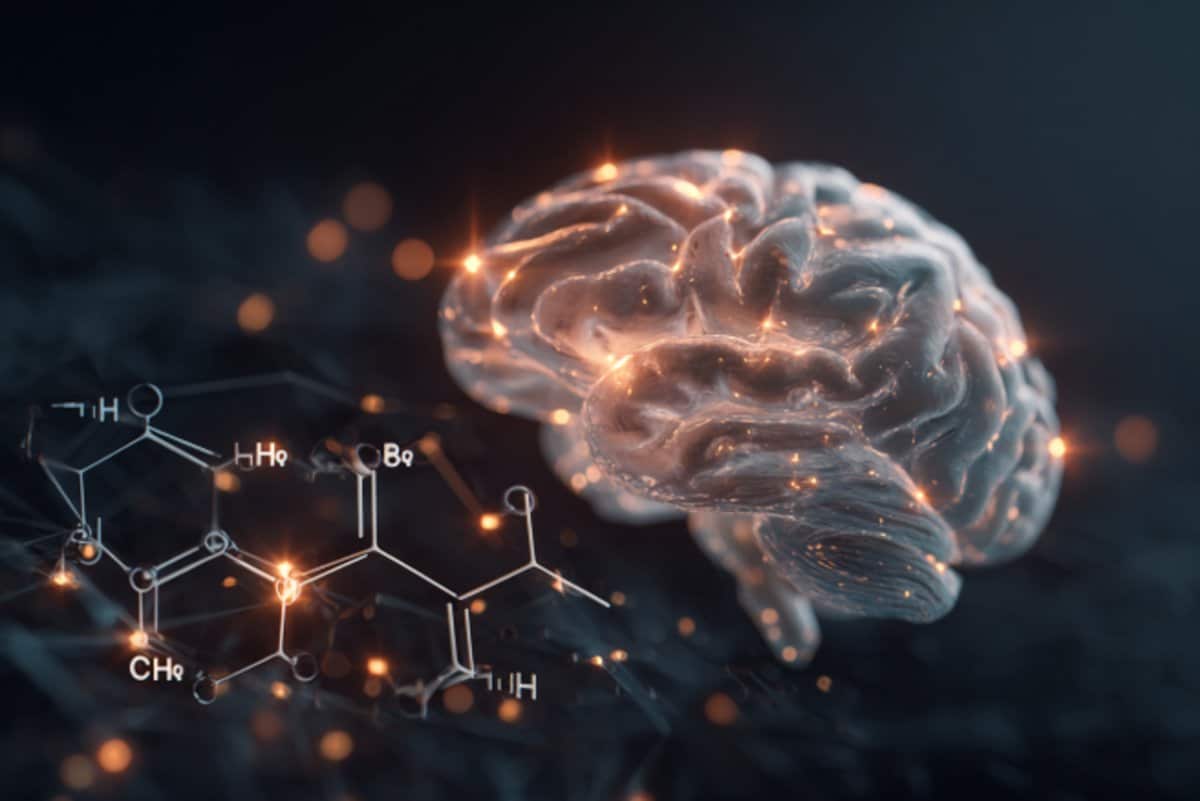
Abstract: A up to date find out about finds that individual mind cells reply now not best to smells but in addition to photographs and written phrases linked to these scents, offering deeper perception into human scent belief. Researchers discovered that neurons within the olfactory cortex and different mind areas, just like the hippocampus and amygdala, distinguish between other smells and affiliate them with visible cues.This analysis, the usage of knowledge from epilepsy sufferers, bridges an opening between animal and human research on olfactory processing. Remarkably, person neurons answered to smell, symbol, and phrase, suggesting that scent processing integrates visible and semantic data early on. Those findings may result in long run inventions in “olfactory aids.” The find out about emphasizes the interconnected nature of scent and visible reminiscence within the human mind.Key FactsNeurons within the olfactory cortex reply to smells, pictures, and phrases alike.The find out about discovered the amygdala differentiates between delightful and ugly odors.This analysis bridges wisdom gaps in human and animal olfactory processing research.Supply: College of BonnWe continuously best notice how vital our sense of scent is when it’s now not there: meals infrequently tastes just right, or we now not react to risks such because the scent of smoke. Researchers on the College Health facility Bonn (UKB), the College of Bonn and the College of Aachen have investigated the neuronal mechanisms of human scent belief for the primary time. Person nerve cells within the mind acknowledge odors and react particularly to the scent, the picture and the written phrase of an object, as an example a banana.The result of this find out about shut a long-standing wisdom hole between animal and human scent analysis and feature now been revealed within the famend magazine Nature.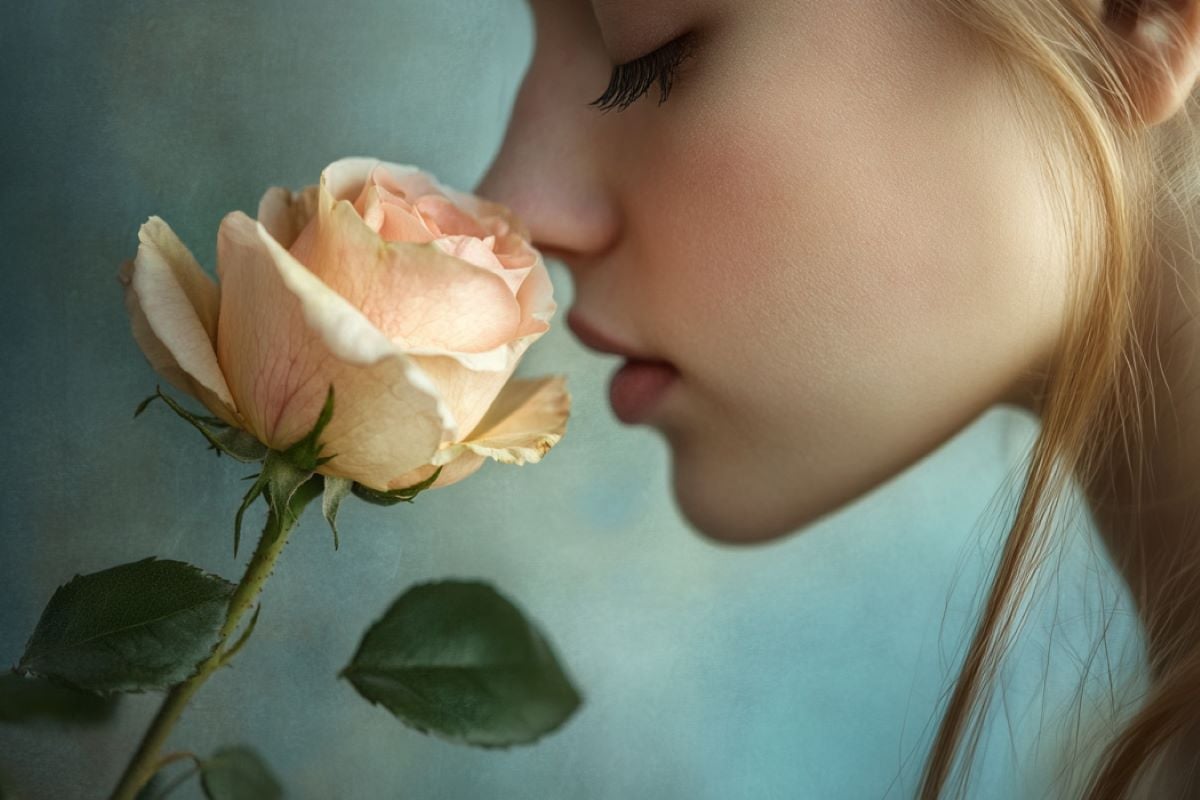  In a subsequent step, the researchers investigated the relationship between the belief of scents and photographs. Credit score: Neuroscience NewsImaging tactics similar to useful magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) have prior to now printed which areas of the human mind are curious about olfactory belief. Alternatively, those strategies don’t permit the sense of scent to be investigated on the basic degree of person nerve cells.“Subsequently, our figuring out of scent processing on the mobile degree is principally according to animal research, and it has now not been transparent to what extent those effects may also be transferred to people,” says co-corresponding creator Prof. Florian Mormann from the Division of Epileptology on the UKB, who may be a member of the Transdisciplinary Analysis Space (TRA) “Lifestyles & Well being” on the College of Bonn.Nerve cells within the mind determine odorsProf. Mormann’s analysis workforce has now succeeded for the primary time in recording the job of person nerve cells right through smelling.This used to be best conceivable for the reason that researchers labored along with sufferers from the Health center for Epileptology on the UKB, probably the most greatest epilepsy facilities in Europe, who had electrodes implanted of their brains for diagnostic functions. They have been offered with each delightful and ugly scents, similar to previous fish.