It is authentic. Astronomers peering on the setting of Venus have immediately detected transparent indicators of atomic oxygen in sunlight, putting about above the planet’s poisonous clouds.Atomic oxygen is understood to exist within the planet’s setting, in keeping with theoretical fashions, and has even been immediately detected immediately on Venus’ nightside; however the dayside detection way we now have new perception into the dynamics of the Venusian setting, and the movement patterns therein, say a group led through physicist Heinz-Wilhelm Hübers of the German Aerospace Heart (DLR).Venus is an international that scientists are itching to check in higher element. It is very similar to Earth in some ways; however completely, hellishly other in others. Its mass and composition are like Earth’s, however the place Earth is opulent, verdant, rainy, and crawling with existence, Venus is a demise pit. It is cloaked with thick, choking clouds most commonly composed of carbon dioxide, making a greenhouse surroundings that ends up in moderate floor temperatures round 464 levels Celsius (867 Fahrenheit).The ones clouds drop acid rain on Venus, and all the setting rotates across the planet at an amazing price. Winds a ways underneath Venus’s cloud tops can scream alongside at round 700 kilometers (greater than 400 miles) according to hour. On Earth, the best possible wind velocity ever recorded used to be a storm gust of 407 kilometers (253 miles) according to hour.We do not understand how Venus and Earth ended up so very other from one some other, however finding out our neighbor may assist us determine it out. Used to be Venus as soon as at the similar trail as Earth, and took a improper flip someplace? Or used to be it the evil dual from the beginning?Figuring out the ambience of Venus may assist us perceive the diversities between it and Earth. And one of the crucial techniques to do this is through following the oxygen.Atomic oxygen is not just like the oxygen that you simply breathe. The latter is molecular oxygen, or O2, consisting of 2 oxygen atoms sure in combination. Atomic oxygen is composed of unmarried, lone oxygen atoms, and it does not generally tend to remaining very lengthy, as a result of it is extremely reactive and simply bonds to different atoms. Right here on Earth, it is plentiful at prime altitudes, the place it’s created through the photodissociation of molecular oxygen. Mainly, sun photons ruin aside the atmospheric O2.A equivalent procedure is assumed to happen on Venus. Venus’ setting is predominantly carbon dioxide; when gentle from the Solar hits this CO2, photodissociation splits the molecules into atomic oxygen and carbon monoxide. The carbon monoxide may be topic to photodissociation.When those atoms shuttle round to Venus’ nightside, they recombine into carbon dioxide, a procedure that reasons the planet’s nightside to glow. Atomic oxygen has been noticed as a part of this procedure, however had by no means sooner than been noticed at the dayside.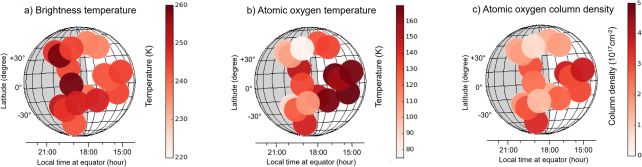 Map of the places, temperature, and density of atomic oxygen on Venus. (Hübers et al., Nat. Commun., 2023)Hübers and his group studied information gathered through Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) flying prime in Earth’s personal setting, within the terahertz wavelength vary that straddles microwave and far-infrared. On 3 separate events, the airplane flew, amassing information on 17 places on Venus: seven at the dayside, 9 at the nightside and one on the terminator.In any respect 17 places, the group detected atomic oxygen, peaking in focus at an altitude of about 100 kilometers (62 miles). This corresponds to an altitude that sits immediately between two dominant atmospheric movement patterns on Venus: the robust super-rotating go with the flow underneath 70 kilometers that rotates counter to the spin of the planet, and the subsolar-to-antisolar go with the flow within the higher setting above 120 kilometers.This implies, the researchers say, that atomic oxygen represents a heretofore untapped useful resource to probe this atmospheric transitional zone on Venus.”Long run observations, particularly close to the antisolar and subsolar issues but additionally in any respect sun zenith angles, will supply a extra detailed image of this ordinary area and give a boost to long run area missions to Venus,” the researchers write.”Along side measurements of atomic oxygen within the atmospheres of Earth and Mars, those information would possibly assist to reinforce our working out of the way and why Venus and Earth atmospheres are so other.”The analysis has been revealed in Nature Communications.
Map of the places, temperature, and density of atomic oxygen on Venus. (Hübers et al., Nat. Commun., 2023)Hübers and his group studied information gathered through Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) flying prime in Earth’s personal setting, within the terahertz wavelength vary that straddles microwave and far-infrared. On 3 separate events, the airplane flew, amassing information on 17 places on Venus: seven at the dayside, 9 at the nightside and one on the terminator.In any respect 17 places, the group detected atomic oxygen, peaking in focus at an altitude of about 100 kilometers (62 miles). This corresponds to an altitude that sits immediately between two dominant atmospheric movement patterns on Venus: the robust super-rotating go with the flow underneath 70 kilometers that rotates counter to the spin of the planet, and the subsolar-to-antisolar go with the flow within the higher setting above 120 kilometers.This implies, the researchers say, that atomic oxygen represents a heretofore untapped useful resource to probe this atmospheric transitional zone on Venus.”Long run observations, particularly close to the antisolar and subsolar issues but additionally in any respect sun zenith angles, will supply a extra detailed image of this ordinary area and give a boost to long run area missions to Venus,” the researchers write.”Along side measurements of atomic oxygen within the atmospheres of Earth and Mars, those information would possibly assist to reinforce our working out of the way and why Venus and Earth atmospheres are so other.”The analysis has been revealed in Nature Communications.
It is Respectable: Oxygen Has Been Without delay Detected in Venus’ Dayside Surroundings