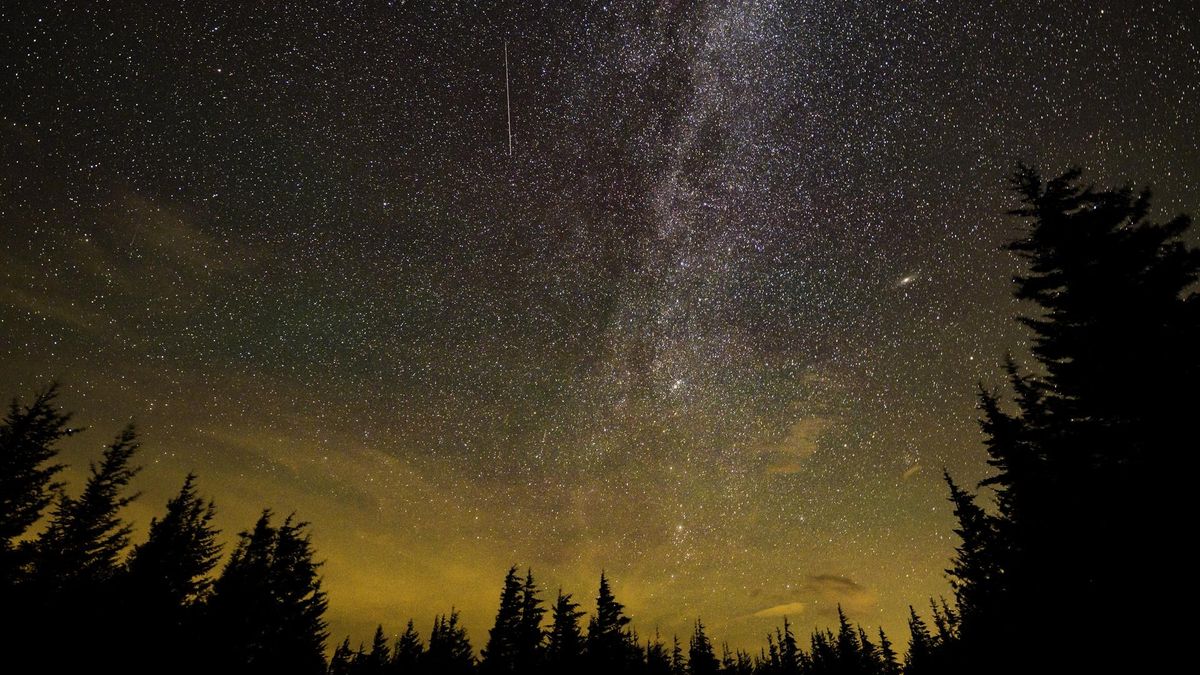
Astronomers the usage of the James Webb Area Telescope to see again in time into the farthest reaches of the universe have discovered surprising proof for another idea of gravity.
Present fashions of galaxy formation within the early cosmos expect the presence of extra gravity brought about via darkish subject to drag subject material into slowly forming galaxies. Alternatively, another idea of gravity first proposed in 1998 referred to as Changed Newtonian Dynamics (MOND) means that constructions within the early universe shaped in no time with out the desire for theoretical darkish subject.
Now, researchers from Case Western Reserve College say that scans of historical galaxies accrued via the JWST appear to contradict the recurrently accredited predictions of probably the most broadly accredited Chilly Darkish Subject idea, Lambda-CDM. As a substitute, the readings appear to toughen a foundation for MOND, which might drive astronomers and cosmologists to rethink this selection and long-controversial idea of gravity.
The Darkish Subject Debate
The Lambda-CDM type has lengthy posited that darkish subject, an elusive and invisible type of subject, is very important for explaining the construction of the universe. Consistent with this type, darkish subject’s gravitational affect formed galaxies and brought about the formation of large-scale constructions. It predicts that historical galaxies within the early universe will have to seem small and dim, as they have been progressively pulled in combination via darkish subject over cosmic time.
Alternatively, McGaugh and his colleagues argue that those predictions don’t fit JWST observations. As a substitute, the newly noticed galaxies seem vivid, broad, and entirely shaped, whilst scientists peer deeper into the universe’s previous. This surprising brightness at once demanding situations the traditional figuring out of galaxy formation pushed via darkish subject.