“We found out that specific nerve cells within the human mind react to odors. In response to their job, we have been in a position to exactly expect which smell used to be being smelled,” says first creator Marcel Kehl, a doctoral pupil on the College of Bonn in Prof. Mormann’s running workforce on the UKB.The measurements confirmed that other mind areas similar to the principle olfactory cortex, anatomically referred to as the piriform cortex, and in addition positive spaces of the medial temporal lobe, particularly the amygdala, the hippocampus and the entorhinal cortex, are curious about explicit duties.Whilst the job of nerve cells within the olfactory cortex maximum correctly predicted which smell used to be smelled, neuronal job within the hippocampus used to be in a position to expect whether or not scents have been appropriately recognized.Simplest nerve cells within the amygdala, a area curious about emotional processing, reacted another way relying on whether or not a smell used to be perceived as delightful or unsightly.Nerve cells react to the scent, symbol and identify of the bananaIn a subsequent step, the researchers investigated the relationship between the belief of scents and photographs. To try this, they offered the members within the Bonn find out about with the matching pictures for each and every scent, as an example the smell and later a photograph of a banana, and tested the response of the neurons. Unusually, nerve cells in the principle olfactory cortex answered now not best to scents, but in addition to photographs.“This means that the duty of the human olfactory cortex is going a ways past the natural belief of odors,” says co-corresponding creator Prof. Marc Spehr from the Institute of Biology II at RWTH Aachen College.The researchers found out person nerve cells that reacted particularly to the scent, the picture and the written phrase of – as an example – the banana. This discovery signifies that semantic data are processed early on in human olfactory processing.The effects now not best verify many years of animal research, but in addition display how other mind areas are curious about explicit human scent processing purposes.“That is a very powerful contribution on the best way to interpreting the human olfactory code,” says Prof. Mormann.“Additional analysis on this house is essential in an effort to someday increase olfactory aids that we will be able to use in on a regular basis lifestyles as naturally as glasses or listening to aids.”Investment: The find out about used to be funded through the German Analysis Basis (DFG), the Federal Ministry of Training and Analysis (BMBF) and the state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) as a part of the iBehave venture.About this olfaction and visible neuroscience analysis newsAuthor: Inka Väth
