(© areebarbar – inventory.adobe.com)
(© areebarbar – inventory.adobe.com)
EDINBURGH, Scotland — In 1932, whilst the remainder of the arena used to be grappling with the Nice Melancholy, Scotland used to be busy giving intelligence checks to almost each and every 11-year-old within the nation. Little did the ones youngsters know they have been kickstarting one of the vital illuminating research ever carried out on how our brains age – or that their take a look at rankings would nonetheless be making medical waves just about a century later.The Lothian Start Cohorts learn about, led through researchers on the College of Edinburgh, has adopted loads of folks born in 1921 and 1936, monitoring their cognitive skills from age 11 into their 70s, 80s, and 90s. After 25 years of study, the scientists have unveiled some sudden discoveries about getting older minds, together with the truth that about part of our intelligence in previous age is decided through how vivid we have been as youngsters.Bring to mind it like a cognitive financial savings account – we begin with a definite stability in adolescence, and whilst existence studies can develop or diminish that preliminary deposit, our early cognitive features have an oversized affect on our psychological acuity many years later. The learn about discovered that anyone who scored neatly on intelligence checks at age 11 used to be more likely to carry out neatly on equivalent checks of their 70s and past.However what concerning the different part of the equation? The researchers came upon that quite a lot of elements affect how neatly we take care of our psychological edge as we age. Some are inside our keep an eye on, like staying bodily energetic and socially engaged, whilst others aren’t, corresponding to our genetic make-up. Alternatively, the results of any unmarried issue have a tendency to be small – there’s no magic bullet for retaining our brains younger.The learn about’s setup used to be remarkably complete. Within the authentic 1932 and 1947 trying out days, virtually each and every 11-year-old kid in Scotland (over 87,000 in 1932 and 70,000 in 1947) took the similar intelligence take a look at. A long time later, researchers tracked down loads of those people dwelling within the Edinburgh space and satisfied them to take part in detailed follow-up research.The members, now of their later years, underwent common trying out each and every few years. They finished cognitive checks, bodily examinations, and mind scans. They equipped blood samples for genetic research and different organic markers. Some even agreed to donate their brains after loss of life for additional analysis.Some of the learn about’s maximum hanging findings used to be the dramatic variation in how folks’s brains age. Mind scans of members at age 73 published that some had brains that regarded many years more youthful than others of the very same age. This modification helped provide an explanation for why some folks take care of their psychological sharpness whilst others enjoy extra important cognitive decline.

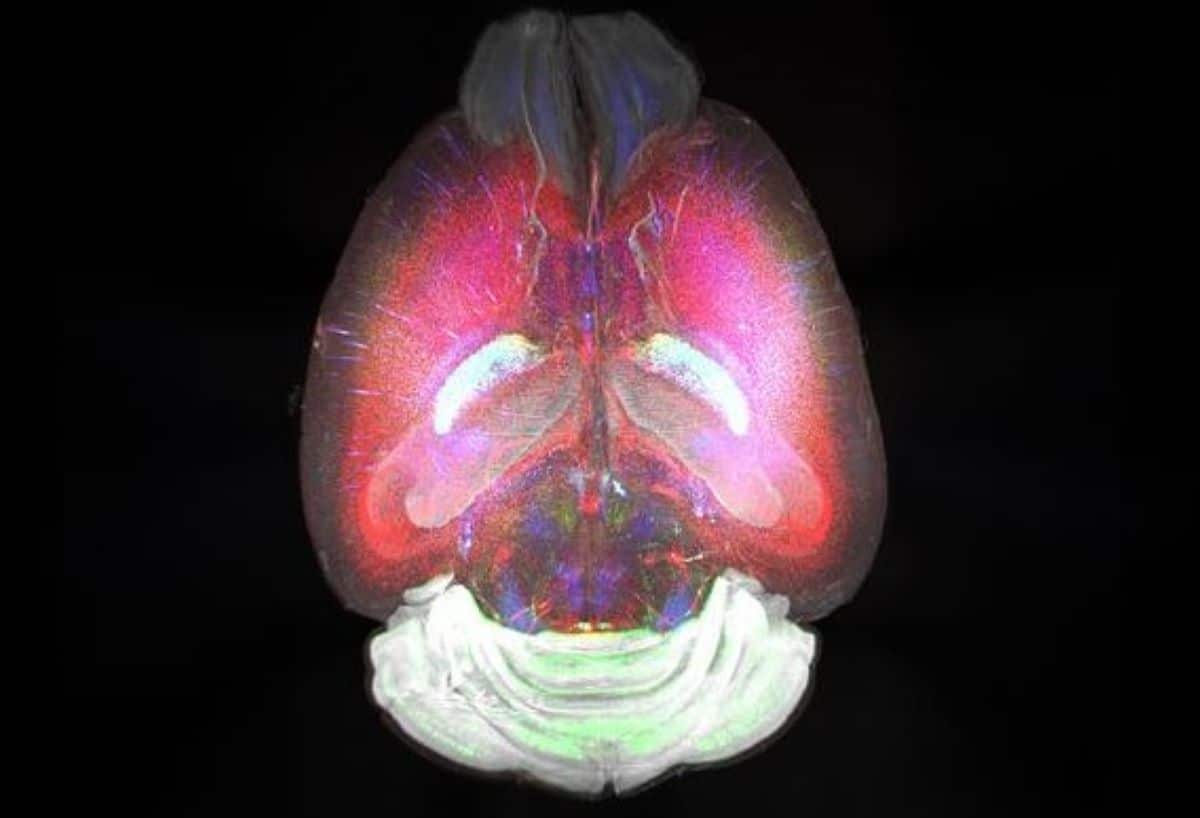
