The usage of the James Webb Area Telescope (JWST), astronomers have came upon an “extraordinarily pink” supermassive black gap rising within the shadowy, early universe.The pink hue of the supermassive black gap, observed because it used to be round 700 million years after the Giant Bang, is the results of the increasing universe. Because the universe balloons outward in all instructions, mild touring towards us will get “redshifted,” and the redshifted mild on this case signifies a cloak of thick fuel and dirt shrouding the black gap.Inspecting JWST knowledge, the astronomy crew led through Lukas Furtak and Adi Zitrin of the Ben-Gurion College of the Negev, used to be additionally in a position to decide the mass of the supermassive black gap. At round 40 million instances the mass of the solar, it’s all of a sudden huge compared to the galaxy wherein it is living. The crew additionally discovered that the supermassive black gap, which is situated round 12.9 billion light-years clear of Earth, is hastily feasting at the fuel and dirt round it. In different phrases, it is rising.Comparable: Brightest quasar ever observed is powered through black gap that eats a ‘solar an afternoon'”We have been very excited when JWST began sending its first knowledge. We have been scanning the knowledge that arrived for the UNCOVER program, and 3 very compact but red-blooming items prominently stood out and stuck our eyes,” Furtak stated in a observation. “Their ‘red-dot’ look instantly led us to suspect that it used to be a quasar-like object.”The ‘3 pink dots’Quasars are created when copious quantities of topic encompass supermassive black holes like this one. This topic paperwork a disk of fuel and dirt known as an accretion disk that step by step feeds the black gap. The immense gravitational affect of the black gap churns this topic, producing intense temperatures and inflicting it to glow. Moreover, topic that does not fall into the supermassive black gap is channeled to the cosmic titan’s poles. Debris in those areas are sped up to speeds coming near that of sunshine as extremely collimated jets. As those relativistic jets are blasted out, the eruptions are accompanied through shiny electromagnetic emissions.On account of those phenomena, quasars powered through supermassive black holes in energetic galactic nuclei (AGN) are regularly so shiny that the sunshine they emit regularly outshines the mixed mild of each and every superstar within the galaxy that surrounds them. The huge quantity of radiation being emitted from round this actual supermassive black gap led to it to tackle a small point-like