Scientists looking for the fossilized stays of historic microbes on Mars now have a greater concept of what indicators they must be in search of, due to a brand new learn about of Earthly microbial fossils embedded within the mineral gypsum that used to be produced when the Mediterranean Ocean dried up over 5 million years in the past.Mars used to be as soon as rainy, with rivers and lakes or even an ocean that existed at the Pink Planet between about 4.1 and three.7 billion years in the past. That liquid water has now all long gone, both frozen into polar ice caps or as permafrost underneath the skin, or evaporated into the ambience and misplaced to area. When water evaporates, it leaves at the back of sulfate minerals that were dissolved within the water — a easy faculty experiment of boiling away rain water finds this.Such a minerals is gypsum, which “has been extensively detected at the Martian floor and is understood for its outstanding fossilization possible,” stated Youcef Sellam, who’s a PhD pupil on the College of Bern, in a remark. “It paperwork swiftly, trapping microorganisms sooner than decomposition happens, and preserves organic buildings and chemical biosignatures.”Sellam travelled again to his nation of beginning, Algeria, to pattern gypsum from a quarry referred to as Sidi Boutbal, which is situated in a area that after upon a time used to be underneath the water of the Mediterranean. Between 5.96 and 5.33 million years in the past, tectonic forces closed what’s now the Strait of Gibraltar, quickly reducing off the Mediterranean from the Atlantic Ocean, prompting the Mediterranean to nearly totally dry up. This left at the back of ample salt and sulfate deposits, together with gypsum, in an atmosphere that used to be similar to how Mars’ dried-up lake- and river-beds are these days.”Those deposits supply a very good terrestrial analog for Martian sulfate deposits,” stated Sellam.To investigate what used to be within the gypsum-rich samples, Sellam subjected them to a miniature laser-powered mass spectrometer, one selected as a result of it’s sufficiently small to suit on a spacecraft and subsequently may just function an explanation of thought for this sort of device that can fly to the Pink Planet at some point.”Our laser ablation ionization mass spectrometer, a spaceflight-prototype device, can successfully come across biosignatures in sulfate minerals,” stated Sellam. “This generation might be built-in into long run Mars rovers or landers for in-situ research.”Breaking area information, the most recent updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!The laser, when fired on the pattern, blasts away crusty subject material at the floor of the pattern, super-heating that subject material in order that it evaporates right into a plasma — a cloud of ionized atoms and molecules. A microscope then observes that plasma, figuring out the molecules inside.Sellam discovered lengthy, twisting, microscopic filaments of a kind in the past recognized as being microbial