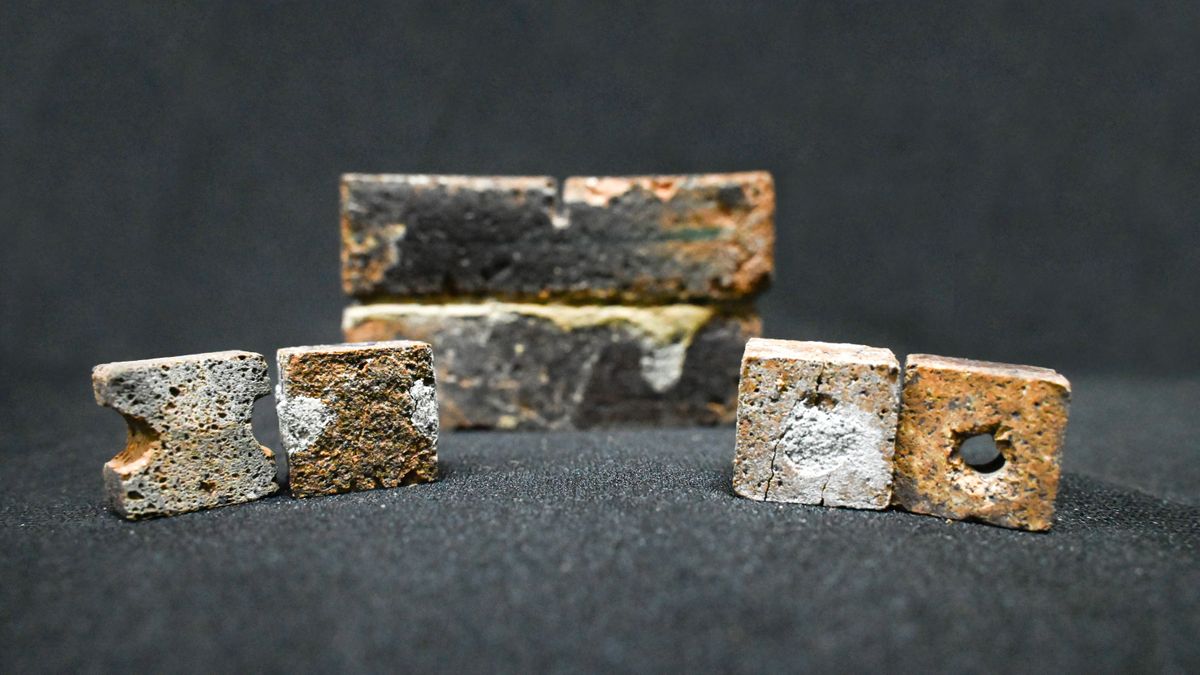
If all is going to plot, scientists might one day start construction outposts at the moon — and a few mavens imagine that those outposts may well be built with bricks constructed from lunar regolith. And now, a brand new learn about in response to lunar regolith simulant experiments means that if those moon-dust bricks crack, micro organism may well be used to seal them again up.The usage of as many native lunar sources as imaginable to build a base at the moon is very important to stay prices down; launching massive plenty of subject material from Earth to the moon may be very pricey. Thus, making bricks out of lunar regolith has lengthy been mooted as a possible resolution. Many groups all over the world, together with researchers on the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), were experimenting making these types of bricks with lunar regolith simulants.Regolith, for context, refers back to the free filth and rocks protecting the outside of the moon. Precise samples of lunar regolith are uncommon and valuable, and due to this fact simulants, which intention to duplicate various kinds of regolith, are used for experiments as a substitute. In the past, the IISc researchers discovered some way of the use of a terrestrial soil bacterium known as Sporosarcina pasteurii to make bricks out of regolith simulant. The micro organism are ready to transform urea — which the micro organism produce as waste — and calcium into calcium carbonate crystals. When blended with guar gum this is extracted from guar beans, those crystals are ready to bind regolith debris in combination to shape bricks.Later, the similar staff experimented with making lunar bricks via sintering, which concerned heating a compact mixture of regolith simulant with polyvinyl alcohol, which is a soluble polymer, to extraordinarily top temperatures in a furnace. The bricks shaped via sintering gave the impression even more potent than the bacterium-built bricks — on the other hand, the prerequisites at the moon are lovely critical.Uncovered to the vacuum of house, lunar bricks would have to resist a temperature vary of a top of 250 levels Fahrenheit (121 levels Celsius) to a low of -208 levels Fahrenheit (–133 levels Celsius) right through the process a lunar day, which might position excessive thermal rigidity at the bricks. They’d even be matter to bombardment through micrometeorites and cosmic rays.”Temperature adjustments may also be a lot more dramatic at the lunar floor, which is able to, over a time period, have a vital impact,” Koushik Viswanathan of the IISc’s Division of Mechanical Engineering stated in a remark. “Sintered bricks are brittle. If in case you have a crack and it grows, all of the construction can briefly fall aside.”Subsequently, having the ability to adequately restore bricks at the moon earlier than a lunar outpost crumbles to filth could be crucial. So, Viswanathan and associates returned to their previous thought of the use of Sporosarcina pasteurii, however this time to not make the bricks themselves, however to create a sealant that may fill in cracks and holes within the bricks.Breaking house information, the newest updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!The staff sintered bricks out of regolith simulant, after which carried out a large number of forms of injury to them — holes, V-shaped notches and semi-circular notches, for example — all of which might outcome from structural fatigue. The researchers then poured a combination, which they discuss with as a slurry, concocted from a mixture of Sporosarcina pasteurii, guar gum and regolith simulant, over the bricks and left them for a couple of days, permitting the slurry to seep into the bricks and fill any holes or cracks.The micro organism did two issues. One, it made calcium carbonate that successfully stuffed the cracks, and two, produced biopolymers that allowed the mix to bond with the brick, making it forged as soon as once more. The staff discovered that this returned 28 to 54% of a brick’s earlier compressive energy, even supposing it does not reasonably go back the bricks to their unique energy.”We had been to begin with no longer positive if the micro organism would bind to the sintered brick,” stated the IISc’s Aloke Kumar. “However we discovered that the micro organism can’t simplest solidify the slurry but additionally adhere neatly to this different mass.”Conducting this in a laboratory is something, however doing so in tricky prerequisites at the moon is any other factor.”Some of the giant questions is in regards to the conduct of those micro organism in extraterrestrial prerequisites,” stated Kumar. “Will their nature trade? Will they forestall doing [the carbonate production]? The ones issues are nonetheless unknown.”To take a look at and solution a few of these questions, the staff is proposing to ship a pattern of Sporosarcina pasteurii into house as a part of the coming near near Gaganyaan undertaking, which would be the first crewed Indian house undertaking, taking 3 astronauts past Earth as early as 2026.”If that occurs, to our wisdom, it’s going to be the primary experiment of its sort with this kind of micro organism,” stated Viswanathan.The analysis was once revealed on March 27 within the magazine Frontiers in Area Applied sciences.
How micro organism may lend a hand construct and handle towns at the moon