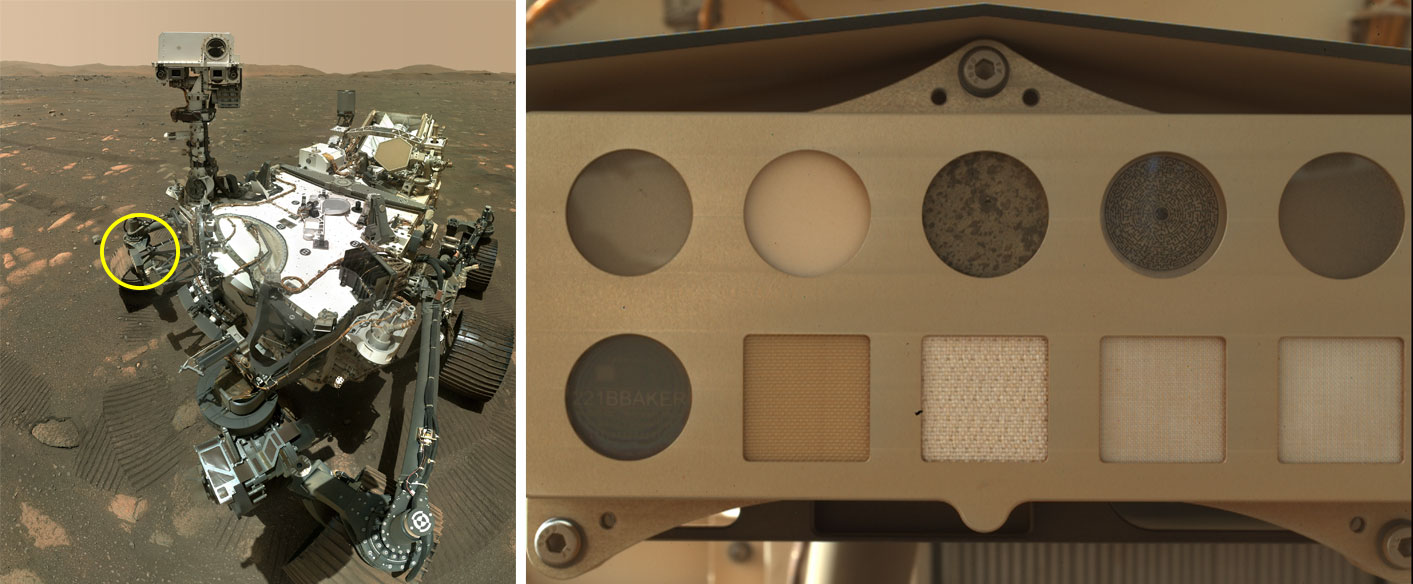
The rover carries a number of swatches of spacesuit fabrics, and scientists are assessing how they’ve held up after 4 years at the Pink Planet.
NASA’s Perseverance rover landed on Mars in 2021 to seek for indicators of historical microbial existence and to lend a hand scientists perceive the planet’s local weather and geography. However every other key goal is to pave the best way for human exploration of Mars, and as a part of that effort, the rover carries a suite of 5 spacesuit subject material samples. Now, after the ones samples have persisted 4 years of publicity on Mars’ dusty, radiation-soaked floor, scientists are starting the following section of learning them.
The tip function is to are expecting as it should be the usable life of a Mars spacesuit. What the company learns about how the fabrics carry out on Mars will tell the design of long term spacesuits for the primary astronauts at the Pink Planet.
“This is without doubt one of the forward-looking facets of the rover’s challenge — no longer simply fascinated about its present science, but additionally about what comes subsequent,” mentioned planetary scientist Marc Fries of NASA’s Johnson House Middle in Houston, who helped give you the spacesuit fabrics. “We’re making ready for folks to ultimately pass and discover Mars.”
The swatches, each and every three-quarters of an inch sq. (20 millimeters sq.), are a part of a calibration goal used to check the settings of SHERLOC (Scanning Liveable Environments with Raman & Luminescence for Organics and Chemical substances), an software at the finish of Perseverance’s arm.