look in JWST knowledge. “Research of the thing’s colours indicated that it used to be now not an ordinary star-forming galaxy. This additional supported the supermassive blackhole speculation,” Rachel Bezanson, from the College of Pittsburgh and co-lead of the UNCOVER program, stated within the observation. “Along side its compact dimension, it turned into glaring this used to be most probably a supermassive black gap, even if it used to be nonetheless other from different quasars discovered at the ones early instances.”The early quasar shouldn’t have been visual even to the robust infrared eye of the JWST with no little lend a hand from an impact predicted through Albert Einstein in 1915.Einstein’s lensEinstein’s principle of common relativity suggests items of mass warp the very material of area and time, which might be in point of fact united as a unmarried entity known as “spacetime.” The idea continues on that gravity arises on account of that curvature. The better the mass of an object, the extra “excessive” the curvature of spacetime is.Now not most effective does this curvature subsequently inform planets how you can transfer round stars and stars and how you can transfer across the facilities in their house galaxies, however it additionally adjustments paths of sunshine coming from the ones stars.The nearer to the thing of mass that mild travels, the extra its trail is “bent.” Other paths of sunshine from a unmarried background object can thus be bent through a foreground, or “lensing object,” and shift the illusion of the background object’s location. Occasionally, the impact may even purpose the background object to look in a couple of puts in the similar symbol of the sky. Different instances, mild from the background object is solely amplified, and that object is magnified. This phenomenon is referred to as “gravitational lensing.”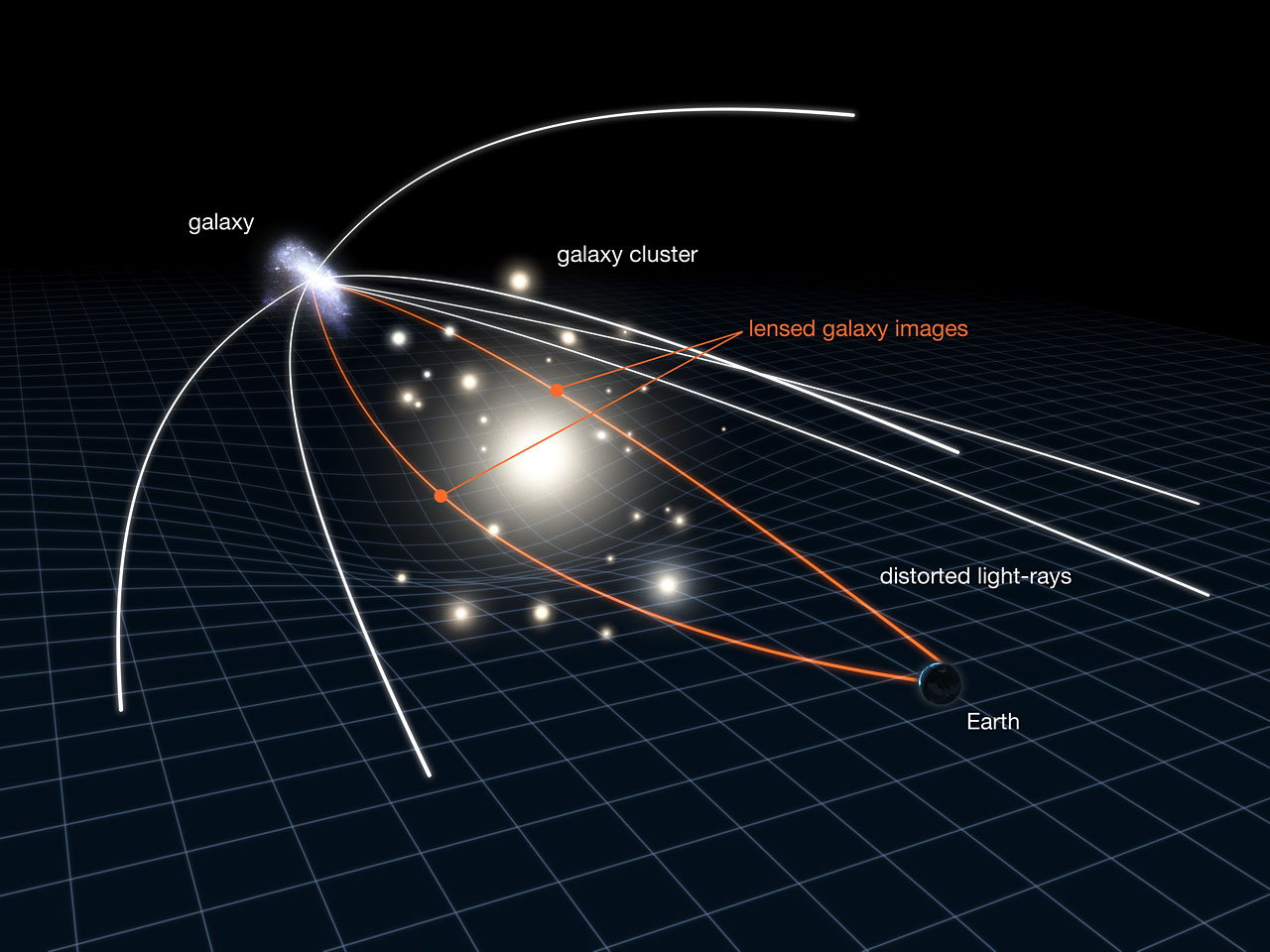 A diagram presentations how mild from a background object is curved through a foreground frame. (Symbol credit score: NASA, ESA & L. Calçada)On this case, the JWST used a galaxy cluster known as Abell 2744 as a foreground lensing frame to magnify mild from background galaxies, which might be in a different way too far away to peer. This published the extraordinarily pink quasar they zeroed-in on, in the beginning within the type of 3 pink dots.”We used a numerical lensing fashion that we had built for the galaxy cluster to decide that the 3 pink dots needed to be a couple of photographs of the similar background supply, observed when the universe used to be just a few 700 million years previous,” Zitrin stated.
