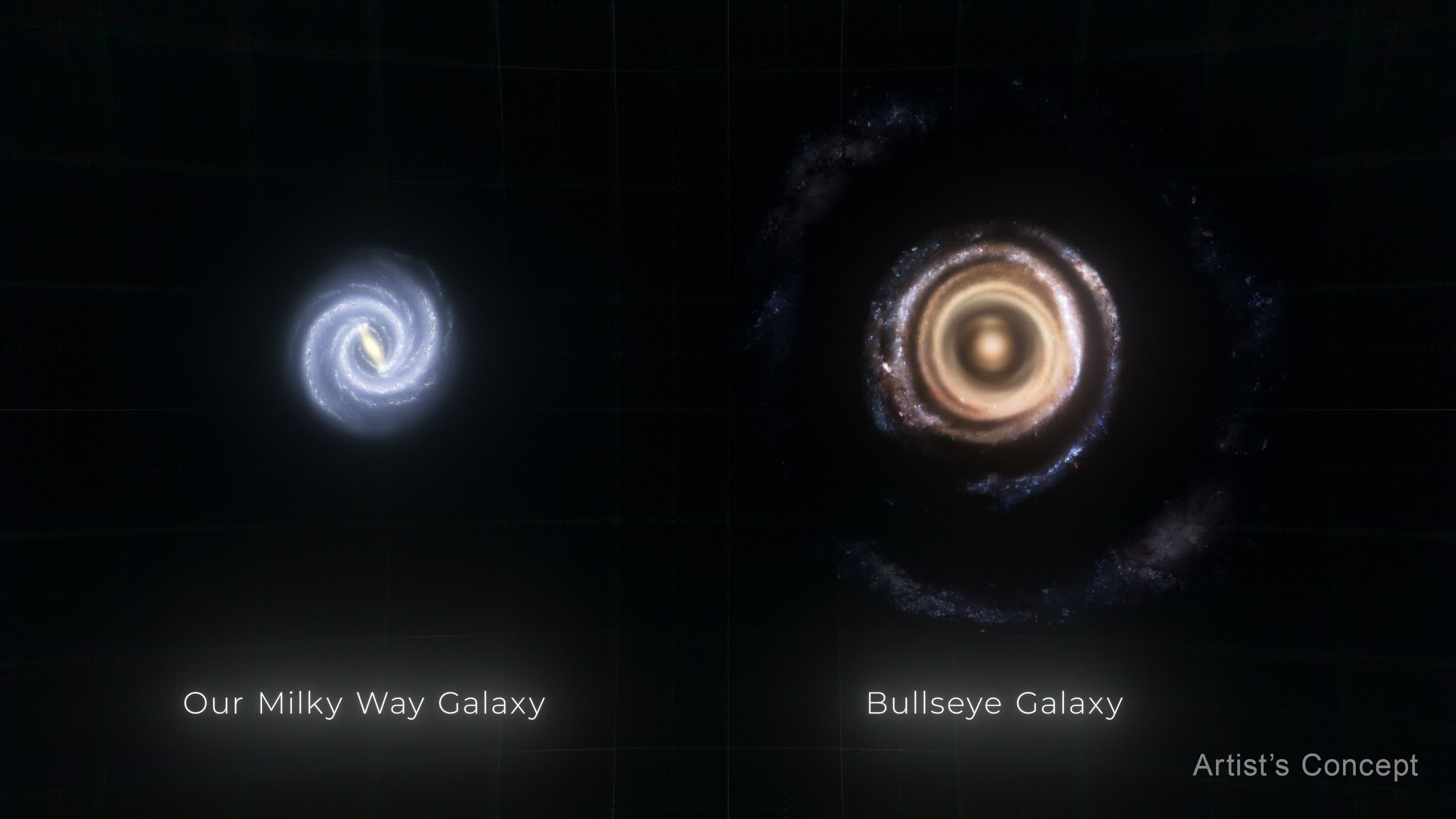
The large image: NASA’s Hubble Area Telescope has captured an atypical cosmic tournament that astronomers are calling the “Bullseye.” The large galaxy LEDA 1313424 has been seen with an unparalleled 9 star-filled rings, the results of a dramatic collision with a smaller blue dwarf galaxy.
The invention used to be made by means of Imad Pasha, a doctoral scholar at Yale College, who stumbled upon the original galaxy whilst inspecting a ground-based imaging survey. “This used to be a serendipitous discovery,” Pasha defined. “After I noticed a galaxy with a number of transparent rings, I used to be straight away interested in it. I needed to prevent to research it.”
