Thousand-mile-per-hour winds are blowing a hail of tiny quartz crystals throughout the silicate-enhanced, sizzling sizzling environment of a far off gasoline large planet known as WASP-17b, the James Webb House Telescope (JWST) has discovered.”We knew from Hubble [Space Telescope] observations that there will have to be aerosols — tiny debris making up clouds or haze — in WASP-17b’s environment, however we didn’t be expecting them to be manufactured from quartz,” Daniel Grant of the College of Bristol in the United Kingdom and chief of a brand new learn about at the discovery, mentioned in a remark.WASP-17b is an unbelievable global. Orbiting each 3.7 days at a distance of simply 7.8 million kilometers (4.9 million miles) from its superstar, which sits 1,300 mild years clear of Earth, WASP-17b is so as regards to its stellar host that its dayside temperature rises to a staggering 1,500 levels Celsius (roughly 2,700 levels Fahrenheit). Since the environment is so sizzling in this exoplanet, the sector has in fact expanded to about 285,000 kilometers (176,892 miles) throughout, which is simply shy of two times the diameter of Jupiter. And that’s the reason regardless of WASP-17b having best about part of Jupiter’s total mass. WASP-17b is among the “puffiest” planets identified — and its bloated environment makes it an ideal goal for the James Webb House Telescope.Comparable: James Webb House Telescope spotlights stunning younger stars in a galaxy subsequent door (picture)Grant and fellow astronomers watched WASP-17b transit its superstar the use of the JWST’s Mid-Infrared Tool (MIRI). Because the exoplanet moved in entrance of its superstar from the JWST’s standpoint, MIRI detected starlight that was once blocked by means of the puffy planet itself however partly absorbed by means of the sector’s environment. Such measurements lead to a so-called transmission spectrum, wherein positive wavelengths are blocked out by means of specific atmospheric molecules.Like Jupiter, WASP-17b gave the look to be most commonly made out of hydrogen and helium. As well as, MIRI detected carbon dioxide, water vapor and, at a wavelength of 8.6 microns, the absorption signature of natural quartz crystals. Blended with earlier observations with the Hubble House Telescope, those crystals are judged to be formed like the similar pointy, hexagonal prisms as quartz is on Earth, however only a meager 10 nanometers in dimension. 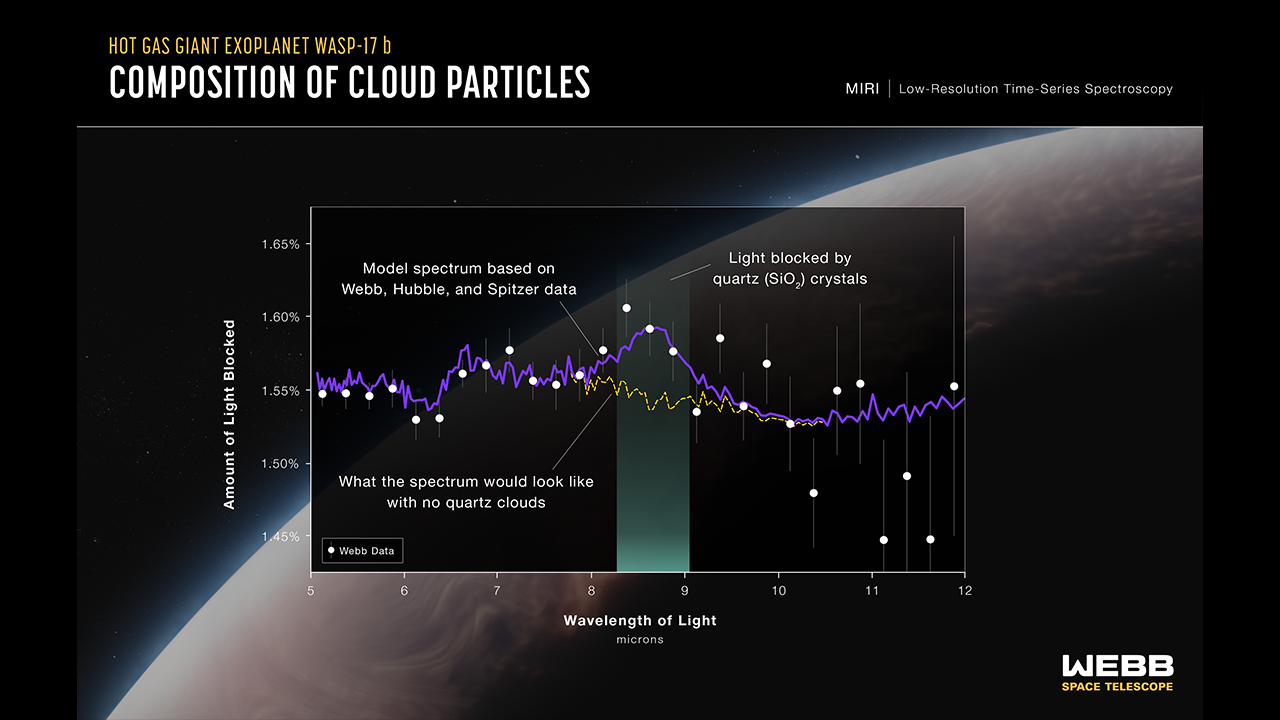 The transmission spectrum of WASP-17b, appearing how the quartz is obstructing mild at a wavelength of 8.6 microns. (Symbol credit score: NASA/ESA/CSA/Ralf Crawford (STScI))Quartz is a type of silicate, which might be minerals wealthy in silica and oxygen. Silicates are exceptionally commonplace — the entire rocky our bodies within the sun gadget are made out of them, and silicates have in the past been detected within the atmospheres of sizzling Jupiter exoplanets earlier than. Alternatively, in the ones circumstances they’d been extra advanced, magnesium-rich crystals of olivine and pyroxene.”We absolutely anticipated to look magnesium