When other people take into accounts the hazards of local weather exchange, the theory of abrupt adjustments is lovely frightening. Motion pictures like “The Day After The following day” feed that concern, with visions of not possible storms and populations fleeing to flee swiftly converting temperatures.
Whilst Hollywood obviously takes liberties with the velocity and magnitude of failures, a number of contemporary research have raised real-world alarms {that a} a very powerful ocean present that circulates warmth to northern international locations would possibly close down this century, with doubtlessly disastrous penalties.
That situation has took place previously, maximum not too long ago greater than 16,000 years in the past. Alternatively, it depends upon Greenland losing numerous ice into the sea.
Our new analysis, revealed within the magazine Science, means that whilst Greenland is certainly shedding large and worrisome volumes of ice presently, that would possibly no longer proceed for lengthy sufficient to close down the present by itself. A more in-depth have a look at proof from the previous presentations why.
Blood and water
The Atlantic present device distributes warmth and vitamins on a world scale, similar to the human circulatory device distributes warmth and vitamins across the frame.
Heat water from the tropics circulates northward alongside the U.S. Atlantic coast ahead of crossing the Atlantic. As one of the crucial heat water evaporates and the outside water cools, it turns into saltier and denser. Denser water sinks, and this chillier, denser water circulates again south at intensity. The differences in warmth and salinity gasoline the pumping center of the device.
If the Atlantic move device weakened, it might result in an international of local weather chaos.
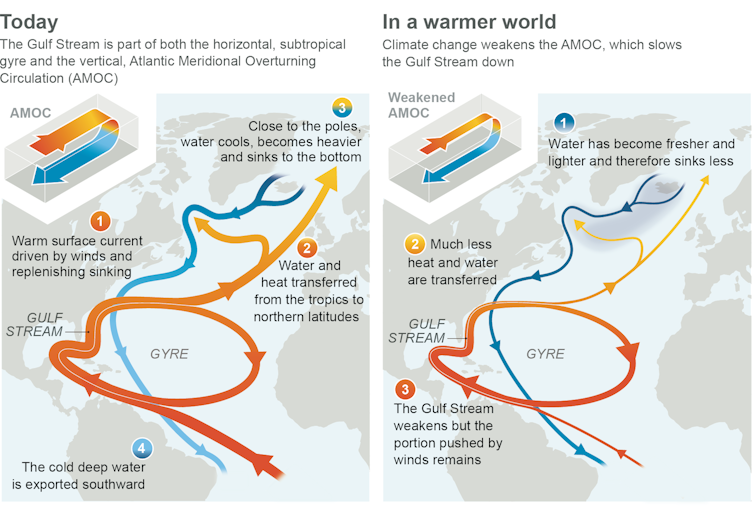
How the Atlantic Ocean move would exchange because it slowed.
IPCC sixth Evaluation Record
Ice sheets are made of clean water, so the speedy free up of icebergs into the Atlantic Ocean can decrease the sea’s salinity and sluggish the pumping center. If the outside water is not in a position to sink deep and the move collapses, dramatic cooling would most likely happen throughout Europe and North The us. Each the Amazon rain woodland and Africa’s Sahel area would turn into dryer, and Antarctica’s warming and melting would boost up, all in an issue of years to many years.
As of late, the Greenland ice sheet is melting swiftly, and a few scientists fear that the Atlantic present device could also be headed for a local weather tipping level this century. However is that fear warranted?
To reply to that, we want to glance again in time.
A radioactive discovery
Within the Nineteen Eighties, a junior scientist named Hartmut Heinrich and his colleagues extracted a sequence of deep-sea sediment cores from the sea flooring to review whether or not nuclear waste may well be safely buried within the deep North Atlantic.
Sediment cores comprise a historical past of the entirety that amassed on that a part of the sea flooring over masses of hundreds of years. Heinrich discovered a number of layers with plenty of mineral grains and rock fragments from land.