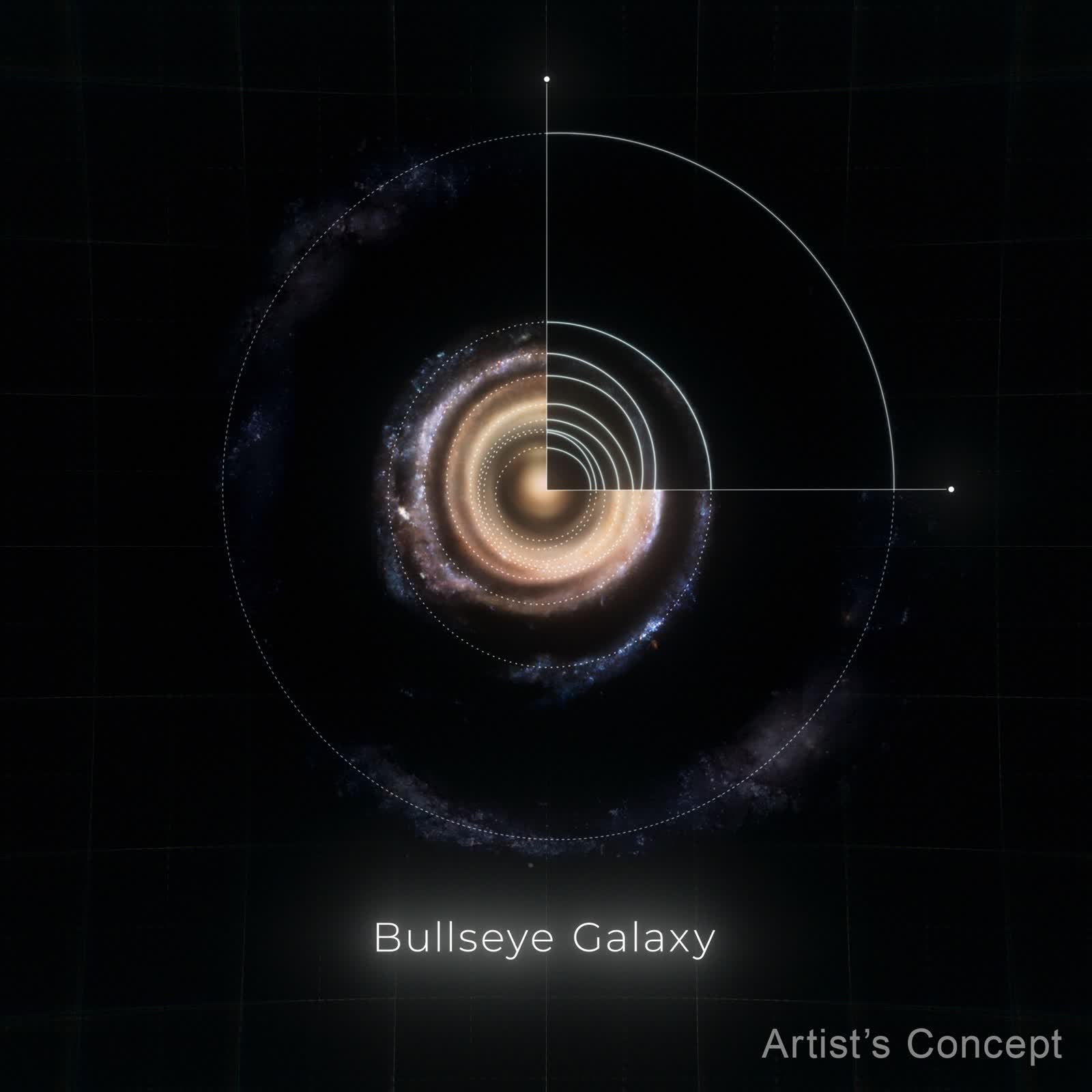
Next observations the usage of each the Hubble Area Telescope and the W. M. Keck Observatory in Hawaii showed the presence of 9 rings, a long way surpassing the former document of 2 or 3 rings seen in different galaxies.

The rings are believed to have shaped 50 million years in the past when a blue dwarf galaxy plunged throughout the heart of LEDA 1313424 like an arrow. This cosmic collision created ripples very similar to the ones shaped when a pebble is dropped right into a pond.
That is an especially uncommon tournament, in line with Professor Pieter G. van Dokkum, a co-author of the find out about, which seemed in The Astrophysical Magazine Letters. “We are catching the Bullseye at an excessively particular second in time. There is a very slim window after the have an effect on when a galaxy like this may have such a lot of rings.”
The Bullseye galaxy dwarfs our Milky Means, measuring an outstanding 250,000 light-years throughout – just about two and a part occasions greater than our house galaxy. The blue dwarf galaxy accountable for developing this cosmic spectacle now lies 130,000 light-years away, hooked up to the Bullseye by means of a skinny path of fuel.
The Hubble Area Telescope’s outstanding solution used to be instrumental in figuring out many of the rings, in particular the ones clustered on the galaxy’s heart. “This could had been not possible with out Hubble,” Pasha mentioned.

In all probability most fun for the medical neighborhood is how the Bullseye galaxy aligns with present theoretical fashions. “That principle used to be evolved for the day that anyone noticed such a lot of rings,” van Dokkum defined. “It’s immensely pleasant to verify this long-standing prediction with the Bullseye galaxy.”
The rings’ formation and growth intently fit predictions, with the primary rings forming temporarily and spreading outward, adopted by means of next rings created because the dwarf galaxy handed thru.
This discovery opens up new avenues for analysis into galaxy collisions and their long-term results. Astronomers will now paintings to decide which stars existed sooner than and after the collision and the way the galaxy would possibly evolve over billions of years.
The risk discovery of the Bullseye galaxy additionally hints at the potential of long run findings. Van Dokkum is especially serious about the potentialities presented by means of NASA’s upcoming Nancy Grace Roman Area Telescope. “As soon as NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Area Telescope starts science operations, fascinating items will come out a lot more simply. We can find out how uncommon those impressive occasions in reality are.”