The James Webb Area Telescope (JWST) has noticed proof pointing to asteroids colliding in a neighboring megastar machine. Resultant mud kicked up by means of the collision has a mass equivalent to round 100,000 instances that of the asteroid that killed the dinosaurs.The asteroids had been noticed smashing in combination in Beta Pictoris, a celebrity machine positioned about 63.4 light-years from the sun machine. This megastar machine is understood for its relative formative years; it is simply round 20 to twenty-five million years outdated, which makes it a celestial toddler in comparison to our 4.6 billion-year-old sun machine. The truth that Beta Pictoris continues to be within the throes of early planet formation way the JWST’s statement of colliding asteroids inside this megastar machine may shine a gentle at the unstable processes that formed neighborhoods just like the sun machine of their infancy.Comparable: James Webb Area Telescope spots essentially the most far-off galaxy ever noticed (symbol)”Beta Pictoris is at an age when planet formation within the terrestrial planet zone continues to be ongoing thru massive asteroid collisions, so what we may well be seeing this is principally how rocky planets and different our bodies are forming in actual time,” workforce chief Christine Chen, a Johns Hopkins College astronomer, stated in a commentary.How the JWST noticed adjustments round Beta PictorisThough they are somewhat shut, the space between the sun machine and Beta Pictoris is huge sufficient to make without delay recognizing asteroids colliding within the latter extremely tricky. Past distance, in truth, you would wish to catch a collision amid the dusty torus of gasoline and mud round Beta Pictoris’ younger megastar, known as a “protoplanetary disk.”To make this detection, Chen and associates in comparison new information from the JWST with observations accrued by means of the Spitzer Area Telescope between 2004 and 2005. This published important adjustments within the power signatures of mud grains round Beta Pictoris, with a specific focal point on warmth emitted by means of minerals usually discovered round younger stars in addition to on Earth. They are known as “crystalline silicates.”The detailed measurements taken by means of the JWST allowed the workforce to search for mud debris within the area of Beta Pictoris that Spitzer up to now probed. They discovered no hint of debris noticed by means of Spitzer 20 years in the past. This implied {that a} cataclysmic collision between asteroids or different gadgets round Beta Pictoris had taken position round 20 or so years in the past. One of these smash-up would have pulverized those our bodies, turning them into a bath of debris as advantageous as powdered sugar.Breaking area information, the newest updates on rocket launches, skywatching occasions and extra!”We expect all that mud is what we noticed first of all within the Spitzer information from 2004 and 2005,” Chen stated. “With the JWST’s new information, the most productive rationalization we have now is that, in truth, we witnessed the aftermath of an rare, cataclysmic match between huge asteroid-size our bodies, marking a whole trade in our figuring out of this megastar machine.”Asteroid-collision mud is absent within the JWST photographs as a result of radiation from the megastar Beta Pictoris has since dispersed such a debris. The emissions noticed by means of Spitzer twenty years in the past represented the start of this procedure, when the mud was once being heated by means of stellar radiation and emitting thermal power. Shifting clear of the central megastar has additionally led to the mud to chill, which means its thermal emission is now not going on.