silicates,” mentioned Bristol’s Hannah Wakeford. “However what we’re seeing as an alternative are most probably the construction blocks of the ones, the tiny seed debris wish to shape the bigger silicate grains we stumble on in cooler exoplanets and brown dwarfs.”WASP-27b may be tidally locked, that means it all the time presentations the similar face to its superstar. As winds whip across the planet, wearing alongside the quartz nanoparticles, they shape high-altitude hazes — necessarily diffuse clouds of rock crystals — on the day–evening termination zone. The ones hazes then project into the dayside, and are vaporized within the warmth.Grant defined how crystals of silicate come to be embedded in a planetary environment within the first position.”WASP-17b is terribly sizzling … and the force the place the quartz crystals shape excessive within the environment is best about one-thousandth of what we enjoy on Earth’s floor,” he mentioned. “In those stipulations, cast crystals can shape at once from gasoline, with out going via a liquid segment first.”The findings had been printed in October in Astrophysical Magazine Letters.
The transmission spectrum of WASP-17b, appearing how the quartz is obstructing mild at a wavelength of 8.6 microns. (Symbol credit score: NASA/ESA/CSA/Ralf Crawford (STScI))Quartz is a type of silicate, which might be minerals wealthy in silica and oxygen. Silicates are exceptionally commonplace — the entire rocky our bodies within the sun gadget are made out of them, and silicates have in the past been detected within the atmospheres of sizzling Jupiter exoplanets earlier than. Alternatively, in the ones circumstances they’d been extra advanced, magnesium-rich crystals of olivine and pyroxene.”We absolutely anticipated to look magnesium silicates,” mentioned Bristol’s Hannah Wakeford. “However what we’re seeing as an alternative are most probably the construction blocks of the ones, the tiny seed debris wish to shape the bigger silicate grains we stumble on in cooler exoplanets and brown dwarfs.”WASP-27b may be tidally locked, that means it all the time presentations the similar face to its superstar. As winds whip across the planet, wearing alongside the quartz nanoparticles, they shape high-altitude hazes — necessarily diffuse clouds of rock crystals — on the day–evening termination zone. The ones hazes then project into the dayside, and are vaporized within the warmth.Grant defined how crystals of silicate come to be embedded in a planetary environment within the first position.”WASP-17b is terribly sizzling … and the force the place the quartz crystals shape excessive within the environment is best about one-thousandth of what we enjoy on Earth’s floor,” he mentioned. “In those stipulations, cast crystals can shape at once from gasoline, with out going via a liquid segment first.”The findings had been printed in October in Astrophysical Magazine Letters.
James Webb House Telescope detects quartz crystals in an exoplanet’s environment








:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/DELLChart-ad2e3d3a96334cb383a6517c2d850ad8.gif)



