jennifer Stern of NASA Goddard, a co-author of a paper at the analysis, mentioned in a observation. “Rainy-dry biking would point out alternation between more-habitable and less-habitable environments, whilst cryogenic temperatures within the mid-latitudes of Mars would point out a less-habitable setting the place maximum water is locked up in ice and now not to be had for chemistry or biology, and what’s there’s extraordinarily salty and unsightly for existence.”Those two eventualities are not new ideas. Different proof on Mars, from positive rock formations to the presence of particular minerals, helps either one of them. However this actual find out about marks the primary time isotopic proof from rock samples enhance them.However there’s some unhealthy information that comes along side those effects. “Our samples aren’t in step with an historical setting with existence (biosphere) at the floor of Mars,” mentioned NASA Goddard’s David Burtt, the lead writer of the paper. “[A]lthough this doesn’t rule out the potential of an underground biosphere or a floor biosphere that started and ended earlier than those carbonates shaped.”Breaking house information, the newest updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!And so the paintings continues…
How did Mars develop into an uninhabitable barren region? Interest rover rock samples can have solutions