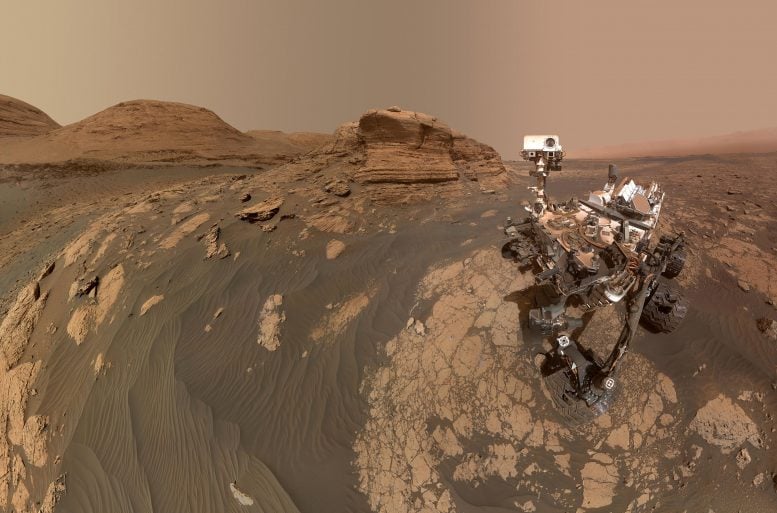
NASA’s Interest Mars rover used two cameras to create this selfie in entrance of Mont Mercou, a rock outcrop that stands 20 toes (6 meters) tall. New research by way of Penn State researchers finds that a lot of the craters on Mars these days can have as soon as been liveable rivers. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSSCuriosity rover findings point out a large number of craters on Mars will have as soon as been flowing rivers, hinting at conceivable historical existence stipulations.New research of knowledge from the Interest rover finds that a lot of the craters on Mars these days can have as soon as been liveable rivers.“We’re discovering proof that Mars was once most likely a planet of rivers,” stated Benjamin Cardenas, assistant professor of geosciences at Penn State and lead writer on a brand new paper pronouncing the invention. “We see indicators of this in every single place the planet.”Erosion Simulation and FindingsIn a learn about printed in Geophysical Analysis Letters, the researchers used numerical fashions to simulate erosion on Mars over millennia and located that commonplace crater formations — referred to as bench-and-nose landforms — are perhaps remnants of historical riverbeds.The learn about was once the primary to map the erosion of historical Martian soil by way of coaching a pc style on a mixture of satellite tv for pc information, Interest pictures, and 3-d scans of the stratigraphy — or layers of rock, referred to as strata, deposited over tens of millions of years — underneath the Gulf of Mexico seafloor. The research published a brand new interpretation for commonplace Martian crater formations which, till now, have by no means been related to eroded river deposits.
NASA’s Interest Mars rover used two cameras to create this selfie in entrance of Mont Mercou, a rock outcrop that stands 20 toes (6 meters) tall. New research by way of Penn State researchers finds that a lot of the craters on Mars these days can have as soon as been liveable rivers. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSSCuriosity rover findings point out a large number of craters on Mars will have as soon as been flowing rivers, hinting at conceivable historical existence stipulations.New research of knowledge from the Interest rover finds that a lot of the craters on Mars these days can have as soon as been liveable rivers.“We’re discovering proof that Mars was once most likely a planet of rivers,” stated Benjamin Cardenas, assistant professor of geosciences at Penn State and lead writer on a brand new paper pronouncing the invention. “We see indicators of this in every single place the planet.”Erosion Simulation and FindingsIn a learn about printed in Geophysical Analysis Letters, the researchers used numerical fashions to simulate erosion on Mars over millennia and located that commonplace crater formations — referred to as bench-and-nose landforms — are perhaps remnants of historical riverbeds.The learn about was once the primary to map the erosion of historical Martian soil by way of coaching a pc style on a mixture of satellite tv for pc information, Interest pictures, and 3-d scans of the stratigraphy — or layers of rock, referred to as strata, deposited over tens of millions of years — underneath the Gulf of Mexico seafloor. The research published a brand new interpretation for commonplace Martian crater formations which, till now, have by no means been related to eroded river deposits. Bench-and-slope morphology pictured on Mars and nostril morphology from the bottom at Mars’ Mont Mercou outcrop. Credit score: NASA/Caltech-JPL/MSSS“We have now the whole thing to be told about Mars by way of higher figuring out how those river deposits may also be interpreted stratigraphically, enthusiastic about rocks these days as layers of sediment deposited through the years,” Cardenas stated. “This research isn’t snapshot, however a document of exchange. What we see on Mars these days is the remnants of an energetic geologic historical past, now not some panorama frozen in time.”Contrasting Previous StudiesPrior research of satellite tv for pc information from Mars had recognized erosional landforms referred to as fluvial ridges as being conceivable applicants for historical river deposits. The usage of information gathered by way of the Interest rover at Gale crater, the group discovered indicators of river deposits that don’t seem to be related to fluvial ridges, however relatively bench-and-nose landforms that experience by no means been related to historical river deposits.