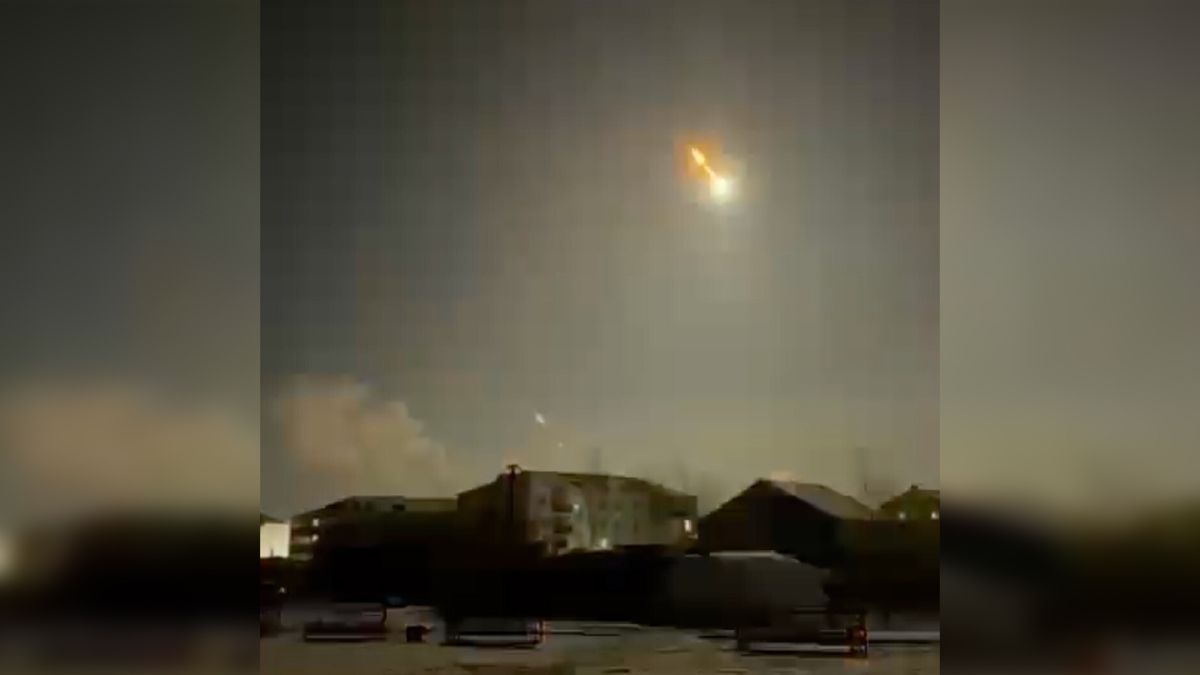
A small asteroid lit up the skies over northern Siberia Wednesday (Dec. 4) after burning up in Earth’s environment in a “impressive” (but innocuous) fireball.Astronomers noticed the gap rock, measuring 28 inches (70 centimeters) in diameter, within the early hours on Wednesday native time, simply hours sooner than the gap rock entered the ambience.”Due to observations from astronomers all over the world, our alert device used to be in a position to expect this influence to inside +/- 10 seconds,” the Eu House Company (ESA) wrote in a publish on X, previously Twitter.C0WEPC5, because the asteroid has been quickly named, entered Earth’s environment at 1:15 a.m. native time on Dec. 4 over Russia’s faraway Sakha Republic, sometimes called Yakutia, in northeastern Siberia. Native officers have been put on alert, the Sakha emergencies ministry famous, however no harm used to be reported all over the development.Comparable: Tiny asteroid detected hours sooner than hitting Earth to turn into 4th ‘approaching impactor’ of 2024Footage of the fireball used to be shared via the Sakha Republic Ministry Of Inner Affairs on Telegram. The pictures used to be from colleagues on the Division of the Ministry of Inner Affairs of Russia for the Olekminsky District and town citizens.NASA’s Asteroid Terrestrial-impact Closing Alert Gadget (ATLAS) noticed the gap rock 12 hours sooner than it entered our environment, ESA mentioned, making it the fourth so-called “approaching impactor” detected to this point this 12 months, and the eleventh one detected general.Breaking area information, the newest updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!The primary asteroid to be detected and tracked on this means used to be a 13-foot-wide (4-meter-wide) area rock known as 2008 TC3, which broke up above Sudan in October 2008. However the device did not hit upon every other one till January 2014, when California’s Mount Lemmon observatory spotted meteoroid 2014 AA a number of hours sooner than it streaked via our skies. Alternatively, since then, our talent to seek out those impactors has a great deal progressed and area businesses at the moment are detecting a number of approaching impactors annually.Whilst asteroids like C0WEPC5 pose no danger to the planet, having those detection programs in position offers astronomers the chance to spot and deflect higher and extra bad items on a collision route with Earth.Consequently, each NASA and ESA have devoted techniques for recognizing and monitoring those near-Earth items. Thankfully, no recognized asteroid poses a danger to Earth for no less than the following 100 years.
‘Impressive’ asteroid blazes over Siberia simply hours after it used to be detected