Astronomers have witnessed the titanic collision between two neutron stars that resulted within the delivery of the smallest black hollow ever noticed and solid valuable metals like gold, silver, and uranium. The staff’s snapshot of this violent and robust collision, which passed off 130 million light-years clear of us within the galaxy NGC 4993, used to be created with a variety of tools, together with the Hubble Area Telescope. It’ll confidently paint an image of the “previous, provide, and long term” of the mergers of those dense lifeless stars. This might divulge the origins of components heavier than iron, which cannot be solid in even essentially the most large stars. The collision and merger of the neutron stars ends up in a formidable blast of sunshine referred to as a “kilonova.” Because the wreckage of this tournament expands at just about the velocity of sunshine, the kilonova illuminates its environment with mild as vivid as loads of thousands and thousands of suns.A staff of researchers led via scientists for the Cosmic DAWN Heart on the Neils Bohr Institute arrived at this new image of neutron celebrity mergers once they set about investigating the mysteries of kilonovas.”We will now see the instant the place atomic nuclei and electrons are uniting within the afterglow,” staff member Rasmus Damgaard, a researcher on the Cosmic DAWN Heart, stated in a observation. For the primary time, we see the advent of atoms, we will be able to measure the temperature of the topic, and we will be able to see the microphysics on this far off explosion.””It’s like admiring 3 cosmic background radiation surrounding us from each side, however right here, we get to look the whole thing from the out of doors. We see earlier than, throughout, and after the instant of delivery of the atoms.”The gold for your jewellery got here from the universe’s maximum violents eventsNeutron stars are born when stars no less than 8 occasions as large because the solar exhaust their gasoline for nuclear fusion and will not give a boost to themselves in opposition to their very own gravity.Breaking area information, the newest updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!The outer layers of those stars are blasted away in supernova explosions, leaving a stellar remnant with a mass equivalent to between 1 and a couple of suns overwhelmed right into a diameter of round 12 miles (20 kilometers). The cave in of the core forces electrons and protons in combination, making a sea of debris referred to as neutrons. This subject matter is so dense {that a} mere sugar dice’s value of neutron celebrity topic would weigh 1 billion lots if dropped at Earth. That is about the similar as cramming 150,000,000 elephants into the similar area {that a} sugar dice occupies.It’s most likely no marvel that this excessive and unique topic performs a key position in growing components heavier than iron. An indication displays a cloud of subject matter erupting from a collision of neutron stars (Symbol credit score: NASA Goddard/CI Lab)Neutron stars do not all the time are living in isolation. A few of these lifeless stars occupy binary methods in conjunction with a better half dwelling celebrity. In uncommon circumstances, this better half celebrity could also be large sufficient to create a neutron celebrity, and it is not “kicked away” via the supernova explosion that creates the primary neutron celebrity.The result’s a gadget with two neutron stars orbiting each and every different. Those items are so dense that as they swirl round each and every different, they generate ripples in spacetime (the 4-dimensional unification of area and time) referred to as gravitational waves that ripple via area, wearing away angular momentum.Because the gadget loses angular momentum, the orbit of the neutron stars tightens, that means that the neutron stars transfer nearer to one another. This ends up in gravitational waves rippling away sooner and sooner, wearing away increasingly more angular momentum.This example ends when neutron stars are shut sufficient for his or her immense gravity to take over and drag those extraordinarily dense lifeless stars in combination to collide and merge.This collision sprays out neutron-rich topic with temperatures of many billions of levels, hundreds of occasions warmer than the solar. Those temperatures are so scorching that they’re very similar to the ones of the impulsively inflating universe only one 2d after the Large Bang.