“This implies that there might be undiscovered river deposits in different places on this planet, and that a fair better phase of the Martian sedimentary document can have been constructed by way of rivers throughout a liveable length of Mars’ historical past,” Cardenas stated. “On Earth, river corridors are so necessary for existence, chemical cycles, nutrient cycles, and sediment cycles. The whole thing is pointing to those rivers behaving in a similar way on Mars.”Style Design and Earth ComparisonsIn designing their laptop style, Cardenas and his group discovered a brand new use for 25-year-old scans of Earth’s stratigraphy. Accrued by way of oil corporations, the scans of underneath the Gulf of Mexico seafloor supplied a super comparability to Mars, Cardenas defined.The group simulated Mars-like erosion the use of the 3-d scans of tangible, recorded stratigraphy on Earth. After they ran the simulation, the style published erosional Martian landscapes that shaped topographic benches and noses, relatively than fluvial ridges, showing nearly similar to landforms seen by way of the Interest rover within the Gale crater.“Our analysis signifies that Mars can have had way more rivers than up to now believed, which definitely paints a extra constructive view of historical existence on Mars,” Cardenas stated. “It provides a imaginative and prescient of Mars the place many of the planet as soon as had the fitting stipulations for existence.”Reference: “Landforms Related With the Side-Managed Exhumation of Crater-Filling Alluvial Strata on Mars” by way of Benjamin T. Cardenas and Kaitlyn Stacey, 8 August 2023, Geophysical Analysis Letters.
Bench-and-slope morphology pictured on Mars and nostril morphology from the bottom at Mars’ Mont Mercou outcrop. Credit score: NASA/Caltech-JPL/MSSS“We have now the whole thing to be told about Mars by way of higher figuring out how those river deposits may also be interpreted stratigraphically, enthusiastic about rocks these days as layers of sediment deposited through the years,” Cardenas stated. “This research isn’t snapshot, however a document of exchange. What we see on Mars these days is the remnants of an energetic geologic historical past, now not some panorama frozen in time.”Contrasting Previous StudiesPrior research of satellite tv for pc information from Mars had recognized erosional landforms referred to as fluvial ridges as being conceivable applicants for historical river deposits. The usage of information gathered by way of the Interest rover at Gale crater, the group discovered indicators of river deposits that don’t seem to be related to fluvial ridges, however relatively bench-and-nose landforms that experience by no means been related to historical river deposits.“This implies that there might be undiscovered river deposits in different places on this planet, and that a fair better phase of the Martian sedimentary document can have been constructed by way of rivers throughout a liveable length of Mars’ historical past,” Cardenas stated. “On Earth, river corridors are so necessary for existence, chemical cycles, nutrient cycles, and sediment cycles. The whole thing is pointing to those rivers behaving in a similar way on Mars.”Style Design and Earth ComparisonsIn designing their laptop style, Cardenas and his group discovered a brand new use for 25-year-old scans of Earth’s stratigraphy. Accrued by way of oil corporations, the scans of underneath the Gulf of Mexico seafloor supplied a super comparability to Mars, Cardenas defined.The group simulated Mars-like erosion the use of the 3-d scans of tangible, recorded stratigraphy on Earth. After they ran the simulation, the style published erosional Martian landscapes that shaped topographic benches and noses, relatively than fluvial ridges, showing nearly similar to landforms seen by way of the Interest rover within the Gale crater.“Our analysis signifies that Mars can have had way more rivers than up to now believed, which definitely paints a extra constructive view of historical existence on Mars,” Cardenas stated. “It provides a imaginative and prescient of Mars the place many of the planet as soon as had the fitting stipulations for existence.”Reference: “Landforms Related With the Side-Managed Exhumation of Crater-Filling Alluvial Strata on Mars” by way of Benjamin T. Cardenas and Kaitlyn Stacey, 8 August 2023, Geophysical Analysis Letters.
DOI: 10.1029/2023GL103618The different co-author at the paper is Kaitlyn Stacey, a doctoral candidate in planetary geosciences at Penn State. A NASA Sun Machine Workings Grant funded this paintings.
Interest’s New Discovery: Historic Riverbeds on Mars and the Doable for Lifestyles