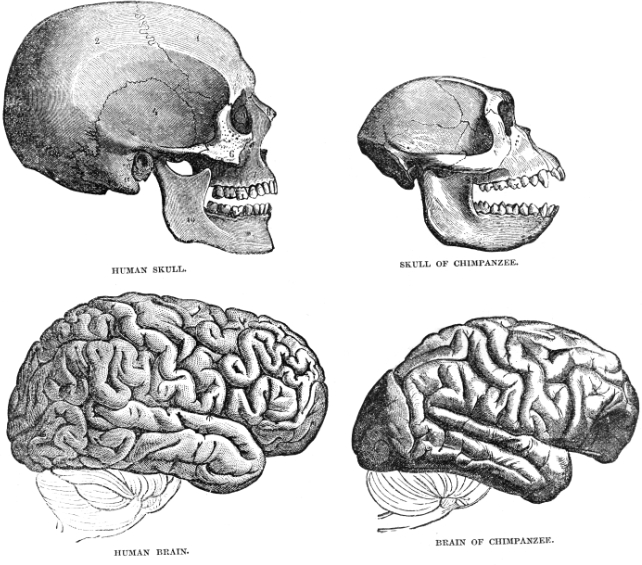
On this tailored excerpt from “Limitless Lifestyles: The Tale of Eggs, Evolution, and Lifestyles on Earth,” (Pegasus Books, 2024) creator Jules Howard examines the invasiveness of the placenta — how a ways it permeates into the wall of the uterus and the maternal tissue — in mammals after the dinosaur-killing asteroid struck.Even though it has no longer been preserved within the fossil document, the range of placentae amongst modern day mammals means that, about 10 or 20 million years after the end-Cretaceous, at across the time that the animals of the Messel Pit have been alive, the mammal placenta was once replacing. Herbal variety was once tweaking this organ.In lots of instances, it was once settling on the person placentae best possible ready to extract as a lot calories from the maternal host as conceivable. But, unusually, in some lineages the placenta perceived to take a step again, changing into much less, quite than extra, invasive. Having a look at knowledge throughout 60 mammal species, a development turns into obvious.Plotting the invasiveness of every placenta (judged in part via what number of blood- amassing, finger-like projections the placenta has) towards vital life-history main points, akin to how lengthy a species takes to mature and what number of offspring every 12 months a species may produce, the least invasive mammal placentae are the ones related to a extra fast tempo of existence.Species that are living speedy and die younger, in different phrases, seem to finally end up evolving a much less invasive placenta.Mind dimension is any other marker that tracks carefully with how invasive a placenta evolves to be. Now not simply how huge the mind is in terms of the frame, but in addition how briefly the mind grows earlier than delivery. Each components correlate with particularly invasive placentae. The way it works is modest: The larger a mammal’s mind evolves to be, the larger selective drive is positioned at the placenta to obtain calories for the expansion of the embryo, which, naturally, drives the evolution of an ever-hungrier placenta.Mammals are, as a gaggle, extra brainy than different equivalent sized organisms, however this wasn’t all the time as key a characteristic of our sort. It perceived to occur regularly, after the dying of dinosaurs and because the Cenozoic Technology (66 million years in the past to the current) started to growth. Scientists had at the beginning idea that this relative building up in mind dimension was once merely a byproduct of the evolution of bigger frame dimension in mammals, however not too long ago (the use of third-dimensional fashions of fossilized mammal skulls) this assumption has been extra conscientiously examined.Get the arena’s most attractive discoveries delivered instantly in your inbox.To start with, it kind of feels, within the 10 million years after the era-ending meteorite, mammal frame dimension greater and, fairly, so too did mind dimension. However then, obviously visual at fossil websites like Messel, mind dimension in sure lineages will increase at a better than anticipated price in comparison to frame dimension. Mammal brains, in some lineages, got a metaphorical shot within the arm. So why? In the event that they price each mom and fetus extra to provide, in particular within the embryo degree, what’s so just right about large brains?The researchers who first made this commentary about mind sizes in mammals, evaluating third-dimensional fashions of fossilized skulls, suppose that this development came about as a result of pageant. To start with — with out dinosaurs and different huge land animals — vegetation, bugs and different sources have been simple to reap and pageant between people was once low. On this setting, energy-sapping brains have been expensive and pointless.However later, when mammals different and established themselves — when there was once extra pageant for niches, for meals and sources — smarter people have been relatively extra a hit in some species. In the case of the transmission of genes, huge brains started to pay out and, in some lineages, larger and higher brains began to conform. In some mammalian teams as of late, akin to dolphins, rodents and in particular primates (monkeys and apes), the ratio of mind dimension to frame dimension has persevered to extend with time. In people, possibly the wiliest of all primates, the fashion persevered with aplomb. Human brains are about two times the scale as chimp brains at delivery. (Symbol credit score: AnjoKanFotografie /Getty Pictures)There’s no denying the choice drive at paintings right here: large brains in point of fact are inordinately pricey for our bodies to construct. And human brains really fluctuate from the mind of our nearest kin, the chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes). At delivery, as an example, a chimpanzee’s mind is 130 cubic centimeters (8 cubic inches) after which triples in dimension within the following 3 years.Examine that to the human mind. At delivery, the human mind is greater than two times the scale of a chimpanzee’s and, in six years, it quadruples in dimension. Even though our mind takes up simply 2% of our overall frame weight, this organ consumes between 20% and 25% of our resting calories finances. The human mind prices one thing like 420 energy an afternoon to run, 4 instances greater than the chimpanzee’s mind.For this reason the connection between human mom and kid, hooked up by means of the placenta, has transform, evolutionarily, so strained in our species. Extra strained, it kind of feels, than in some other mammal.Liam Drew, creator of the authoritative “I, Mammal” (Bloomsbury Sigma, 2018) issues out precisely how twisted this dating turns into. For starters there may be preeclampsia, when the mummy’s frame is going thru a life-threatening surge in blood drive because the human fetus will increase the velocity of blood drift throughout the placenta.Put merely, it needs to be bathed in as a lot life-giving blood as conceivable. And there may be gestational diabetes, led to via the fetus’ try to co-opt maternal keep an eye on of blood sugars — predictably, it needs greater than the mummy is in a position to give.
Human brains are about two times the scale as chimp brains at delivery. (Symbol credit score: AnjoKanFotografie /Getty Pictures)There’s no denying the choice drive at paintings right here: large brains in point of fact are inordinately pricey for our bodies to construct. And human brains really fluctuate from the mind of our nearest kin, the chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes). At delivery, as an example, a chimpanzee’s mind is 130 cubic centimeters (8 cubic inches) after which triples in dimension within the following 3 years.Examine that to the human mind. At delivery, the human mind is greater than two times the scale of a chimpanzee’s and, in six years, it quadruples in dimension. Even though our mind takes up simply 2% of our overall frame weight, this organ consumes between 20% and 25% of our resting calories finances. The human mind prices one thing like 420 energy an afternoon to run, 4 instances greater than the chimpanzee’s mind.For this reason the connection between human mom and kid, hooked up by means of the placenta, has transform, evolutionarily, so strained in our species. Extra strained, it kind of feels, than in some other mammal.Liam Drew, creator of the authoritative “I, Mammal” (Bloomsbury Sigma, 2018) issues out precisely how twisted this dating turns into. For starters there may be preeclampsia, when the mummy’s frame is going thru a life-threatening surge in blood drive because the human fetus will increase the velocity of blood drift throughout the placenta.Put merely, it needs to be bathed in as a lot life-giving blood as conceivable. And there may be gestational diabetes, led to via the fetus’ try to co-opt maternal keep an eye on of blood sugars — predictably, it needs greater than the mummy is in a position to give. The placenta has advanced ways to get up to the fetus wishes from the mummy. (Symbol credit score: Shutterstock)Preeclampsia impacts about 5% of human women sporting a unmarried child to time period. Upload extra offspring into the combination, twins or triplets say, every of whom will continuously have their very own placenta, and preeclampsia charges building up to 1 in 3 pregnancies. This makes childbirth a dangerous job for human women.There are different methods that the placenta has advanced to get what it wishes for the embryo. Staggeringly, we now know that the placenta makes use of a distinct protein (known as PP13) to inflame the tissue round tiny veins within the uterus, inflicting the mummy’s immune device to take a position closely in immune defenses. It is a vintage distraction methodology advanced via the placenta: If the mummy’s immune device is firefighting in different places, it’s much less prone to center of attention its consideration on fighting the placenta’s energetic uterine encroachments.What effects from all of this, says Cat Bohannon, creator of “Eve: The Actual Starting place of Our Species” (Knopf, 2023) is a “nine-month stalemate”: “ladies’s our bodies are in particular tailored to the trials of being pregnant no longer just so we will be able to get pregnant however so we will be able to live on it,” she writes.The extremely invasive human placenta, influenced via our monumental mind and (most definitely to a lesser extent) our slow-and-steady existence historical past, additionally explains any other quirk of our species, the phenomenon of