 Mind structural (MRI) scans from a choice of people from the Lothian Start Cohort 1936 taken all the way through Wave 2 (when all members have been about 73 years previous). Panel A displays world atrophy (mind volumetric shrinkage) ordered from least (best left) to maximum (backside proper). Panel B displays general white subject hyperintensity quantity (expanding from best left to backside proper). Panels A and B are reproduced from Cox and Deary (2022) in Mind Ageing, 2, 100032 (74); this newsletter is an open get admission to article dispensed beneath the phrases of the Inventive Commons CC BY 4.0 license and the determine is reproduced right here, with thank you, beneath that license. Panel C displays white subject pathways of a middle-aged male grownup, known the use of diffusion MRI. Perspectives from left to proper: awesome, lateral, anterior, inferior. (Credit score: Ian J. Deary)
Mind structural (MRI) scans from a choice of people from the Lothian Start Cohort 1936 taken all the way through Wave 2 (when all members have been about 73 years previous). Panel A displays world atrophy (mind volumetric shrinkage) ordered from least (best left) to maximum (backside proper). Panel B displays general white subject hyperintensity quantity (expanding from best left to backside proper). Panels A and B are reproduced from Cox and Deary (2022) in Mind Ageing, 2, 100032 (74); this newsletter is an open get admission to article dispensed beneath the phrases of the Inventive Commons CC BY 4.0 license and the determine is reproduced right here, with thank you, beneath that license. Panel C displays white subject pathways of a middle-aged male grownup, known the use of diffusion MRI. Perspectives from left to proper: awesome, lateral, anterior, inferior. (Credit score: Ian J. Deary)
“What’s in particular attention-grabbing is that even after seven many years, we discovered correlations of about 0.7 between adolescence and older-age cognitive rankings,” explains learn about co-author Ian Deary, a professor at Edinburgh, in a observation. “Which means slightly below part of the variance in intelligence in older age used to be already provide at age 11.”The analysis additionally challenged some not unusual assumptions. For example, many elements that appear to have an effect on cognitive skill in previous age – like bodily health, social engagement, and irritation ranges – grew to become out to be in part defined through adolescence intelligence. In different phrases, smarter children have been much more likely to take care of wholesome life and interact in mentally stimulating actions during their lives.However it’s no longer all predetermined through adolescence skill. The researchers known a number of elements that seem to assist take care of cognitive serve as, together with training, bodily task, and no longer smoking. Alternatively, every issue’s particular person impact has a tendency to be modest – suggesting that the most efficient technique to cognitive getting older is to make a couple of small sure adjustments slightly than in search of a unmarried answer.The learn about has additionally contributed to our working out of ways genes affect cognitive getting older. Whilst genetic elements play a task, their results are complicated and ceaselessly tiny. One exception is the APOE e4 gene variant, which used to be discovered to be related to decrease cognitive efficiency in previous age however, curiously, confirmed no impact on adolescence cognitive skill.The researchers made some other attention-grabbing discovery about DNA methylation – chemical adjustments to our DNA that may alternate with age. They discovered that those age-related DNA adjustments may expect how lengthy folks would reside, providing a brand new option to measure organic getting older on the molecular stage.Most likely maximum encouragingly, the learn about confirmed that cognitive decline isn’t inevitable or