The samples come with a work of polycarbonate helmet visor; Vectran, a cut-resistant subject material used for the fingers of astronaut gloves; two types of Teflon, which has dust-repelling nonstick houses; and a recurrently used spacesuit subject material known as Ortho-Material. This final cloth options a couple of layers, together with Nomex, a flame-resistant subject material present in firefighter outfits; Gore-Tex, which is water-proof however breathable; and Kevlar, a powerful subject material utilized in bulletproof vests that makes spacesuits extra rip-resistant.
Mars is some distance from hospitable. It has freezing temperatures, tremendous filth that may keep on with sun panels and spacesuits (inflicting put on and tear at the latter), and a floor rife with perchlorates, one of those corrosive salt that may be poisonous to people.
There’s additionally a lot of sun radiation. In contrast to Earth, which has a magnetic box that deflects a lot of the Solar’s radiation, Mars misplaced its magnetic box billions of years in the past, adopted via a lot of its environment. Its floor has little coverage from the Solar’s ultraviolet gentle (which is why researchers have seemed into how rock formations and caves may supply astronauts some shielding).
“Mars is a in point of fact harsh, difficult position,” mentioned SHERLOC science workforce member Joby Razzell Hollis of the Herbal Historical past Museum in London. “Don’t underestimate that — the radiation specifically is lovely nasty.”
Razzell Hollis was once a postdoctoral fellow at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California from 2018 to 2021, the place he helped get ready SHERLOC for arrival on Mars and participated in science operations as soon as the rover landed. A fabrics scientist, Razzell Hollis has in the past studied the chemical results of daylight on a brand new roughly sun panel constituted of plastic, in addition to on plastic air pollution floating within the Earth’s oceans.
He likened the ones results to how white plastic garden chairs turn out to be yellow and brittle after years in daylight. Kind of the similar factor occurs on Mars, however the weathering most likely occurs sooner on account of the prime publicity to ultraviolet gentle there.
The important thing to growing more secure spacesuit fabrics will probably be working out how temporarily they’d put on down at the Martian floor. About 50% of the adjustments SHERLOC witnessed within the samples took place inside of Perseverance’s first 200 days on Mars, with the Vectran showing to switch first.
Some other nuance will probably be understanding how a lot sun radiation other portions of a spacesuit can have to resist. As an example, an astronaut’s shoulders will probably be extra uncovered — and most likely come upon extra radiation — than his or her fingers.
The SHERLOC workforce is operating on a science paper detailing preliminary information on how the samples have fared on Mars. In the meantime, scientists at NASA Johnson are desperate to simulate that weathering in particular chambers that mimic the carbon dioxide environment, air power, and ultraviolet gentle at the Martian floor. They may then examine the consequences generated on Earth whilst striking the fabrics to the check with the ones observed within the SHERLOC information. As an example, the researchers may just stretch the fabrics till they damage to test in the event that they turn out to be extra brittle through the years.
“The material fabrics are designed to be difficult however versatile, in order that they give protection to astronauts however can bend freely,” Fries mentioned. “We need to know the level to which the materials lose their energy and versatility through the years. Because the materials weaken, they may be able to fray and tear, permitting a spacesuit to leak each warmth and air.”
A key goal for Perseverance’s challenge on Mars is astrobiology, together with the seek for indicators of historical microbial existence. The rover is characterizing the planet’s geology and previous local weather, to lend a hand pave the best way for human exploration of the Pink Planet, and is the primary challenge to gather and cache Martian rock and regolith.
NASA’s Mars Pattern Go back Program, in cooperation with ESA (Ecu House Company), is designed to ship spacecraft to Mars to gather those sealed samples from the outside and go back them to Earth for in-depth research.
The Mars 2020 Perseverance challenge is a part of NASA’s Mars Exploration Program (MEP) portfolio and the company’s Moon to Mars exploration means, which contains Artemis missions to the Moon that may lend a hand get ready for human exploration of the Pink Planet.
NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is controlled for the company via Caltech in Pasadena, California, constructed and manages operations of the Perseverance rover.
For extra about Perseverance:
Andrew Just right
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif.
818-393-2433
andrew.c.just right@jpl.nasa.gov
Karen Fox / Molly Wasser
NASA Headquarters, Washington
202-358-1600
karen.c.fox@nasa.gov / molly.l.wasser@nasa.gov