fossils belonging to sulfur-oxidizing micro organism.Those fossil remnants had been surrounded by way of clay minerals in addition to dolomite and pyrite. This actual mixture of fossils and minerals is especially telling. Dolomite dissolves in acidic environments, and Mars is thought to have had very acidic waters. Alternatively, prokaryotes (primitive, single-celled microbes missing a definite nucleus and membrane) can paintings to extend the alkalinity in their atmosphere. If prokaryotic existence existed on historic Mars, it would have helped dolomite shape. As well as, prokaryotes too can assist clays shape sooner.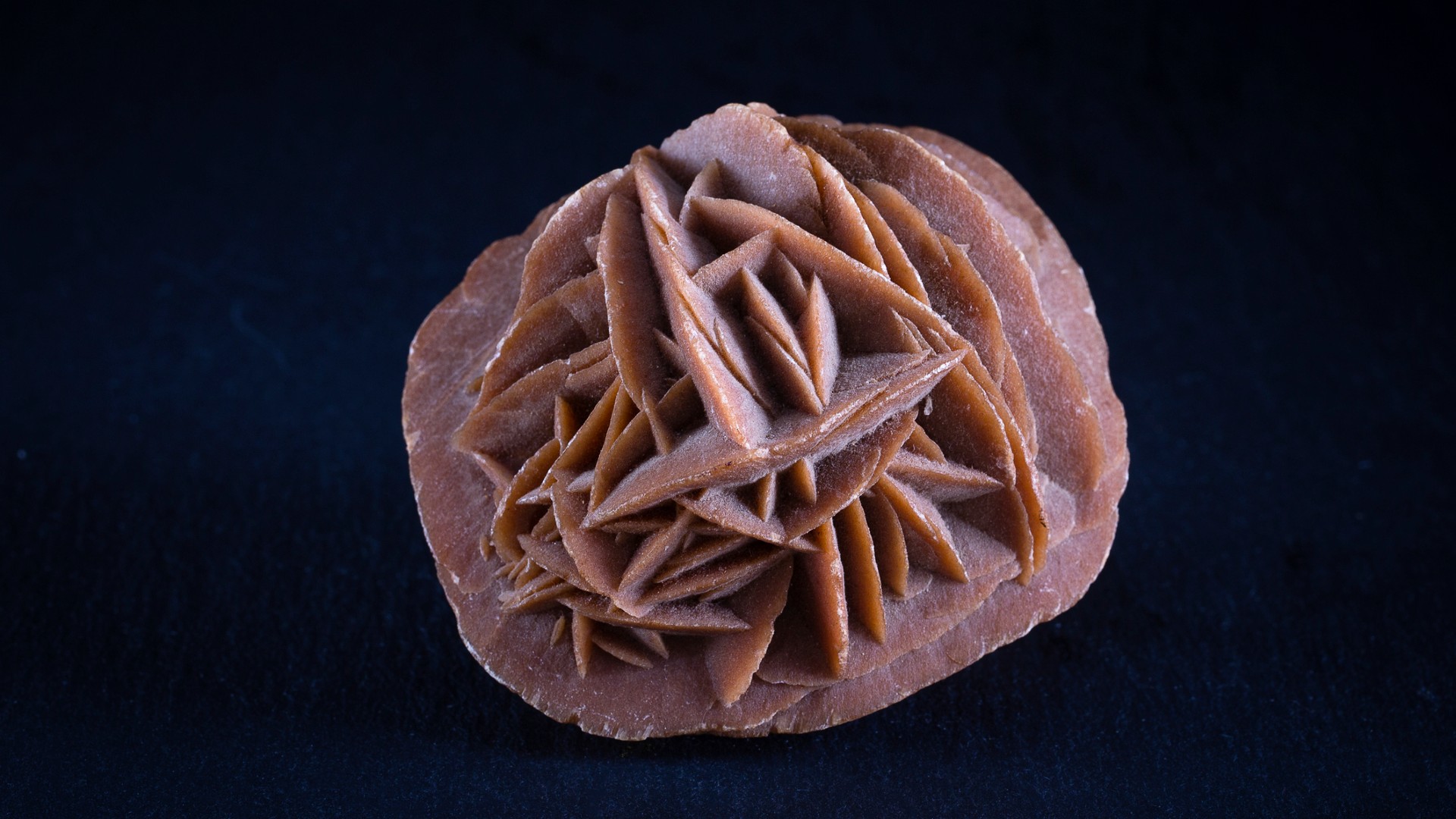 A “barren region rose,” a crystal composed of gypsum, water and sand, shaped in deserts as shallow water evaporates. (Symbol credit score: intek1/Getty Photographs)Sellam had the benefit of already realizing what microbial fossil remnants he may just anticipate finding his Algerian gypsum pattern, however we can’t make sure that shall we readily establish Martian microbial fossils — their unknown alien nature may cause them to tough to differentiate from microscopic rock formations. Alternatively, discovering issues that appear to be the might be fossils embedded in gypsum surrounded by way of clay and particularly dolomite could be a robust indication that the fossil-like buildings are organic, given the relationship between the ones minerals and existence.”Our findings supply a methodological framework for detecting biosignatures in Martian sulfate minerals, doubtlessly guiding long run Mars exploration missions,” stated Sellam.Mars missions subsequently want to be in search of dolomite and clay in gypsum-rich Martian samples to supply a large clue as to the place we may in finding proof of historic existence at the Pink Planet. Alternatively, Sellam says that there’s nonetheless a lot to do sooner than this technique of discovering Martian microbes will also be thought to be watertight.”Whilst our findings strongly beef up the biogenicity of the fossil filaments in gypsum, distinguishing true biosignatures from abiotic mineral formations stays a problem,” he stated. “An extra unbiased detection means would support the boldness in existence detection. Moreover, Mars has distinctive environmental prerequisites, which might have an effect on biosignature preservation over geological sessions. Additional research are wanted.”Nonetheless, Sellam is proud to have led “the primary astrobiology learn about to contain Algeria,” and believes that his findings are a big step in opposition to discovering proof of existence on Mars.Certainly, that day may just come quickly. The following rover challenge to release for the Pink Planet would be the Ecu Area Company’s Rosalind Franklin rover, scheduled to blast off sooner than the tip of this decade. Rosalind Franklin can be provided with numerous mass spectrometers designed to check the mineralogy of Mars and seek for proof of previous microbial existence.Then there is additionally the samples accumulated by way of NASA’s Perseverance rover, which nonetheless want to be accumulated from Mars and taken again to Earth for detailed research, with a bit of luck within the subsequent decade.Sellam’s paintings used to be printed on Feb. 25 in Frontiers in Astronomy and Area Sciences