A diagram presentations how mild from a background object is curved through a foreground frame. (Symbol credit score: NASA, ESA & L. Calçada)On this case, the JWST used a galaxy cluster known as Abell 2744 as a foreground lensing frame to magnify mild from background galaxies, which might be in a different way too far away to peer. This published the extraordinarily pink quasar they zeroed-in on, in the beginning within the type of 3 pink dots.”We used a numerical lensing fashion that we had built for the galaxy cluster to decide that the 3 pink dots needed to be a couple of photographs of the similar background supply, observed when the universe used to be just a few 700 million years previous,” Zitrin stated.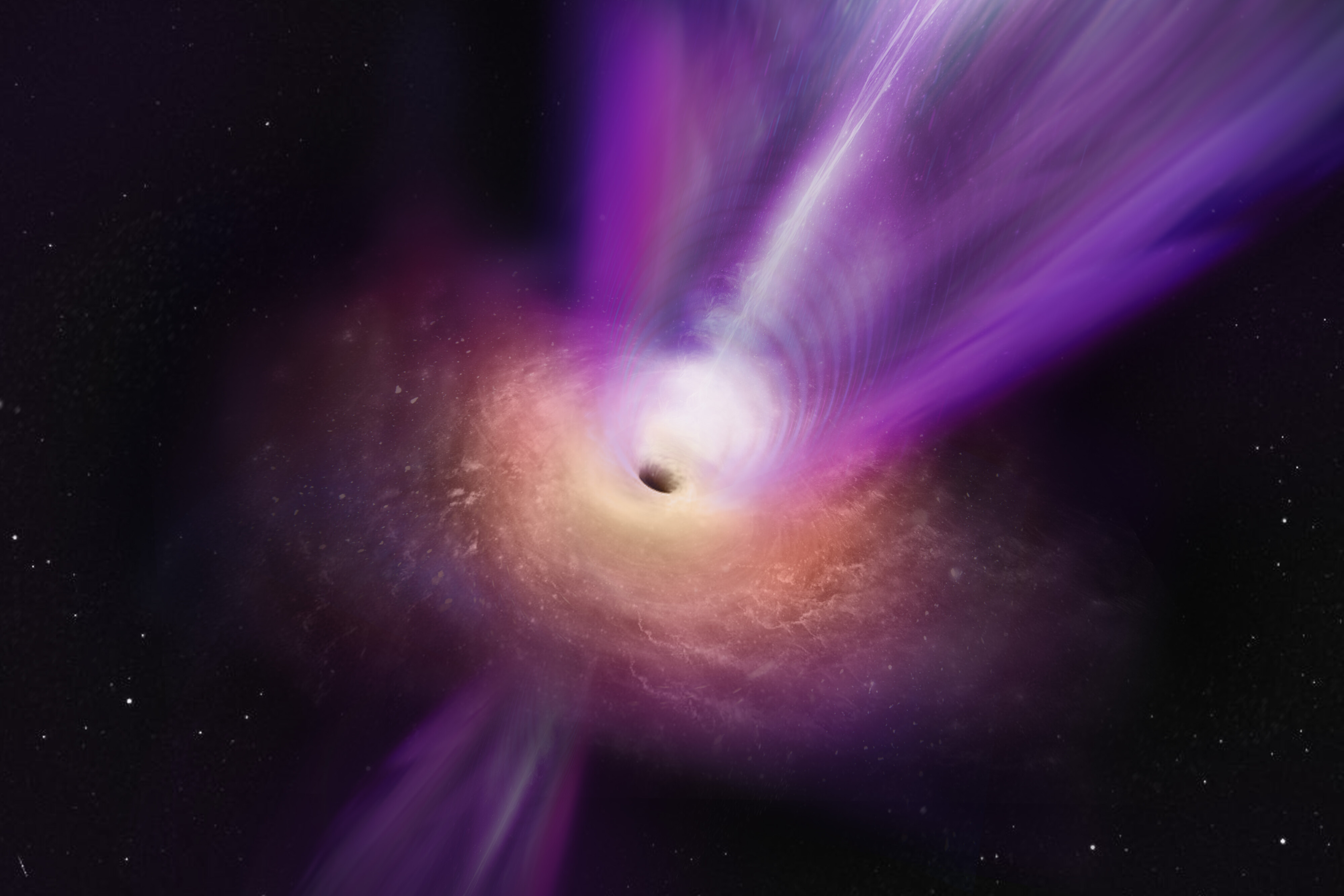 An artist’s impact of a supermassive black gap and its robust jet. Astronomers need to understand how those items reached super lots within the early universe. (Symbol credit score: S. Dagnello (NRAO/AUI/NSF))Additional research of the background supply published its mild should have come from a compact area.”All of the mild of that galaxy should are compatible inside of a tiny area the scale of a present-day superstar cluster. The gravitational lensing magnification of the supply gave us beautiful limits at the dimension,” crew member and Princeton College researcher Jenny Greene stated within the observation. “Even packing the entire imaginable stars into any such small area, the black gap finally ends up being no less than 1% of the entire mass of the gadget.”The invention additional provides to the thriller of ways supermassive black holes, which can also be hundreds of thousands (and even billions) of instances as huge because the solar, grew to such massive sizes throughout the universe’s infancy.”A number of different supermassive black holes within the early universe have now been discovered to turn a equivalent conduct, which results in some intriguing perspectives of the black gap and host galaxy enlargement, and the interaction between them, which isn’t neatly understood,” Greene stated.The JWST has detected a wealth of “little pink dots” over the years. Those may additionally point out feeding supermassive black hole-powered quasars within the early universe, possibly that means a putting black gap enlargement conundrum may quickly be solved.”In some way, it is the astrophysical identical of the hen and egg downside,” Zitrin concluded. “We don’t lately know which got here first — the galaxy or black gap, how huge the primary black holes have been, and the way they grew.”The crew’s analysis used to be revealed on Feb. 14 within the magazine Nature.
