The James Webb Area Telescope (JWST) has double checked the paintings of its older sibling, the Hubble Area Telescope. Hubble’s measurements of the growth charge of the universe are exemplary, the trailblazing observatory discovered, additional ratcheting up the so-called “Hubble rigidity.”Placing it merely, measurements of the growth charge of the universe, outlined via a belongings known as the Hubble consistent, simply do not upload up. Similar: Darkish power is forcing the universe to amplify. This new observatory would possibly display us howOn one hand, observations of the cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation, which is sort of a child image of the cosmos from simply 379,000 years after the Giant Bang, say the universe must be increasing nowadays at a charge of about 67.8 kilometers according to 2nd according to megaparsec. Because of this each quantity of area one million parsecs (3.26 million mild years) throughout must be increasing at a charge of 67.8 kilometers (42.1 miles) each 2nd.Another strategy to measure this enlargement is via mountaineering onto the cosmic distance ladder, the place each and every rung is shaped via a special astrophysical milestone akin to Cepheid variable stars and Sort Ia supernovas. How vibrant those items are can let us know their distances, which we will then examine to their redshift values to decide how a lot the universe has expanded whilst their mild has been touring to us. The issue, then again, is this system offers us a fully other worth of the Hubble consistent: Someplace round 73.2 kilometers (45.5 miles) according to 2nd according to megaparsec.The obvious paradox between the 2 measurements is what cosmologists have began calling the Hubble rigidity. No one is aware of what’s inflicting it, however some hypotheses name for brand spanking new physics to give an explanation for the plain contradiction.One conceivable clarification is that there’s a dimension error at the backside rung of the cosmic distance ladder, which is house to the Cepheid variables. Those are stars with luminosities that predictably differ as the celebrities pulse out and in. The longer the pulsation length between moments of utmost luminosity, the larger that most luminosity is. This era–luminosity relation lets in us to appropriately calculate their distances to Earth; it is conceivable to measure the pulsation length to calculate most luminosity, then, in accordance with how vibrant a Cepheid variable seems within the sky to us, we will determine how a long way away it will have to be to look that vibrant.It is not reasonably a foolproof means, although.The Hubble Area Telescope is in a position to follow Cepheid variables in far-off galaxies, however the extra far-off they’re, the tougher they grow to be to tell apart amongst all of the different stars that crowd round them. As such, there used to be a priority that unresolved stars adjoining to Cepheid variables in those far flung galaxies had been including to the Cepheids’ obvious brightness values, developing an unseen and systematic error within the measurements. Interstellar mud too can impact the brightness of Cepheid variables, dimming them from our vantage level on Earth.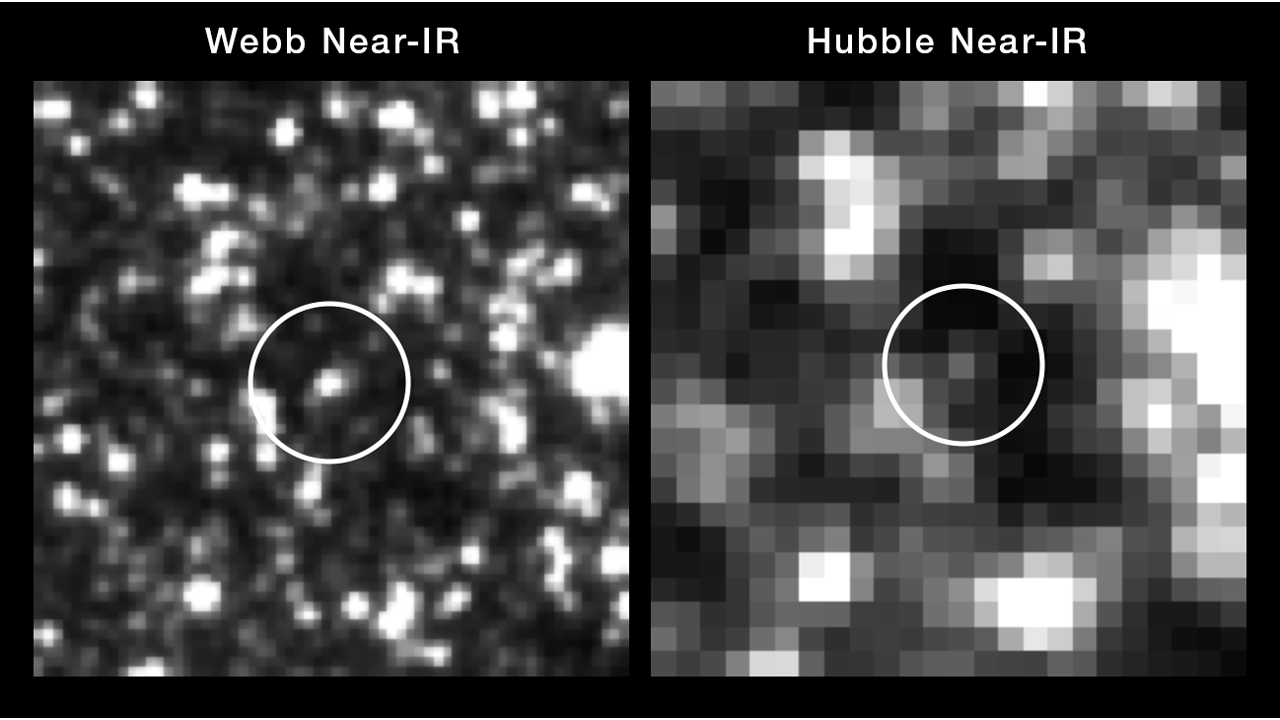 An instance of one of the crucial Cepheids in NGC 5468 imaged via the Hubble Area Telescope (proper) after which a lot more obviously via the JWST (left). (Symbol credit score: NASA/ESA/CSA/STScI/Adam G. Riess (JHU/STScI))However new measurements completed with the James Webb Area Telescope of 5 galaxies web hosting a mixed overall of greater than 1000 Cepheid variables have dominated this conceivable error out. The JWST’s infrared imaginative and prescient is in a position to lower in the course of the interstellar mud, whilst its larger solution lets in it to obviously get to the bottom of the Cepheid variables in order that they stick out from the group. From those JWST measurements, astronomers led via Adam Riess of Johns Hopkins College made up our minds that Hubble’s authentic measurements had been