Stars intruding into the solar’s cosmic yard will have shifted Earth’s orbit within the far-off previous, triggering main local weather occasions in our planet’s historical past. The gravitational affect of those intruder stars has additionally impacted the orbit of different planets within the sun device, inflicting minor deviations known as perturbations. New analysis appears to be like on the impact of those encounters between the solar and different stars on backward forecasts of Earth’s orbit round its superstar and local weather results bobbing up from shifts in that orbit and our planet’s orientation. “Perturbations — a minor deviation during a celestial frame, led to by means of the gravitational enchantment of a neighboring frame — from passing stars regulate the long-term orbital evolution of the solar’s planets, together with Earth,” analysis workforce chief Nathan Kaib, a senior scientist on the Planetary Science Institute in Tucson, Arizona, stated in a commentary. “One explanation why that is necessary is since the geologic report displays that adjustments within the Earth’s orbital eccentricity accompany fluctuations within the Earth’s local weather,” Kaib added. “If we wish to absolute best seek for the reasons of historical local weather anomalies, you will need to have an concept of what Earth’s orbit gave the look of throughout the ones episodes.”Comparable: Local weather trade: Reasons and effectsAs the solar and different stars orbit the middle of the Milky Means galaxy, they sometimes move every different quite carefully, cosmically talking.The solar is believed to come back inside 50,000 AU of any other superstar each million years or so, and inside 20,000 AU of a neighbor each 20 million years or so, on moderate. (One AU, or astronomical unit, is the common Earth-sun distance — about 93 million miles, or 150 million kilometers.)So, over the process the 4.6 billion years that the sun device has existed, it’s been influenced by means of many of those stellar encounters. The brand new analysis is the primary to issue such occasions into the “backward forecasts” of our planet’s orbit and local weather used to expect the previous orbital evolution of Earth and the opposite sun device planets.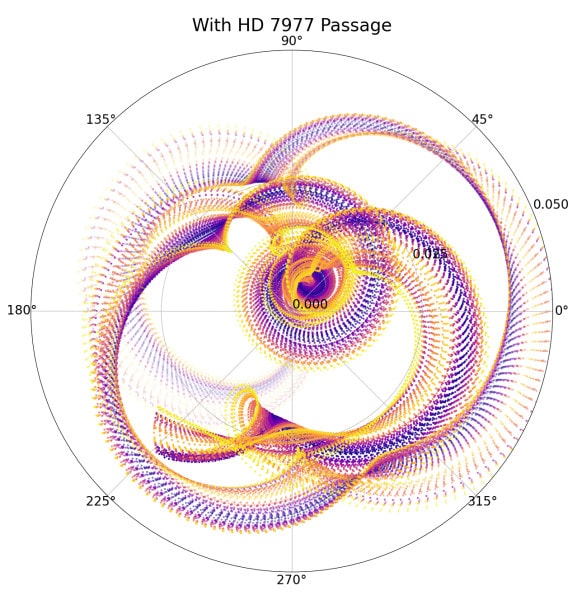 Representation of the uncertainty in fashions of Earth’s orbit 56 million years in the past because of a possible previous passage of the sun-like superstar HD7977 2.8 million years in the past. (Symbol credit score: N. Kaib/PSI.)Earth’s orbital eccentricity — the quantity in which the circle it attracts across the solar is flattened — is strongly suffering from the orbits of the sun device’s large planets, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.Stars passing the sun device perturb the orbits of those large planets and this, in flip, alters Earth’s trajectory across the solar. Because of this the large planets act as hyperlinks between passing stars and the orbit of Earth. Like forward-looking climate forecasts, the extra time that backward local weather fashions try to quilt, the bigger uncertainties develop. Kaib and his workforce discovered that, when factoring in stellar encounters, orbital uncertainties develop abruptly and fashions briefly transform unreliable. There are two main results of this, consistent with the researchers. First, scientists had been too assured when predicting Earth’s orbit and its eccentricity appropriately at sure issues in our planet’s historical past. 2d, there are issues throughout Earth’s historical past when stellar encounters have made conceivable sure orbital regimes — prolonged classes of specifically prime or low eccentricity — that don’t seem to be observed in present fashions. Kaib stated that one instance of such an episode might be the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Most that took place round 56 million years in the past, throughout which Earth’s temperature rose by means of 9 to fourteen levels Fahrenheit (5 to eight levels Celsius). “It has already been proposed that Earth’s orbital eccentricity was once significantly prime throughout this tournament, however our effects display that passing stars make detailed predictions of Earth’s previous orbital evolution at the moment extremely unsure, and