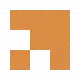A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifts off from Kennedy House Heart in Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Feb. 15, 2024. The rocket is wearing Intuitive Machines’ lunar lander on its technique to the moon, with a deliberate Feb. 22 landing.
John Raoux/AP
disguise caption
toggle caption
John Raoux/AP

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifts off from Kennedy House Heart in Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Feb. 15, 2024. The rocket is wearing Intuitive Machines’ lunar lander on its technique to the moon, with a deliberate Feb. 22 landing.
John Raoux/AP
Some other American corporate is having a pass at getting the U.S. again to the moon. An uncrewed lunar lander that introduced from Cape Canaveral, Fla., ultimate week is scheduled to land close to the moon’s south pole on Thursday. The lander, named Odysseus, comes from the Houston corporate Intuitive Machines, and used to be despatched on its lunar trail by means of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket. If all is going easily, Intuitive Machines will be the first personal corporate to achieve the moon. It could even be the primary American lunar touchdown in additional than 50 years. It is all a part of a brand new entrance within the area race, this time between personal firms making an attempt to get to the moon, and towards NASA’s larger function of increasing the chances of otherworldly exploration.
Previous makes an attempt at a moon touchdown from the non-public sector, by means of firms in Israel, Japan, and the U.S. ultimate month, have been a bust.


Whilst the distance company conquered the moon touchdown all through the Apollo generation that resulted in 1972, it needs to get astronauts again to moon at a lower price. To try this, NASA has been subcontracting some paintings to the non-public sector thru its Business Lunar Payload Services and products (CLPS) program. The speculation is that NASA may someday use firms like Intuitive Machines to ship provides and gear to astronauts. NASA says it paid Intuitive Machines $118 million for the Odyssey lander challenge. Through comparability, it normally prices NASA between $500 million to $1 billion to construct a lander, in line with Thomas Zurbuchen, a former affiliate administrator for science at NASA who ran a value estimate whilst on the company. The moon’s in large part unexplored south pole area attracts explicit intrigue for its water ice positioned in craters which may be siphoned for rocket gas and, after all, maintain people, doubtlessly extending area missions. NASA is sending a gaggle of tools with the lander that, if all is going smartly, will deliver again details about the lunar atmosphere. However it is a giant “if.” A month in the past, an try by means of Pittsburgh-based Astrobotic Era to ship its lander Peregrine to the moon went awry after a malfunction brought about a propellant leak.
We’ve got been to the moon earlier than. Why is that this new area frontier so difficult? The U.S. effectively despatched people to the moon a long time in the past. So, why have those uncrewed lunar missions been fraught with top possibility and failure? For one, the economic technique comes to a decent price range. “If you have limitless finances like they did all through on the Apollo days, sure, you’ll do improbable issues,” Intuitive Machines vp of area methods Trent Martin stated at a press convention on Tuesday. “Now, are we able to give you the option to do it for a lower price, the place there’s a market that isn’t pushed only by means of govt finances?” The non-public sector efforts also are running with a distinct blueprint on those missions, the usage of new era, in line with NASA. “We are not looking to re-do Apollo,” stated Joel Kearns, the deputy affiliate administrator for exploration in NASA’s science challenge directorate. “We are going after medical and era research that were not even envisioned again within the time of Apollo to reply to primary medical questions. And we are going to a area of the moon that folks and robots have by no means been to.” Geoff Brumfiel contributed reporting.