An indication displays a cloud of subject matter erupting from a collision of neutron stars (Symbol credit score: NASA Goddard/CI Lab)Neutron stars do not all the time are living in isolation. A few of these lifeless stars occupy binary methods in conjunction with a better half dwelling celebrity. In uncommon circumstances, this better half celebrity could also be large sufficient to create a neutron celebrity, and it is not “kicked away” via the supernova explosion that creates the primary neutron celebrity.The result’s a gadget with two neutron stars orbiting each and every different. Those items are so dense that as they swirl round each and every different, they generate ripples in spacetime (the 4-dimensional unification of area and time) referred to as gravitational waves that ripple via area, wearing away angular momentum.Because the gadget loses angular momentum, the orbit of the neutron stars tightens, that means that the neutron stars transfer nearer to one another. This ends up in gravitational waves rippling away sooner and sooner, wearing away increasingly more angular momentum.This example ends when neutron stars are shut sufficient for his or her immense gravity to take over and drag those extraordinarily dense lifeless stars in combination to collide and merge.This collision sprays out neutron-rich topic with temperatures of many billions of levels, hundreds of occasions warmer than the solar. Those temperatures are so scorching that they’re very similar to the ones of the impulsively inflating universe only one 2d after the Large Bang. 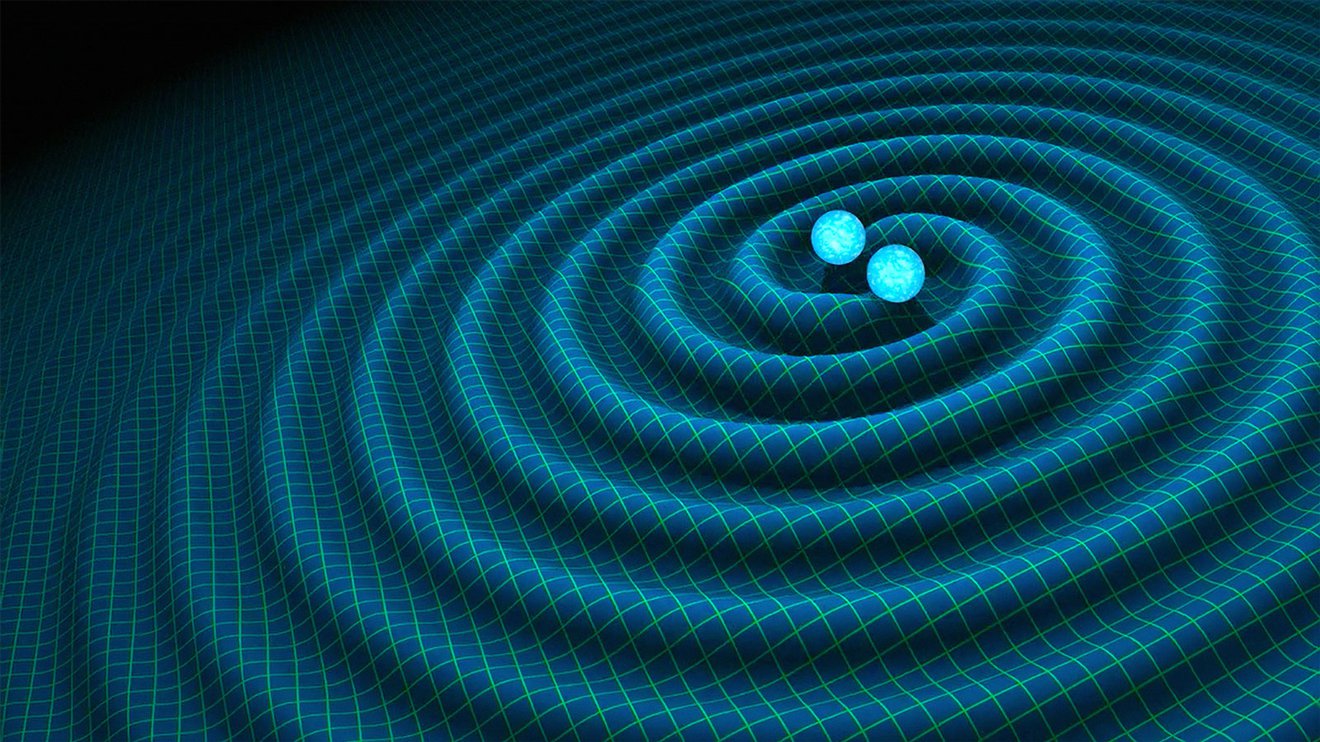 An artist’s depiction of colliding neutron stars sending out ripples in spacetime referred to as gravitational waves. (Symbol credit score: R. Harm/Caltech-JPL)Ejected debris like electrons and neutrons dance across the frame, birthed via the colliding neutron stars, which impulsively cave in to shape a black hollow in a fog of plasma that cools over the following few days.Atoms on this cooling cloud of plasma temporarily take hold of loose neutrons by means of what is named the fast neutron seize task (r-process) and in addition ensnare loose electrons. This creates very heavy however volatile debris that impulsively decay. This decay releases the sunshine that astronomers see as kilonovas, but it surely additionally creates lighter components which are nonetheless heavier than iron, like gold, silver and uranium. This staff noticed the afterglow of debris being snatched to forge heavy components like Strontium and Yttrium, reasoning that different heavy components have been certainly created within the aftermath of this neutron celebrity collision.”The topic expands so speedy and features in measurement so impulsively, to the level the place it takes hours for the sunshine to trip around the explosion,” staff member Kasper Heintz, a researcher on the Niels Bohr Institute, stated. “This is the reason, simply by staring at the far off finish of the fireball, we will be able to see additional again within the historical past of the explosion. Nearer to us, the electrons have hooked to atomic nuclei, however at the different facet, at the some distance facet of the child black hollow, the ‘provide’ remains to be simply the long run.”The staff’s effects do not have been conceivable with out the collaboration of telescopes around the globe and past.”This astrophysical explosion develops dramatically hour via hour, so no unmarried telescope can practice its complete tale. The viewing attitude of the person telescopes to the development is blocked via the rotation of the Earth,” staff chief and Neils Bohr Institute researcher Albert Sneppen stated within the observation. “However via combining the present measurements from Australia, South Africa, and the Hubble Area Telescope, we will be able to practice its construction in nice element.”The staff’s paper used to be revealed on Wednesday (Oct. 30) within the magazine Astronomy & Astrophysics.
An artist’s depiction of colliding neutron stars sending out ripples in spacetime referred to as gravitational waves. (Symbol credit score: R. Harm/Caltech-JPL)Ejected debris like electrons and neutrons dance across the frame, birthed via the colliding neutron stars, which impulsively cave in to shape a black hollow in a fog of plasma that cools over the following few days.Atoms on this cooling cloud of plasma temporarily take hold of loose neutrons by means of what is named the fast neutron seize task (r-process) and in addition ensnare loose electrons. This creates very heavy however volatile debris that impulsively decay. This decay releases the sunshine that astronomers see as kilonovas, but it surely additionally creates lighter components which are nonetheless heavier than iron, like gold, silver and uranium. This staff noticed the afterglow of debris being snatched to forge heavy components like Strontium and Yttrium, reasoning that different heavy components have been certainly created within the aftermath of this neutron celebrity collision.”The topic expands so speedy and features in measurement so impulsively, to the level the place it takes hours for the sunshine to trip around the explosion,” staff member Kasper Heintz, a researcher on the Niels Bohr Institute, stated. “This is the reason, simply by staring at the far off finish of the fireball, we will be able to see additional again within the historical past of the explosion. Nearer to us, the electrons have hooked to atomic nuclei, however at the different facet, at the some distance facet of the child black hollow, the ‘provide’ remains to be simply the long run.”The staff’s effects do not have been conceivable with out the collaboration of telescopes around the globe and past.”This astrophysical explosion develops dramatically hour via hour, so no unmarried telescope can practice its complete tale. The viewing attitude of the person telescopes to the development is blocked via the rotation of the Earth,” staff chief and Neils Bohr Institute researcher Albert Sneppen stated within the observation. “However via combining the present measurements from Australia, South Africa, and the Hubble Area Telescope, we will be able to practice its construction in nice element.”The staff’s paper used to be revealed on Wednesday (Oct. 30) within the magazine Astronomy & Astrophysics.
Hubble watches neutron stars collide and explode to create black hollow and ‘delivery atoms’