A “barren region rose,” a crystal composed of gypsum, water and sand, shaped in deserts as shallow water evaporates. (Symbol credit score: intek1/Getty Photographs)Sellam had the benefit of already realizing what microbial fossil remnants he may just anticipate finding his Algerian gypsum pattern, however we can’t make sure that shall we readily establish Martian microbial fossils — their unknown alien nature may cause them to tough to differentiate from microscopic rock formations. Alternatively, discovering issues that appear to be the might be fossils embedded in gypsum surrounded by way of clay and particularly dolomite could be a robust indication that the fossil-like buildings are organic, given the relationship between the ones minerals and existence.”Our findings supply a methodological framework for detecting biosignatures in Martian sulfate minerals, doubtlessly guiding long run Mars exploration missions,” stated Sellam.Mars missions subsequently want to be in search of dolomite and clay in gypsum-rich Martian samples to supply a large clue as to the place we may in finding proof of historic existence at the Pink Planet. Alternatively, Sellam says that there’s nonetheless a lot to do sooner than this technique of discovering Martian microbes will also be thought to be watertight.”Whilst our findings strongly beef up the biogenicity of the fossil filaments in gypsum, distinguishing true biosignatures from abiotic mineral formations stays a problem,” he stated. “An extra unbiased detection means would support the boldness in existence detection. Moreover, Mars has distinctive environmental prerequisites, which might have an effect on biosignature preservation over geological sessions. Additional research are wanted.”Nonetheless, Sellam is proud to have led “the primary astrobiology learn about to contain Algeria,” and believes that his findings are a big step in opposition to discovering proof of existence on Mars.Certainly, that day may just come quickly. The following rover challenge to release for the Pink Planet would be the Ecu Area Company’s Rosalind Franklin rover, scheduled to blast off sooner than the tip of this decade. Rosalind Franklin can be provided with numerous mass spectrometers designed to check the mineralogy of Mars and seek for proof of previous microbial existence.Then there is additionally the samples accumulated by way of NASA’s Perseverance rover, which nonetheless want to be accumulated from Mars and taken again to Earth for detailed research, with a bit of luck within the subsequent decade.Sellam’s paintings used to be printed on Feb. 25 in Frontiers in Astronomy and Area Sciences
If Mars has microbe fossils, a laser and rock quarry in Algeria may just assist in finding them