spot on.”We now have now spanned the entire vary of what Hubble noticed and we will rule out a dimension error as the reason for the Hubble rigidity with very prime self belief,” mentioned Riess in a commentary.The 5 galaxies noticed via the JWST, probably the most far-off of which is NGC 5468 at 130 million light-years from us, have additionally hosted a mixed overall of 8 Sort Ia supernovas over contemporary many years. Those supernovas, which sign the destruction of white dwarfs, have a standardizable luminosity curve, and shape the following rung at the cosmic distance ladder above Cepheids. For the reason that previous rung is needed to calibrate the following rung, the JWST’s observations of Cepheid variables due to this fact makes the space measurements the use of Sort Ia supernovae — which can be vibrant sufficient to be noticed in a lot more far-off galaxies than Cepheids — extra correct. And so they too let us know that there’s a contradiction within the other measurements of the Hubble consistent.”With dimension mistakes negated, what stays is the actual and thrilling chance now we have misunderstood the universe,” mentioned Riess.The group’s effects are a very long time coming, having up to now been to be had at the pre-print server arxiv and incomes chatter past due remaining 12 months. However now that they are printed absolutely, most likely we will in spite of everything shut the bankruptcy of blaming Hubble rigidity on none rather than Hubble itself.The result of Riess’ group had been printed on sixth February in The Astrophysical Magazine Letters.
An instance of one of the crucial Cepheids in NGC 5468 imaged via the Hubble Area Telescope (proper) after which a lot more obviously via the JWST (left). (Symbol credit score: NASA/ESA/CSA/STScI/Adam G. Riess (JHU/STScI))However new measurements completed with the James Webb Area Telescope of 5 galaxies web hosting a mixed overall of greater than 1000 Cepheid variables have dominated this conceivable error out. The JWST’s infrared imaginative and prescient is in a position to lower in the course of the interstellar mud, whilst its larger solution lets in it to obviously get to the bottom of the Cepheid variables in order that they stick out from the group. From those JWST measurements, astronomers led via Adam Riess of Johns Hopkins College made up our minds that Hubble’s authentic measurements had been spot on.”We now have now spanned the entire vary of what Hubble noticed and we will rule out a dimension error as the reason for the Hubble rigidity with very prime self belief,” mentioned Riess in a commentary.The 5 galaxies noticed via the JWST, probably the most far-off of which is NGC 5468 at 130 million light-years from us, have additionally hosted a mixed overall of 8 Sort Ia supernovas over contemporary many years. Those supernovas, which sign the destruction of white dwarfs, have a standardizable luminosity curve, and shape the following rung at the cosmic distance ladder above Cepheids. For the reason that previous rung is needed to calibrate the following rung, the JWST’s observations of Cepheid variables due to this fact makes the space measurements the use of Sort Ia supernovae — which can be vibrant sufficient to be noticed in a lot more far-off galaxies than Cepheids — extra correct. And so they too let us know that there’s a contradiction within the other measurements of the Hubble consistent.”With dimension mistakes negated, what stays is the actual and thrilling chance now we have misunderstood the universe,” mentioned Riess.The group’s effects are a very long time coming, having up to now been to be had at the pre-print server arxiv and incomes chatter past due remaining 12 months. However now that they are printed absolutely, most likely we will in spite of everything shut the bankruptcy of blaming Hubble rigidity on none rather than Hubble itself.The result of Riess’ group had been printed on sixth February in The Astrophysical Magazine Letters.
James Webb Area Telescope complicates increasing universe paradox via checking Hubble’s paintings