The sediment grains had been too huge to had been carried to the center of the sea via the wind or ocean currents on my own. Heinrich discovered they should had been introduced there via icebergs, which had picked up the rock and mineral when the icebergs had been nonetheless a part of glaciers on land.
The layers with probably the most rock and mineral particles, from a time when the icebergs should have pop out in power, coincided with serious weakening of the Atlantic present device. The ones classes are actually referred to as Heinrich occasions.
As paleoclimate scientists, we use herbal information comparable to sediment cores to grasp the previous. Through measuring uranium isotopes within the sediments, we had been in a position to resolve the deposition charge of sediments dropped via icebergs. The volume of particles allowed us to estimate how a lot recent water the ones icebergs added to the sea and examine it with lately to evaluate whether or not historical past would possibly repeat itself within the close to long term.
Why a shutdown isn’t most likely quickly
So, is the Atlantic present device headed for a local weather tipping level on account of Greenland melting? We predict it’s not likely within the coming many years.
Whilst Greenland is shedding large volumes of ice presently – worryingly related to a midrange Heinrich match – the ice loss will most likely no longer proceed for lengthy sufficient to close down the present by itself.
Icebergs are a lot more efficient at disrupting the present than meltwater from land, partially as a result of icebergs can raise recent water at once out to the places the place the present sinks. Long term warming, alternatively, will power the Greenland ice sheet to recede clear of the coast too quickly to ship sufficient recent water via iceberg.
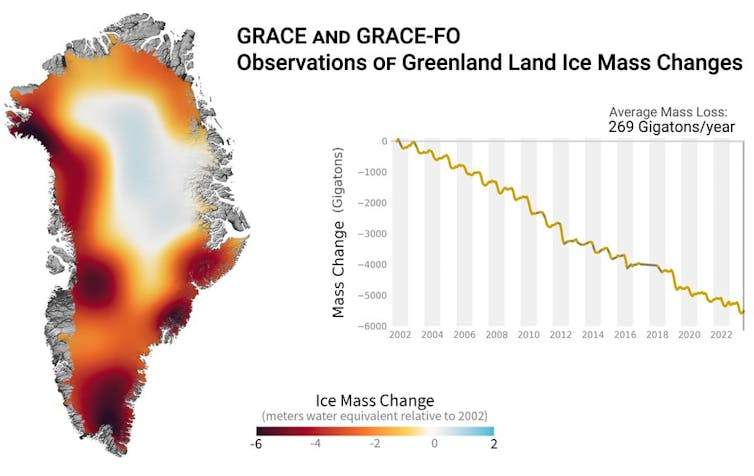
Greenland’s ice loss, measured from the Grace and Grace-FO satellites.
NASA
The energy of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Move, or AMOC, is projected to say no 24% to 39% via 2100. Through then, Greenland’s iceberg formation will probably be nearer to the weakest Heinrich occasions of the previous. Heinrich occasions, by contrast, lasted 200 years or so.
As an alternative of icebergs, meltwater pouring into the Atlantic on the island’s edge is projected to turn into the main explanation for Greenland’s thinning. Meltwater nonetheless sends recent water into the sea, nevertheless it mixes with seawater and has a tendency to transport alongside the coast somewhat than at once freshening the open ocean as drifting icebergs do.
That doesn’t imply the present isn’t in danger
The long run trajectory of the Atlantic present device can be made up our minds via a mix of the decelerating however simpler icebergs and the accelerating however much less influential floor runoff. That will probably be compounded via emerging ocean floor temperatures that might additional sluggish the present.
So, the Earth’s pumping center may nonetheless be in danger, however historical past means that the chance isn’t as coming near near as some other people concern.
In “The Day After The following day,” a slowdown of the Atlantic present device iced over New York Town. In response to our analysis, we might take some convenience in understanding that the sort of situation is not likely in our lifetimes. Nonetheless, tough efforts to prevent local weather exchange stay vital to make sure the security of long term generations.




.webp)






