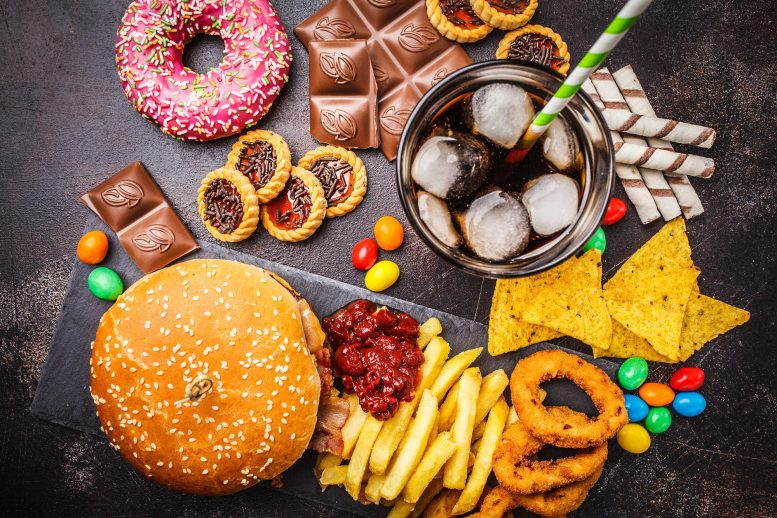
A brand new find out about highlights the hyperlink between excessive intake of ultra-processed meals and an greater possibility of more than a few well being problems, together with most cancers, middle and lung sicknesses, psychological well being issues, and untimely dying. Regardless of earlier analysis at the matter, this complete assessment of just about 10 million members underscores the pressing want for public well being interventions and extra analysis into the damaging results of those meals. Findings underscore want for pressing analysis to know how ultra-processed meals have an effect on well being and measures to focus on and cut back publicity.Constant proof displays that upper publicity to ultra-processed meals is related to an greater possibility of 32 harmful well being results together with most cancers, main middle and lung stipulations, psychological well being issues, and early dying.The findings, printed just lately via The BMJ, display that diets excessive in ultra-processed meals is also damaging to many frame techniques and underscore the will for pressing measures that focus on and purpose to cut back nutritional publicity to those merchandise and higher perceive the mechanisms linking them to deficient well being.Extremely-processed meals, together with packaged baked items and snacks, fizzy beverages, sugary cereals, and ready-to-eat or warmth merchandise, go through more than one business processes and frequently include colours, emulsifiers, flavors, and different components. Those merchandise additionally have a tendency to be excessive in added sugar, fats, and/or salt, however are low in nutrients and fiber.They are able to account for as much as 58% of overall day by day power consumption in some high-income international locations, and feature impulsively greater in lots of low and middle-income international locations in fresh a long time.Complete Assessment of the EvidenceMany earlier research and meta-analyses have connected extremely processed meals to deficient well being, however no complete assessment has but equipped a large review of the proof on this house.To bridge this hole, researchers performed an umbrella assessment (a high-level proof abstract) of 45 distinct pooled meta-analyses from 14 assessment articles associating ultra-processed meals with hostile well being results.The assessment articles have been all printed prior to now 3 years and concerned virtually 10 million members. None have been funded via firms concerned within the manufacturing of ultra-processed meals.Estimates of publicity to ultra-processed meals have been received from a mixture of meals frequency questionnaires, 24-hour nutritional recollects, and nutritional historical past and have been measured as upper as opposed to decrease intake, further servings according to day, or a ten% increment.The researchers graded the proof as convincing, extremely suggestive, suggestive, susceptible, or no proof. In addition they assessed the standard of proof as excessive, reasonable, low, or very low.General, the effects display that upper publicity to ultra-processed meals was once constantly related to an greater possibility of 32 hostile well being results.Convincing proof confirmed that upper ultra-processed meals consumption was once related to round a 50% greater possibility of cardiovascular disease-related dying, a 48-53% upper possibility of tension and commonplace psychological issues, and a 12% higher possibility of kind 2 diabetes.Extremely suggestive proof additionally indicated that upper ultra-processed meals consumption was once related to a 21% higher possibility of dying from any purpose, a 40-66% greater possibility of middle disease-related dying, weight problems, kind 2 diabetes, and sleep issues, and a 22% greater possibility of melancholy.Proof for the associations of ultra-processed meals publicity with bronchial asthma, gastrointestinal well being, some cancers, and cardiometabolic possibility components, corresponding to excessive blood fat and coffee ranges of ‘just right’ ldl cholesterol, stays restricted.Requires Motion and Additional ResearchThe researchers recognize that umbrella opinions can most effective supply high-level overviews and they may be able to’t rule out the likelihood that different unmeasured components and permutations in assessing ultra-processed meals consumption can have