In a subsequent step, the researchers investigated the relationship between the belief of scents and photographs. Credit score: Neuroscience NewsImaging tactics similar to useful magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) have prior to now printed which areas of the human mind are curious about olfactory belief. Alternatively, those strategies don’t permit the sense of scent to be investigated on the basic degree of person nerve cells.“Subsequently, our figuring out of scent processing on the mobile degree is principally according to animal research, and it has now not been transparent to what extent those effects may also be transferred to people,” says co-corresponding creator Prof. Florian Mormann from the Division of Epileptology on the UKB, who may be a member of the Transdisciplinary Analysis Space (TRA) “Lifestyles & Well being” on the College of Bonn.Nerve cells within the mind determine odorsProf. Mormann’s analysis workforce has now succeeded for the primary time in recording the job of person nerve cells right through smelling.This used to be best conceivable for the reason that researchers labored along with sufferers from the Health center for Epileptology on the UKB, probably the most greatest epilepsy facilities in Europe, who had electrodes implanted of their brains for diagnostic functions. They have been offered with each delightful and ugly scents, similar to previous fish.“We found out that specific nerve cells within the human mind react to odors. In response to their job, we have been in a position to exactly expect which smell used to be being smelled,” says first creator Marcel Kehl, a doctoral pupil on the College of Bonn in Prof. Mormann’s running workforce on the UKB.The measurements confirmed that other mind areas similar to the principle olfactory cortex, anatomically referred to as the piriform cortex, and in addition positive spaces of the medial temporal lobe, particularly the amygdala, the hippocampus and the entorhinal cortex, are curious about explicit duties.Whilst the job of nerve cells within the olfactory cortex maximum correctly predicted which smell used to be smelled, neuronal job within the hippocampus used to be in a position to expect whether or not scents have been appropriately recognized.Simplest nerve cells within the amygdala, a area curious about emotional processing, reacted another way relying on whether or not a smell used to be perceived as delightful or unsightly.Nerve cells react to the scent, symbol and identify of the bananaIn a subsequent step, the researchers investigated the relationship between the belief of scents and photographs. To try this, they offered the members within the Bonn find out about with the matching pictures for each and every scent, as an example the smell and later a photograph of a banana, and tested the response of the neurons. Unusually, nerve cells in the principle olfactory cortex answered now not best to scents, but in addition to photographs.“This means that the duty of the human olfactory cortex is going a ways past the natural belief of odors,” says co-corresponding creator Prof. Marc Spehr from the Institute of Biology II at RWTH Aachen College.The researchers found out person nerve cells that reacted particularly to the scent, the picture and the written phrase of – as an example – the banana. This discovery signifies that semantic data are processed early on in human olfactory processing.The effects now not best verify many years of animal research, but in addition display how other mind areas are curious about explicit human scent processing purposes.