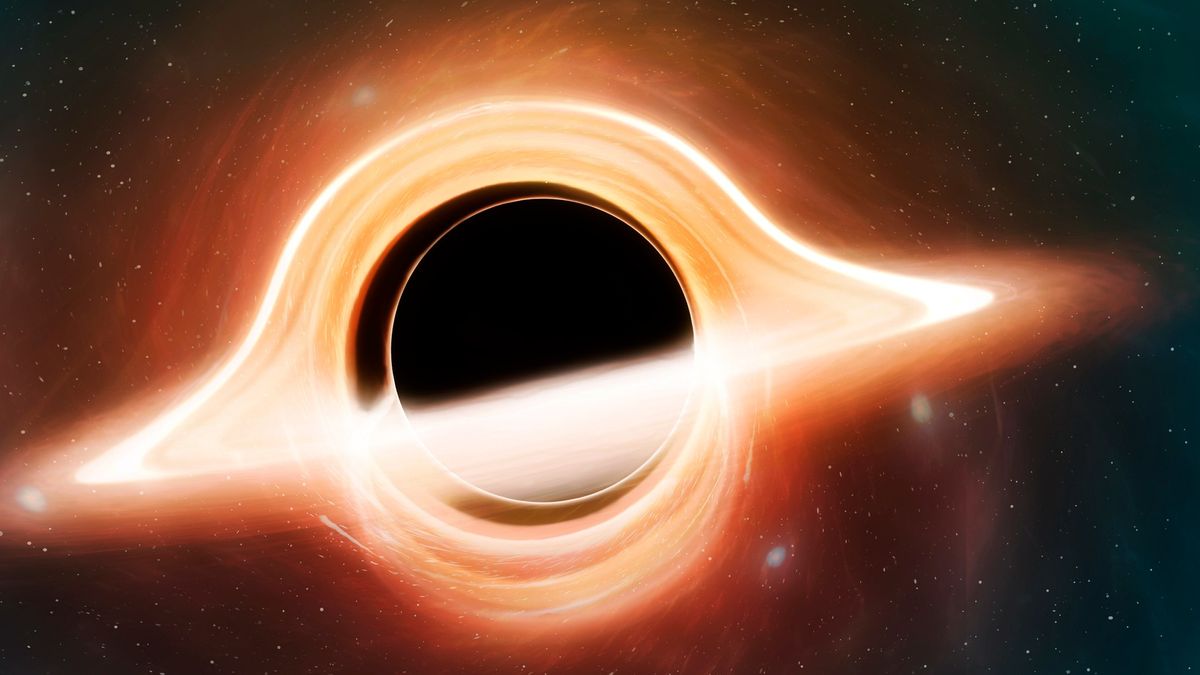
The James Webb House Telescope (JWST) has noticed the oldest black hollow ever noticed, an historic monster with the mass of one.6 million suns lurking 13 billion years within the universe’s previous. The James Webb House Telescope, whose cameras allow it to appear again in time to our universe’s beginnings, noticed the supermassive black hollow on the middle of the child galaxy GN-z11 simply 440 million years after the universe started.And the space-time rupture is not by myself, it is certainly one of numerous black holes that gorged themselves to terrifying scales throughout the cosmic morning time — the duration about 100 million years after the Giant Bang when the younger universe started sparkling for one billion years.Similar: This supermassive black hollow is essentially the most far-off ever noticed in X-raysHow the cosmic whirlpools ballooned in scale so impulsively after the universe started is not transparent. However searching for a solution may assist provide an explanation for how these days’s supermassive black holes — which anchor whole galaxies together with our Milky Approach — grew to such mind-boggling sizes. The researchers printed their findings previous this yr to the preprint database arXiv, however the analysis has now not but been peer-reviewed.Black holes within the early universe “cannot develop quietly and gently as many black holes do within the native [present-day] universe,” lead-author Roberto Maiolino, a professor of astrophysics on the College of Cambridge, informed Are living Science. “They will have to revel in some unusual delivery or formation, and a few unusual enlargement.”Nearer to the present-day, astronomers consider black holes are born from the cave in of huge stars. However alternatively they arrive to be, they develop via without end gorging on fuel, mud, stars and different black holes. As they banquet, friction reasons the fabric spiraling into the black holes’ maws to warmth up, and so they emit gentle that may be detected via telescopes — turning them into so-called lively galactic nuclei (AGN).Probably the most excessive AGN are quasars, supermassive black holes which might be billions of occasions heavier than the solar and shed their gaseous cocoons with gentle blasts trillions of occasions extra luminous than the brightest stars.As a result of gentle travels at a set pace in the course of the vacuum of area, the deeper that scientists glance into the universe, the extra far off gentle they intercept and the additional again in time they see. To identify the black hollow within the new learn about, the astronomers scanned the sky with two infrared cameras — the JWST’s Mid-Infrared Tool (MIRI) and Close to Infrared Digicam — and used the cameras’ integrated spectrographs to damage down the sunshine into its part frequencies. By way of deconstructing those faint glimmers from the universe’s earliest years, they discovered an surprising spike some of the frequencies contained inside the gentle — a key signal that the recent subject material round a black hollow used to be beaming out faint strains of sunshine around the universe.The preferred explanations for a way those early black holes grew so rapid are that they shaped from the unexpected cave in of huge fuel clouds or that they got here from many mergers between clumps of stars and black holes. However, astronomers have not dominated out that a few of these black holes may have been seeded via hypothesized “primordial” black holes, considered created moments after — and in some theories even ahead of — the universe started.”It isn’t so transparent that [direct collapse] is the one approach to make a black hollow, as a result of you want some particular instances for it to occur,” Maiolino stated. “You wish to have it to be a pristine cloud, but to be enriched via heavy components made via the primary stars, and one this is reasonably huge — from 10,000 to as much as 1,000,000 sun lots.”To forestall the sort of cloud from cooling too briefly and collapsing into huge stars first, it will have to even be beamed with ultraviolet gentle, most probably from a close-by galaxy or black hollow.”So you want this unusual situation the place the cloud isn’t getting enriched [by absorbing exploded star material], however may be subsequent to some other galaxy which is generating a large number of photons,” Maiolino stated. “So we are not essentially searching for a unmarried state of affairs, if truth be told two or extra of them may well be at play.”Initially printed on LiveScience.com.
James Webb House Telescope can have discovered the oldest black hollow within the universe