influenced their effects.On the other hand, their use of rigorous and prespecified systematic find out how to assessment the credibility and high quality of the analyses means that the effects face up to scrutiny. As such, they conclude: “Those findings reinforce pressing mechanistic analysis and public well being movements that search to focus on and reduce ultra-processed meals intake for advanced inhabitants well being.”Extremely-processed meals harm well being and shorten existence, say researchers in a connected editorial. So what can also be executed to regulate and cut back their manufacturing and intake, which is emerging international?They indicate that reformulation does now not get rid of hurt, and profitability discourages producers from switching to make nutritious meals, so public insurance policies and motion on ultra-processed meals are crucial. Those come with front-of-pack labels, proscribing promoting and prohibiting gross sales in or close to colleges and hospitals, and financial and different measures that make unprocessed or minimally processed meals and freshly ready foods as obtainable and to be had as, and less expensive than, ultra-processed meals. It’s now time for United Countries businesses, with member states, to broaden and put into effect a framework conference on ultra-processed meals very similar to the framework on tobacco, and advertise examples of perfect follow, they write.In any case, they are saying multidisciplinary investigations “are had to establish top-of-the-line techniques to regulate and cut back ultra-processing and to quantify and monitor the cost-benefits and different results of all such insurance policies and movements on human well being and welfare, society, tradition, employment, and the surroundings.”Reference: “Extremely-processed meals publicity and hostile well being results: umbrella assessment of epidemiological meta-analyses” via Melissa M Lane, Elizabeth Gamage, Shutong Du, Deborah N Ashtree, Amelia J McGuinness, Sarah Gauci, Phillip Baker, Mark Lawrence, Casey M Rebholz, Bernard Srour, Mathilde Touvier, Felice N Jacka, Adrienne O’Neil, Toby Segasby and Wolfgang Marx, 28 February 2024, BMJ.
A brand new find out about highlights the hyperlink between excessive intake of ultra-processed meals and an greater possibility of more than a few well being problems, together with most cancers, middle and lung sicknesses, psychological well being issues, and untimely dying. Regardless of earlier analysis at the matter, this complete assessment of just about 10 million members underscores the pressing want for public well being interventions and extra analysis into the damaging results of those meals. Findings underscore want for pressing analysis to know how ultra-processed meals have an effect on well being and measures to focus on and cut back publicity.Constant proof displays that upper publicity to ultra-processed meals is related to an greater possibility of 32 harmful well being results together with most cancers, main middle and lung stipulations, psychological well being issues, and early dying.The findings, printed just lately via The BMJ, display that diets excessive in ultra-processed meals is also damaging to many frame techniques and underscore the will for pressing measures that focus on and purpose to cut back nutritional publicity to those merchandise and higher perceive the mechanisms linking them to deficient well being.Extremely-processed meals, together with packaged baked items and snacks, fizzy beverages, sugary cereals, and ready-to-eat or warmth merchandise, go through more than one business processes and frequently include colours, emulsifiers, flavors, and different components. Those merchandise additionally have a tendency to be excessive in added sugar, fats, and/or salt, however are low in nutrients and fiber.They are able to account for as much as 58% of overall day by day power consumption in some high-income international locations, and feature impulsively greater in lots of low and middle-income international locations in fresh a long time.Complete Assessment of the EvidenceMany earlier research and meta-analyses have connected extremely processed meals to deficient well being, however no complete assessment has but equipped a large review of the proof on this house.To bridge this hole, researchers performed an umbrella assessment (a high-level proof abstract) of 45 distinct pooled meta-analyses