uniform. Whilst some members skilled important decreases in psychological skill, others maintained sharp minds neatly into their 80s and 90s. This means that whilst we will’t totally save you cognitive getting older, we might be able to affect its trajectory thru way of life possible choices and environmental elements.From take a look at papers to mind scans, from adolescence mathematics to twilight years’ knowledge, the Lothian Start Cohorts learn about has proven us that cognitive getting older isn’t with reference to maintaining what now we have – it’s about working out the place we began and taking advantage of each and every step alongside the best way.
Paper Abstract
Technique
The learn about started with ancient intelligence take a look at information from the Scottish Psychological Surveys of 1932 and 1947, which examined virtually all 11-year-old youngsters in Scotland. Researchers later recruited 550 folks born in 1921 and 1091 born in 1936 who had taken those authentic checks.
Contributors underwent common trying out each and every few years, together with cognitive checks, bodily examinations, mind imaging, blood checks, and quite a lot of different measurements. The trying out used to be complete, inspecting the entirety from grip energy to DNA methylation patterns. The learn about design allowed researchers to trace adjustments in cognitive skill and quite a lot of well being markers over the years whilst controlling for adolescence intelligence.
Key Effects
Key findings incorporated: roughly 50% of cognitive skill in older age is defined through adolescence intelligence; mind getting older varies dramatically between people of the similar age; genetic elements affect cognitive getting older however maximum genetic results are very small; the APOE e4 gene impacts cognitive skill in previous age however no longer in adolescence; DNA methylation patterns can expect longevity; and a couple of way of life elements every have small however cumulative results on cognitive getting older.
Learn about Obstacles
The learn about essentially taken with members from the Edinburgh space of Scotland, doubtlessly proscribing its generalizability to different populations. There used to be additionally inevitable player attrition over the many years, with more fit people much more likely to proceed collaborating. The learn about lacked information from members’ center years (between age 11 and older age), even though researchers tried to fill this hole thru retrospective reporting and different tactics.
Dialogue & Takeaways
The analysis means that cognitive getting older is influenced through each early-life elements and ongoing way of life possible choices, however no unmarried issue has a big impact. This helps a “marginal beneficial properties” technique to wholesome getting older, the place a couple of small sure adjustments would possibly acquire to supply significant advantages. The learn about emphasizes that cognitive decline isn’t inevitable and varies considerably between people, suggesting alternatives for intervention to advertise more fit mind getting older.
Investment & Disclosures
The analysis has been funded through quite a lot of organizations over its 25-year span, together with Age UK, the United Kingdom Analysis and Innovation our bodies, BBSRC, and MRC. The present paintings is supported through the Nationwide Institutes of Well being, BBSRC, ESRC, MRC, Milton Damerel Accept as true with, and the College of Edinburgh. The authors declared no conflicts of pastime.