An artist’s impact of a supermassive black gap and its robust jet. Astronomers need to understand how those items reached super lots within the early universe. (Symbol credit score: S. Dagnello (NRAO/AUI/NSF))Additional research of the background supply published its mild should have come from a compact area.”All of the mild of that galaxy should are compatible inside of a tiny area the scale of a present-day superstar cluster. The gravitational lensing magnification of the supply gave us beautiful limits at the dimension,” crew member and Princeton College researcher Jenny Greene stated within the observation. “Even packing the entire imaginable stars into any such small area, the black gap finally ends up being no less than 1% of the entire mass of the gadget.”The invention additional provides to the thriller of ways supermassive black holes, which can also be hundreds of thousands (and even billions) of instances as huge because the solar, grew to such massive sizes throughout the universe’s infancy.”A number of different supermassive black holes within the early universe have now been discovered to turn a equivalent conduct, which results in some intriguing perspectives of the black gap and host galaxy enlargement, and the interaction between them, which isn’t neatly understood,” Greene stated.The JWST has detected a wealth of “little pink dots” over the years. Those may additionally point out feeding supermassive black hole-powered quasars within the early universe, possibly that means a putting black gap enlargement conundrum may quickly be solved.”In some way, it is the astrophysical identical of the hen and egg downside,” Zitrin concluded. “We don’t lately know which got here first — the galaxy or black gap, how huge the primary black holes have been, and the way they grew.”The crew’s analysis used to be revealed on Feb. 14 within the magazine Nature.
James Webb Area Telescope reveals ‘extraordinarily pink’ supermassive black gap rising within the early universe





/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25760867/2153819128.jpg)