from 14 assessment articles associating ultra-processed meals with hostile well being results.The assessment articles have been all printed prior to now 3 years and concerned virtually 10 million members. None have been funded via firms concerned within the manufacturing of ultra-processed meals.Estimates of publicity to ultra-processed meals have been received from a mixture of meals frequency questionnaires, 24-hour nutritional recollects, and nutritional historical past and have been measured as upper as opposed to decrease intake, further servings according to day, or a ten% increment.The researchers graded the proof as convincing, extremely suggestive, suggestive, susceptible, or no proof. In addition they assessed the standard of proof as excessive, reasonable, low, or very low.General, the effects display that upper publicity to ultra-processed meals was once constantly related to an greater possibility of 32 hostile well being results.Convincing proof confirmed that upper ultra-processed meals consumption was once related to round a 50% greater possibility of cardiovascular disease-related dying, a 48-53% upper possibility of tension and commonplace psychological issues, and a 12% higher possibility of kind 2 diabetes.Extremely suggestive proof additionally indicated that upper ultra-processed meals consumption was once related to a 21% higher possibility of dying from any purpose, a 40-66% greater possibility of middle disease-related dying, weight problems, kind 2 diabetes, and sleep issues, and a 22% greater possibility of melancholy.Proof for the associations of ultra-processed meals publicity with bronchial asthma, gastrointestinal well being, some cancers, and cardiometabolic possibility components, corresponding to excessive blood fat and coffee ranges of ‘just right’ ldl cholesterol, stays restricted.Requires Motion and Additional ResearchThe researchers recognize that umbrella opinions can most effective supply high-level overviews and they may be able to’t rule out the likelihood that different unmeasured components and permutations in assessing ultra-processed meals consumption can have influenced their effects.On the other hand, their use of rigorous and prespecified systematic find out how to assessment the credibility and high quality of the analyses means that the effects face up to scrutiny. As such, they conclude: “Those findings reinforce pressing mechanistic analysis and public well being movements that search to focus on and reduce ultra-processed meals intake for advanced inhabitants well being.”Extremely-processed meals harm well being and shorten existence, say researchers in a connected editorial. So what can also be executed to regulate and cut back their manufacturing and intake, which is emerging international?They indicate that reformulation does now not get rid of hurt, and profitability discourages producers from switching to make nutritious meals, so public insurance policies and motion on ultra-processed meals are crucial. Those come with front-of-pack labels, proscribing promoting and prohibiting gross sales in or close to colleges and hospitals, and financial and different measures that make unprocessed or minimally processed meals and freshly ready foods as obtainable and to be had as, and less expensive than, ultra-processed meals. It’s now time for United Countries businesses, with member states, to broaden and put into effect a framework conference on ultra-processed meals very similar to the framework on tobacco, and advertise examples of perfect follow, they write.In any case, they are saying multidisciplinary investigations “are had to establish top-of-the-line techniques to regulate and cut back ultra-processing and to quantify and monitor the cost-benefits and different results of all such insurance policies and movements on human well being and welfare, society, tradition, employment, and the surroundings.”Reference: “Extremely-processed meals publicity and hostile well being results: umbrella assessment of epidemiological meta-analyses” via Melissa M Lane, Elizabeth Gamage, Shutong Du, Deborah N Ashtree, Amelia J McGuinness, Sarah Gauci, Phillip Baker, Mark Lawrence, Casey M Rebholz, Bernard Srour, Mathilde Touvier, Felice N Jacka, Adrienne O’Neil, Toby Segasby and Wolfgang Marx, 28 February 2024, BMJ.
DOI: 10.1136/bmj-2023-077310
Intensive Analysis Finds 32 Well being Dangers Connected to Extremely-Processed Meals