“That is a very powerful contribution on the best way to interpreting the human olfactory code,” says Prof. Mormann.“Additional analysis on this house is essential in an effort to someday increase olfactory aids that we will be able to use in on a regular basis lifestyles as naturally as glasses or listening to aids.”Investment: The find out about used to be funded through the German Analysis Basis (DFG), the Federal Ministry of Training and Analysis (BMBF) and the state of North Rhine-Westphalia (NRW) as a part of the iBehave venture.About this olfaction and visible neuroscience analysis newsAuthor: Inka Väth
Supply: College of Bonn
Touch: Inka Väth – College of Bonn
Symbol: The picture is credited to Neuroscience NewsOriginal Analysis: Open get right of entry to.
“Unmarried-neuron representations of odours within the human mind” through Florian Mormann et al. NatureAbstractSingle-neuron representations of odours within the human brainOlfaction is a basic sensory modality that guides animal and human behaviour. Alternatively, the underlying neural processes of human olfaction are nonetheless poorly understood on the basic—this is, the single-neuron—degree.Right here we record recordings of single-neuron job within the piriform cortex and medial temporal lobe in unsleeping people acting an odour ranking and identity process. We recognized odour-modulated neurons inside the piriform cortex, amygdala, entorhinal cortex and hippocampus.In each and every of those areas, neuronal firing correctly encodes odour id. Particularly, repeated odour shows cut back reaction firing charges, demonstrating central repetition suppression and habituation.Other medial temporal lobe areas have distinct roles in odour processing, with amygdala neurons encoding subjective odour valence, and hippocampal neurons predicting behavioural odour identity efficiency.While piriform neurons ideally encode chemical odour id, hippocampal job displays subjective odour belief.Seriously, we determine that piriform cortex neurons reliably encode odour-related pictures, supporting a multimodal position of the human piriform cortex.We additionally follow marked cross-modal coding of each odours and photographs, particularly within the amygdala and piriform cortex. Additionally, we determine neurons that reply to semantically coherent odour and symbol data, demonstrating conceptual coding schemes in olfaction.Our effects bridge the long-standing hole between animal fashions and non-invasive human research and advance our figuring out of odour processing within the human mind through figuring out neuronal odour-coding ideas, regional useful variations and cross-modal integration.
How Mind Cells Establish Smells and Comparable Photographs – Neuroscience Information






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-2159881840-e2e04c33a90644f9b7479e6e93e53199.jpg)