a broader spectrum of orbital conduct is conceivable than up to now idea,” Kaib defined. Kaib and associates had been additionally ready to spot a contemporary stellar come upon between the solar and a celeb getting into the cosmic group of the sun device. There’s a massive uncertainty within the distance at which the superstar HD 7977 handed the solar round 3 million years in the past, with estimated distances starting from simply 4,000 AU to 31,000 AU. However, if the come upon was once a detailed one, it should make backward forecasts of Earth’s orbit much more unreliable. That come upon was once “doubtlessly robust sufficient to vary simulations’ predictions of what Earth’s orbit was once like past roughly 50 million years in the past,” Kaib concluded. “For better come upon distances, HD 7977 shouldn’t have a vital affect on Earth’s come upon distance. Close to the smaller finish of the variety, on the other hand, it will most probably regulate our predictions of Earth’s previous orbit.”The workforce’s analysis was once revealed on-line Feb. 14 in Astrophysical Magazine Letters.
Representation of the uncertainty in fashions of Earth’s orbit 56 million years in the past because of a possible previous passage of the sun-like superstar HD7977 2.8 million years in the past. (Symbol credit score: N. Kaib/PSI.)Earth’s orbital eccentricity — the quantity in which the circle it attracts across the solar is flattened — is strongly suffering from the orbits of the sun device’s large planets, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune.Stars passing the sun device perturb the orbits of those large planets and this, in flip, alters Earth’s trajectory across the solar. Because of this the large planets act as hyperlinks between passing stars and the orbit of Earth. Like forward-looking climate forecasts, the extra time that backward local weather fashions try to quilt, the bigger uncertainties develop. Kaib and his workforce discovered that, when factoring in stellar encounters, orbital uncertainties develop abruptly and fashions briefly transform unreliable. There are two main results of this, consistent with the researchers. First, scientists had been too assured when predicting Earth’s orbit and its eccentricity appropriately at sure issues in our planet’s historical past. 2d, there are issues throughout Earth’s historical past when stellar encounters have made conceivable sure orbital regimes — prolonged classes of specifically prime or low eccentricity — that don’t seem to be observed in present fashions. Kaib stated that one instance of such an episode might be the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Most that took place round 56 million years in the past, throughout which Earth’s temperature rose by means of 9 to fourteen levels Fahrenheit (5 to eight levels Celsius). “It has already been proposed that Earth’s orbital eccentricity was once significantly prime throughout this tournament, however our effects display that passing stars make detailed predictions of Earth’s previous orbital evolution at the moment extremely unsure, and a broader spectrum of orbital conduct is conceivable than up to now idea,” Kaib defined. Kaib and associates had been additionally ready to spot a contemporary stellar come upon between the solar and a celeb getting into the cosmic group of the sun device. There’s a massive uncertainty within the distance at which the superstar HD 7977 handed the solar round 3 million years in the past, with estimated distances starting from simply 4,000 AU to 31,000 AU. However, if the come upon was once a detailed one, it should make backward forecasts of Earth’s orbit much more unreliable. That come upon was once “doubtlessly robust sufficient to vary simulations’ predictions of what Earth’s orbit was once like past roughly 50 million years in the past,” Kaib concluded. “For better come upon distances, HD 7977 shouldn’t have a vital affect on Earth’s come upon distance. Close to the smaller finish of the variety, on the other hand, it will most probably regulate our predictions of Earth’s previous orbit.”The workforce’s analysis was once revealed on-line Feb. 14 in Astrophysical Magazine Letters.
‘Intruder’ stars have modified Earth’s local weather over the eons. This is how.