menstruation. This adaptation is fleetingly uncommon amongst mammals, discovered handiest in some primates, bats and elephant shrews. In people, menstrual bleeding is especially overt and, via now, after studying the former paragraphs, you’ll be able to most definitely wager why.Having an extra-thick uterine lining is helping the feminine live on the doubtless adverse tentacle-like villi of the placenta, will have to being pregnant happen. The liner of the uterus in our species has transform so thick that we can not perhaps reabsorb it each few days or perhaps weeks, as different mammals do. It’s extra environment friendly, in our species no less than and a handful of others, to shed the uterine armament and develop it afresh every cycle able for the following possible implantation.And so, human evolution has came about each because of, and despite, the placenta. Each being pregnant, unthinkingly, should navigate a cautious trail thru it. Each menstruation is testomony to it. It’s in part why menopause exists, to present people an get away from the vigorous prices related to its imposition. This life-history phenomenon handiest exists in a small collection of apes and a few whales and dolphins.In a few years of writing in regards to the insides and outsides of animals, I confess I’ve by no means written of a stranger organ or a more bizarre evolutionary contract. I to find myself quietly saluting the placenta that fought for me in my earliest moments, whilst concurrently feeling apologetic to the maternal host wherein I grew. This can be a world-changing adaptation, in additional techniques than one.
The placenta has advanced ways to get up to the fetus wishes from the mummy. (Symbol credit score: Shutterstock)Preeclampsia impacts about 5% of human women sporting a unmarried child to time period. Upload extra offspring into the combination, twins or triplets say, every of whom will continuously have their very own placenta, and preeclampsia charges building up to 1 in 3 pregnancies. This makes childbirth a dangerous job for human women.There are different methods that the placenta has advanced to get what it wishes for the embryo. Staggeringly, we now know that the placenta makes use of a distinct protein (known as PP13) to inflame the tissue round tiny veins within the uterus, inflicting the mummy’s immune device to take a position closely in immune defenses. It is a vintage distraction methodology advanced via the placenta: If the mummy’s immune device is firefighting in different places, it’s much less prone to center of attention its consideration on fighting the placenta’s energetic uterine encroachments.What effects from all of this, says Cat Bohannon, creator of “Eve: The Actual Starting place of Our Species” (Knopf, 2023) is a “nine-month stalemate”: “ladies’s our bodies are in particular tailored to the trials of being pregnant no longer just so we will be able to get pregnant however so we will be able to live on it,” she writes.The extremely invasive human placenta, influenced via our monumental mind and (most definitely to a lesser extent) our slow-and-steady existence historical past, additionally explains any other quirk of our species, the phenomenon of menstruation. This adaptation is fleetingly uncommon amongst mammals, discovered handiest in some primates, bats and elephant shrews. In people, menstrual bleeding is especially overt and, via now, after studying the former paragraphs, you’ll be able to most definitely wager why.Having an extra-thick uterine lining is helping the feminine live on the doubtless adverse tentacle-like villi of the placenta, will have to being pregnant happen. The liner of the uterus in our species has transform so thick that we can not perhaps reabsorb it each few days or perhaps weeks, as different mammals do. It’s extra environment friendly, in our species no less than and a handful of others, to shed the uterine armament and develop it afresh every cycle able for the following possible implantation.And so, human evolution has came about each because of, and despite, the placenta. Each being pregnant, unthinkingly, should navigate a cautious trail thru it. Each menstruation is testomony to it. It’s in part why menopause exists, to present people an get away from the vigorous prices related to its imposition. This life-history phenomenon handiest exists in a small collection of apes and a few whales and dolphins.In a few years of writing in regards to the insides and outsides of animals, I confess I’ve by no means written of a stranger organ or a more bizarre evolutionary contract. I to find myself quietly saluting the placenta that fought for me in my earliest moments, whilst concurrently feeling apologetic to the maternal host wherein I grew. This can be a world-changing adaptation, in additional techniques than one.