“Astronomers invented darkish subject to provide an explanation for the way you get from an overly clean early universe to special galaxies with quite a lot of empty area between them that we see as of late,” mentioned Stacy McGaugh, professor and director of astronomy at Case Western Reserve, in a press unencumber saying the learn about.
“(However) what the speculation of darkish subject predicted isn’t what we see.”
Particularly, McGaugh mentioned that if the lambda-CDM type have been correct, the additional gravitational pull from darkish subject, which best interacts with different subject thru gravity, would motive small items of subject surrounding nascent galaxies to accrete to the middle slowly.
MOND: A Radical Selection Principle of Gravity
The MOND idea, first proposed in 1983 via Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, provides a special clarification. MOND suggests editing Newton’s 2d regulation to account for discrepancies noticed in galaxy rotation curves with out invoking darkish subject. Those adjustments are related in areas of tiny accelerations, reminiscent of the ones skilled on the universe’s outer edge, the place JWST is now staring at.
In 1998, McGaugh co-authored a seminal paper proposing that galaxy formation came about extra abruptly and didn’t depend on darkish subject. As a substitute, he and his co-authors, together with Federico Lelli, Jay Franck, and James Schombert, theorized that galactic subject material was once temporarily gathered, expanded with the universe, after which collapsed below gravity. This idea contends that galaxies got here in combination early, forming broad, luminous constructions with out the desire for darkish subject.
Proof and Demanding situations
Consistent with McGaugh and associates, JWST’s information aligns extra intently with predictions made via MOND proponents than with Lambda-CDM fashions. For example, McGaugh highlights that the MOND-based predictions of R H Sanders matched observations extra as it should be than the ones made via Lambda-CDM advocates Mo, Mao, and White. But, in spite of the hot luck, MOND stays a contentious idea, as reconciling it with Einstein’s Principle of Basic Relativity—a basis of contemporary physics—has confirmed elusive.
“We will all the time try to regulate a idea to house new details,” McGaugh concedes, acknowledging that whilst details inconsistent with one type don’t necessitate forsaking it fully, the shortcoming to totally give an explanation for observational information would possibly point out a weaker theoretical framework. Even so, some trendy astronomical measurements does nonetheless prefer the darkish subject speculation.
The Ongoing Case for Lambda-CDM
In spite of MOND’s obvious luck in explaining some JWST observations, Lambda-CDM continues to experience huge toughen. The type has as it should be predicted the universe’s enlargement price for the reason that Nineteen Twenties, with proof of a cosmological consistent pushing the universe to ceaselessly amplify. Moreover, whilst the universe is just about flat, a demand for Lambda-CDM, slight deviations stay a gray space for additional exploration.
The wider astrophysical group stays wary, and lots of researchers indicate that Lambda-CDM has withstood a large number of exams and gives a cohesive framework for figuring out the universe. Even so, McGaugh is eager about the continuing debate.
“The expectancy was once that each and every large galaxy we see within the close by universe would have began from those itty-bitty items,” McGaugh mentioned. “That’s no longer what JWST is appearing us.”
McGaugh concedes that discovering a idea suitable with each Basic Relativity and MOND stays an unrealized problem. Alternatively, following the discoveries via the JWST that appear to toughen their MOND thought and its trade idea of gravity, McGaugh says he and his colleagues are feeling reasonably vindicated.
“The secret is, ‘I instructed you so,’” McGaugh mentioned. “I used to be raised to suppose that announcing that was once impolite, however that’s the entire level of the clinical way: Make predictions after which test which come true.”
The paper “Speeded up Construction Formation: The Early Emergence of Large Galaxies and Clusters of Galaxies” seemed on November 12, 2024 within the The Astrophysical Magazine.


Christopher Simple is a Science Fiction and Myth novelist and Head Science Creator at The Debrief. Practice and hook up with him on X, know about his books at plainfiction.com, or electronic mail him at once at christopher@thedebrief.org.
Ryan Whalen covers science and generation for The Debrief. He holds a BA in Historical past and a Grasp of Library and Data Science with a certificates in Information Science. He will also be contacted at ryan@thedebrief.org, and apply him on Twitter @mdntwvlf.











:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/PLTRChart-71ec74b79d4442c2a8719bc71da59b23.gif)