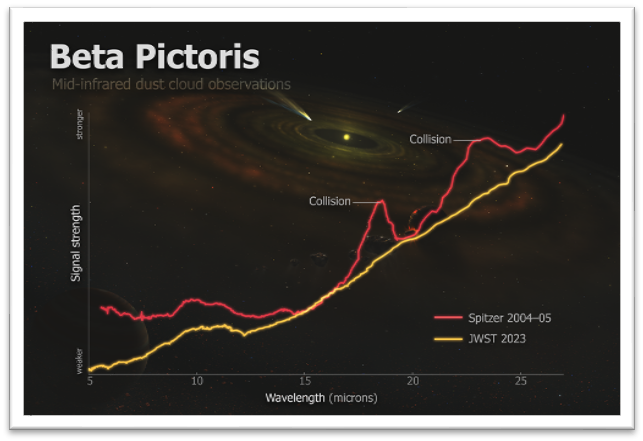 Knowledge accrued by means of the JWST and the Spitzer Area Telescope that signifies collisions between asteroids in Beta Pictoris (Symbol credit score: Roberto Molar Candanosa/Johns Hopkins College)Spitzer’s observations of the area had up to now been assumed to be the results of small our bodies round Beta Pictoris grinding down and often replenishing the mud over the years. On the other hand, the JWST information signifies that this mud in fact is not being replenished when it’s kicked away by means of the central megastar.The relative proximity of Beta Pictoris, identified to host two younger exoplanets, and its formative years has made this planetary machine a first-rate goal for astronomers making an attempt to know the processes that govern planetary formation.”The query we’re looking to contextualize is whether or not this entire strategy of terrestrial and massive planet formation is commonplace or uncommon, and the much more fundamental query: Are planetary programs just like the sun machine that uncommon?” workforce member Kadin Worthen, a doctoral scholar in astrophysics at Johns Hopkins, stated within the commentary. “We are principally looking to know how bizarre or reasonable we’re.”This new analysis highlights the JWST’s capacity to research the intricacies of planetary programs and extrasolar planets, or “exoplanets.” The $10 billion area telescope may lend a hand provide an explanation for why planetary programs every now and then shape just like the sun machine and, different instances, undertake various morphologies. The JWST may additionally lend a hand astronomers uncover how early turbulence round stars affects the atmospheres, water content material and different key facets of habitability for his or her planets. “Maximum discoveries by means of JWST come from issues the telescope has detected without delay,” workforce member Cicero Lu, a former Johns Hopkins doctoral scholar in astrophysics, stated within the commentary. “On this case, the tale is just a little other as a result of our effects come from what JWST didn’t see.”The workforce introduced their resents on Monday (June 10) on the 244th Assembly of the American Astronomical Society in Madison, Wisconsin.
Knowledge accrued by means of the JWST and the Spitzer Area Telescope that signifies collisions between asteroids in Beta Pictoris (Symbol credit score: Roberto Molar Candanosa/Johns Hopkins College)Spitzer’s observations of the area had up to now been assumed to be the results of small our bodies round Beta Pictoris grinding down and often replenishing the mud over the years. On the other hand, the JWST information signifies that this mud in fact is not being replenished when it’s kicked away by means of the central megastar.The relative proximity of Beta Pictoris, identified to host two younger exoplanets, and its formative years has made this planetary machine a first-rate goal for astronomers making an attempt to know the processes that govern planetary formation.”The query we’re looking to contextualize is whether or not this entire strategy of terrestrial and massive planet formation is commonplace or uncommon, and the much more fundamental query: Are planetary programs just like the sun machine that uncommon?” workforce member Kadin Worthen, a doctoral scholar in astrophysics at Johns Hopkins, stated within the commentary. “We are principally looking to know how bizarre or reasonable we’re.”This new analysis highlights the JWST’s capacity to research the intricacies of planetary programs and extrasolar planets, or “exoplanets.” The $10 billion area telescope may lend a hand provide an explanation for why planetary programs every now and then shape just like the sun machine and, different instances, undertake various morphologies. The JWST may additionally lend a hand astronomers uncover how early turbulence round stars affects the atmospheres, water content material and different key facets of habitability for his or her planets. “Maximum discoveries by means of JWST come from issues the telescope has detected without delay,” workforce member Cicero Lu, a former Johns Hopkins doctoral scholar in astrophysics, stated within the commentary. “On this case, the tale is just a little other as a result of our effects come from what JWST didn’t see.”The workforce introduced their resents on Monday (June 10) on the 244th Assembly of the American Astronomical Society in Madison, Wisconsin.
James Webb Area Telescope spots asteroid collision in neighboring megastar machine












:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/INV_MarvellHQ_GettyImages-2169879324-09f1c754fedc468cb36f13803b6fbe9c.jpg)

